Related Research Articles

Retail is the process of selling consumer goods or services to customers through multiple channels of distribution to earn a profit. Retailers satisfy demand identified through a supply chain. The term "retailer" is typically applied where a service provider fills the small orders of many individuals who are end-users, rather than large orders of a small number of wholesale, corporate or government clientele. Shopping generally refers to the act of buying products. Sometimes this is done to obtain final goods, including necessities such as food and clothing; sometimes it takes place as a recreational activity. Recreational shopping often involves window shopping and browsing: it does not always result in a purchase.
John Dutton Conant Little is an Institute Professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology best known for his result in operations research, Little's law.

Distribution is one of the four elements of the marketing mix. Distribution is the process of making a product or service available for the consumer or business user who needs it. This can be done directly by the producer or service provider or using indirect channels with distributors or intermediaries. The other three elements of the marketing mix are product, pricing, and promotion.
In marketing, market segmentation is the process of dividing a broad consumer or business market, normally consisting of existing and potential customers, into sub-groups of consumers based on some type of shared characteristics.

Consumer behaviour is the study of individuals, groups, or organizations and all the activities associated with the purchase, use and disposal of goods and services, and how the consumer's emotions, attitudes and preferences affect buying behaviour. Consumer behaviour emerged in the 1940–50s as a distinct sub-discipline of marketing, but has become an interdisciplinary social science that blends elements from psychology, sociology, social anthropology, anthropology, ethnography, marketing and economics.

Private label products are those manufactured by one company for sale under another company's brand. Private-label goods are available in a wide range of industries from food to cosmetics. Private label brands managed solely by a retailer for sale in a specific chain of stores are called store brands or own brands.
The buying decision process is the decision-making process used by consumers regarding the market transactions before, during, and after the purchase of a good or service. It can be seen as a particular form of a cost–benefit analysis in the presence of multiple alternatives.
A lifestyle brand is a brand that attempts to embody the values, aspirations, interests, attitudes, or opinions of a group or a culture for marketing purposes. Lifestyle brands seek to inspire, guide, and motivate people, with the goal of their products contributing to the definition of the consumer's way of life. As such, they are closely associated with the advertising and other promotions used to gain mind share in their target market. They often operate from an ideology, hoping to attract a relatively high number of people and ultimately become a recognised social phenomenon.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to marketing:
Brand awareness is the extent to which customers are able to recall or recognize a brand under different conditions. Brand awareness is one of two dimensions from brand knowledge, an associative network memory model. Brand awareness is a key consideration in consumer behavior, advertising management, and brand management. The consumer's ability to recognize or recall a brand is central to purchasing decision-making. Purchasing cannot proceed unless a consumer is first aware of a product category and a brand within that category. Awareness does not necessarily mean that the consumer must be able to recall a specific brand name, but they must be able to recall enough distinguishing features for purchasing to proceed.
Founded in 1961, the Marketing Science Institute (MSI) is a corporate-membership-based organization. MSI is unique as the only research-based organization with a network of marketing academics from business schools all over the world as well as marketing executives from 60+ leading companies.
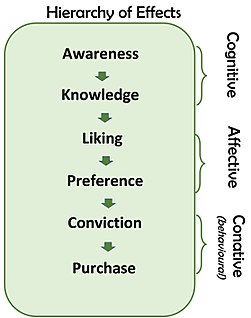
The AIDA model is just one of a class of models known as hierarchy of effects models or hierarchical models, all of which imply that consumers move through a series of steps or stages when they make purchase decisions. These models are linear, sequential models built on an assumption that consumers move through a series of cognitive (thinking) and affective (feeling) stages culminating in a behavioural stage.
The hedonic music consumption model was created by music researchers Kathleen Lacher and Richard Mizeski in 1994. Their goal was to use this model to examine the responses that listening to rock music creates, and to find if these responses influenced the listener's intention to later purchase the music. The article begins with a discussion of why the issue of music consumption is important. Music is then explored as an aesthetic product, prior to a discussion of what hedonic consumption is, as well as its origins, and concludes with an in-depth look at the model itself.
Research into food choice investigates how people select the food they eat. An interdisciplinary topic, food choice comprises psychological and sociological aspects, economic issues and sensory aspects.
Debra Jones Ringold is a professor at the Atkinson Graduate School of Management at Willamette University and is a marketing research consultant. She was selected to advise the U.S. Census Bureau on methods for improving Census participation, data collection methodology and communication of Census data to the public.
David Glen Mick is the Robert Hill Carter Professor in Marketing in the McIntire School of Commerce at the University of Virginia. He is former editor of the Journal of Consumer Research (1999-2003), past President of the Association for Consumer Research (2005), and an elected fellow of the Society for Consumer Psychology. He is credited with being a co-founder in 2005 of Transformative Consumer Research at the Association for Consumer Research. In general, Mick's research has focused on the nature and role of meaning and communication in consumer behavior. More specifically, he has addressed semiotics and consumer behavior, consumer motivations, self-gifts, advertising, materialism, satisfaction, technological products, and, more recently, wisdom and well-being. Mick has been recognized for his research in varied ways. He was awarded the Best Article Award for 1986–1988 in the Journal of Consumer Research. He is also a recipient of the 1999 Harold H. Maynard Award for research in the Journal of Marketing. He has been ranked as one of the top 50 most prolific scholars in the leading marketing journals from 1982 to 2006. He has also been ranked as one of the top-10 most published consumer researchers in the Journal of Consumer Research for the 25-year period of 1977–2002. Mick has been invited to conduct seminars at universities across the world, including Harvard, Duke, Stanford, Oxford, Erasmus (Netherlands), Trinity (Ireland), and the Stockholm School of Economics, among others.
Eric Thomas Bradlow is K.P. Chao Professor, Professor of Marketing, Statistics, Education and Economics, Chairperson Wharton Marketing Department, and Vice-Dean of Analytics at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania. He is known for his work on marketing research methods, missing data problems, and psychometrics. He is a fellow of the American Statistical Association and a fellow the American Education Research Association. Professor Bradlow is also co-founder of GBH Insights, a leading data-focused marketing strategy and insights firm that caters to Fortune 500 companies.
Variety seeking or variety-seeking buying behavior describes a consumer's desire to search for alternative products even if she or he is satisfied with a current product.
Psychographic segmentation has been used in marketing research as a form of market segmentation which divides consumers into sub-groups based on shared psychological characteristics, including subconscious or conscious beliefs, motivations, and priorities to explain and predict consumer behavior. Developed in the 1970´s, it applies behavioral and social sciences to explore to understand consumers’ decision-making processes, consumer attitudes, values, personalities, lifestyles, and communication preferences. It complements demographic and socioeconomic segmentation, and enables marketers to target audiences with messaging to market brands, products or services. Some consider lifestyle segmentation to be interchangeable with psychographic segmentation, marketing experts argue that lifestyle relates specifically to overt behaviors while psychographics relate to consumers' cognitive style, which is based on their "patterns of thinking, feeling and perceiving".
Kelly Goldsmith is an American marketing researcher who specializes in consumer behaviorist and a former reality television contestant. She is currently an associate professor of marketing at the Owen Graduate School of Management at Vanderbilt University.
References
- ↑ "Grocery war: Rivals H-E-B and Walmart battle for turf and shoppers in the region". 3 July 2015.
- ↑ "The Cherry-Picker Problem". 11 February 2010.
- ↑ "Leigh McAlister Faculty Profile". Faculty Profile. UT Austin. Retrieved 19 November 2011.