In software engineering, multitier architecture is a client–server architecture in which presentation, application processing and data management functions are physically separated. The most widespread use of multitier architecture is the three-tier architecture.

The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a reference model from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that "provides a common basis for the coordination of standards development for the purpose of systems interconnection." In the OSI reference model, the communications between systems are split into seven different abstraction layers: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application.
Network architecture is the design of a computer network. It is a framework for the specification of a network's physical components and their functional organization and configuration, its operational principles and procedures, as well as communication protocols used.
A computing platform, digital platform, or software platform is the infrastructure on which software is executed. While the individual components of a computing platform may be obfuscated under layers of abstraction, the summation of the required components comprise the computing platform.

The Windows API, informally WinAPI, is the foundational application programming interface (API) that allows a computer program to access the features of the Microsoft Windows operating system in which the program is running.
In computing, the Windows Sockets API (WSA), later shortened to Winsock, is an application programming interface (API) that defines how Windows network application software should access network services, especially TCP/IP. It defines a standard interface between a Windows TCP/IP client application and the underlying TCP/IP protocol stack. The nomenclature is based on the Berkeley sockets API used in BSD for communications between programs.
In computer networking, a network service is an application running at the network application layer and above, that provides data storage, manipulation, presentation, communication or other capability which is often implemented using a client–server or peer-to-peer architecture based on application layer network protocols.
The 21st Century Network (21CN) programme is the data and voice network transformation project, under way since 2004, of the UK telecommunications company BT Group plc. It was intended to move BT's telephone network from the AXE/System X Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) to an Internet Protocol (IP) system. As well as switching over the PSTN, BT planned to deliver many additional services over their new data network, such as on-demand interactive TV services.

The Department of Defense Architecture Framework (DoDAF) is an architecture framework for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) that provides visualization infrastructure for specific stakeholders concerns through viewpoints organized by various views. These views are artifacts for visualizing, understanding, and assimilating the broad scope and complexities of an architecture description through tabular, structural, behavioral, ontological, pictorial, temporal, graphical, probabilistic, or alternative conceptual means. The current release is DoDAF 2.02.
The Defense Information System Network (DISN) has been the United States Department of Defense's enterprise telecommunications network for providing data, video, and voice services for 40 years.
The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is a vendor-neutral link layer protocol used by network devices for advertising their identity, capabilities, and neighbors on a local area network based on IEEE 802 technology, principally wired Ethernet. The protocol is formally referred to by the IEEE as Station and Media Access Control Connectivity Discovery specified in IEEE 802.1AB with additional support in IEEE 802.3 section 6 clause 79.

An enterprise architecture framework defines how to create and use an enterprise architecture. An architecture framework provides principles and practices for creating and using the architecture description of a system. It structures architects' thinking by dividing the architecture description into domains, layers, or views, and offers models – typically matrices and diagrams – for documenting each view. This allows for making systemic design decisions on all the components of the system and making long-term decisions around new design requirements, sustainability, and support.
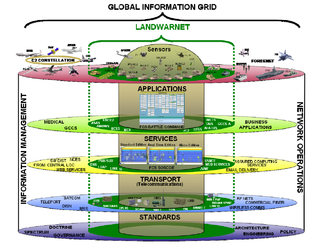
The FCS Network - Brigade Combat Team (BCT) Network consists of five layers that deliver data to forward-deployed Army units.
The Spacecraft Monitoring & Control (SM&C) Working Group of the Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems (CCSDS), which sees the active participation of the main http://www.space.bas.bg/bg/procurement/files/pravilnik%20OP.PDF agencies, is defining a service-oriented architecture consisting of a set of standard end-to-end services between functions resident on board a spacecraft or based on the ground, that are responsible for mission operations.

Information technology infrastructure is defined broadly as a set of information technology (IT) components that are the foundation of an IT service; typically physical components, but also various software and network components.
In intelligent networks (IN) and cellular networks, service layer is a conceptual layer within a network service provider architecture. It aims at providing middleware that serves third-party value-added services and applications at a higher application layer. The service layer provides capability servers owned by a telecommunication network service provider, accessed through open and secure Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) by application layer servers owned by third-party content providers. The service layer also provides an interface to core networks at a lower resource layer. The lower layers may also be named control layer and transport layer.
Operations support systems (OSS), operational support systems in British usage, or Operation System (OpS) in NTT are computer systems used by telecommunications service providers to manage their networks. They support management functions such as network inventory, service provisioning, network configuration and fault management.

In spacecraft design, the function of the thermal control system (TCS) is to keep all the spacecraft's component systems within acceptable temperature ranges during all mission phases. It must cope with the external environment, which can vary in a wide range as the spacecraft is exposed to the extreme coldness found in the shadows of deep space or to the intense heat found in the unfiltered direct sunlight of outer space. A TCS must also moderate the internal heat generated by the operation of the spacecraft it serves.
Middleware is a type of computer software program that provides services to software applications beyond those available from the operating system. It can be described as "software glue".
network architecture concept that leverages IT virtualization technologies to virtualize entire classes of network node functions into building blocks that may connect, or chain together, to create and deliver communication services.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.





