
HeLa is an immortal cell line used in scientific research. It is the oldest and most commonly used human cell line. The line is named after and derived from cervical cancer cells taken on February 8, 1951, from Henrietta Lacks, a 31-year-old African-American mother of five, who died of cancer on October 4, 1951. The cell line was found to be remarkably durable and prolific, which allows it to be used extensively in scientific study.

Leigh syndrome is an inherited neurometabolic disorder that affects the central nervous system. It is named after Archibald Denis Leigh, a British neuropsychiatrist who first described the condition in 1951. Normal levels of thiamine, thiamine monophosphate, and thiamine diphosphate are commonly found but there is a reduced or absent level of thiamine triphosphate. This is thought to be caused by a blockage in the enzyme thiamine-diphosphate kinase, and therefore treatment in some patients would be to take thiamine triphosphate daily.
Acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl functional group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed acetate esters or acetates. Deacetylation is the opposite reaction, the removal of an acetyl group from a chemical compound.

Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT17 gene.

A molecular machine, nanite, or nanomachine is a molecular component that produces quasi-mechanical movements (output) in response to specific stimuli (input). In cellular biology, macromolecular machines frequently perform tasks essential for life, such as DNA replication and ATP synthesis. The expression is often more generally applied to molecules that simply mimic functions that occur at the macroscopic level. The term is also common in nanotechnology where a number of highly complex molecular machines have been proposed that are aimed at the goal of constructing a molecular assembler.

Stair Hole is a small cove located just west of Lulworth Cove in Dorset, southern England. The folded limestone strata known as the Lulworth crumple are particularly visible at Stair Hole. There are several caves visible from the seaward side of Stair Hole; Cathedral Cavern is supported by pillars of rock rising out of the water. The rock structure was created during the Alpine orogeny and exposed by subsequent erosion.

Succinate dehydrogenase complex, subunit A, flavoprotein variant is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SDHA gene. This gene encodes a major catalytic subunit of succinate-ubiquinone oxidoreductase, a complex of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The complex is composed of four nuclear-encoded subunits and is localized in the mitochondrial inner membrane. SDHA contains the FAD binding site where succinate is deprotonated and converted to fumarate. Mutations in this gene have been associated with a form of mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiency known as Leigh Syndrome. A pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 3q29. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.

The proto-oncogene c-Rel is a protein that in humans is encoded by the REL gene. The c-Rel protein is a member of the NF-κB family of transcription factors and contains a Rel homology domain (RHD) at its N-terminus and two C-terminal transactivation domains. c-Rel is a myeloid checkpoint that can be targeted for treating cancer. c-Rel has an important role in B-cell survival and proliferation. The REL gene is amplified or mutated in several human B-cell lymphomas, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Hodgkin's lymphoma.
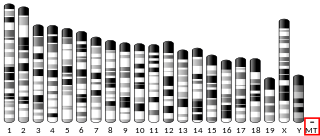
MT-ATP6 is a mitochondrial gene with the full name 'mitochondrially encoded ATP synthase membrane subunit 6' that encodes the ATP synthase Fo subunit 6. This subunit belongs to the Fo complex of the large, transmembrane F-type ATP synthase. This enzyme, which is also known as complex V, is responsible for the final step of oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain. Specifically, one segment of ATP synthase allows positively charged ions, called protons, to flow across a specialized membrane inside mitochondria. Another segment of the enzyme uses the energy created by this proton flow to convert a molecule called adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to ATP. Mutations in the MT-ATP6 gene have been found in approximately 10 to 20 percent of people with Leigh syndrome.

G-protein coupled receptor 31 also known as 12-(S)-HETE receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR31 gene. The human gene is located on chromosome 6q27 and encodes a G-protein coupled receptor protein composed of 319 amino acids.

Homeobox protein MSX-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MSX2 gene.

Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4, also known as melanoma-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (MCSP) or neuron-glial antigen 2 (NG2), is a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan that in humans is encoded by the CSPG4 gene.

Paired box gene 4, also known as PAX4, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PAX4 gene.

Homeobox protein Hox-D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HOXD3 gene.

Multi-junction (MJ) solar cells are solar cells with multiple p–n junctions made of different semiconductor materials. Each material's p-n junction will produce electric current in response to different wavelengths of light. The use of multiple semiconducting materials allows the absorbance of a broader range of wavelengths, improving the cell's sunlight to electrical energy conversion efficiency.
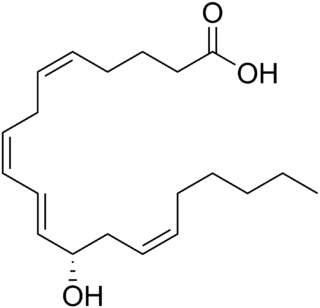
12-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE) is a derivative of the 20 carbon polyunsaturated fatty acid, arachidonic acid, containing a hydroxyl residue at carbon 12 and a 5Z,8Z,10E,14Z Cis–trans isomerism configuration in its four double bonds. It was first found as a product of arachidonic acid metabolism made by human and bovine platelets through their 12S-lipoxygenase enzyme(s). However, the term 12-HETE is ambiguous in that it has been used to indicate not only the initially detected "S" stereoisomer, 12S-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,10E,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid, made by platelets, but also the later detected "R" stereoisomer, 12(R)-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,10E,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid made by other tissues through their 12R-lipoxygenase enzyme, ALOX12B. The two isomers, either directly or after being further metabolized, have been suggested to be involved in a variety of human physiological and pathological reactions. Unlike hormones which are secreted by cells, travel in the circulation to alter the behavior of distant cells, and thereby act as Endocrine signalling agents, these arachidonic acid metabolites act locally as Autocrine signalling and/or Paracrine signaling agents to regulate the behavior of their cells of origin or of nearby cells, respectively. In these roles, they may amplify or dampen, expand or contract cellular and tissue responses to disturbances.

Neurogenin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NEUROG3 gene.
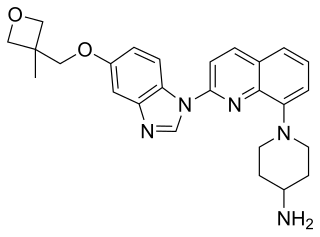
Crenolanib besylate is an investigational inhibitor being developed by AROG Pharmaceuticals, LLC. The compound is currently being evaluated for safety and efficacy in clinical trials for various types of cancer, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), and glioma. Crenolanib is an orally bioavailable benzamidazole that selectively and potently inhibits signaling of wild-type and mutant isoforms of class III receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) FLT3, PDGFR α, and PDGFR β. Unlike most RTK inhibitors, crenolanib is a type I mutant-specific inhibitor that preferentially binds to phosphorylated active kinases with the ‘DFG in’ conformation motif.
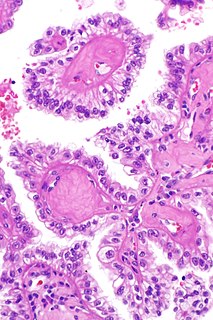
Reed’s syndrome is a rare inherited condition characterised by multiple cutaneous leiomyomas and, in women, uterine leiomyomas. It predisposes for renal cell cancer, an association denominated hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer, and it is also associated with increased risk of uterine leiomyosarcoma. The syndrome is caused by a mutation in the fumarate hydratase gene, which leads to an accumulation of fumarate. The inheritance pattern is autosomal dominant.

Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is the virus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Also colloquially known simply as the coronavirus, it was previously referred to by its provisional name, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and has also been called human coronavirus 2019. First identified in the city of Wuhan, Hubei, China, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 30 January 2020, and a pandemic on 11 March 2020. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that is contagious in humans. As described by the US National Institutes of Health, it is the successor to SARS-CoV-1, the virus that caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak.