
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a small landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembourg City, is one of the four institutional seats of the European Union and the seat of several EU institutions, notably the Court of Justice of the European Union, the highest judicial authority. Luxembourg's culture, people, and languages are greatly influenced by its much larger neighbors France and Germany; for example, Luxembourgish, a Germanic language, is the only national language of the Luxembourgish people and of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, French is the only language for legislation, and all three – Luxembourgish, German and French – are used for administrative matters in the country.
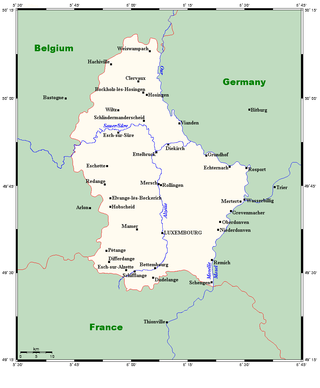
Luxembourg is a small country located in the Low Countries, part of North-West Europe. It borders Belgium for 148 kilometres to the west and north, France (73 km [45 mi]) to the south, and Germany (138 km [86 mi]) to the east. Luxembourg is landlocked, separated from the North Sea by Belgium.

Transport in Luxembourg is ensured principally by road, rail and air. There are also services along the river Moselle which forms the border with Germany. The road network has been significantly modernised in recent years with motorways to adjacent countries. The advent of the high-speed TGV link to Paris has led to renovation of the capital's main railway station while a new Schengen-only passenger terminal at Luxembourg Airport opened in 2017. Trams in the capital were reintroduced in December 2017 and there are plans for light-rail and/or tram-train lines in adjacent areas.
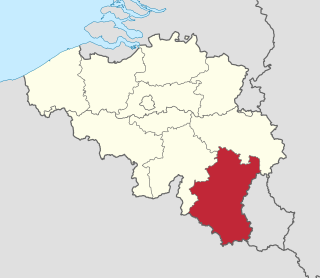
Luxembourg, also called Belgian Luxembourg or West Luxembourg, is the southernmost province of Wallonia within Belgium. It borders the country of Luxembourg to the east, the French departments of Ardennes, Meuse and Meurthe-et-Moselle to the south and southwest, and the Walloon provinces of Namur and Liège to the north. Its capital and largest city is Arlon, in the south-east of the province, near the border of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.

Meurthe-et-Moselle is a département in the Grand Est region of France, named after the rivers Meurthe and Moselle. Its prefecture and largest city is Nancy and it borders the departments of Meuse to the west, Vosges to the south, Moselle and Bas-Rhin and it borders the Belgian province of Luxembourg and the country of Luxembourg by the canton of Esch-sur-Alzette to the north. It had a population of 733,760 in 2019.

The Ardennes, also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in Belgium and Luxembourg, extending into Germany and France.

The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain and later by the Austrian Habsburgs until occupied and annexed by Revolutionary France (1794–1815).

The Sauer or Sûre is a river in Belgium, Luxembourg and Germany. A left tributary of the Moselle, its total length is 173 kilometres (107 mi).

The Our is a river in Belgium, Luxembourg and Germany. It is a left-hand tributary of the river Sauer/Sûre. Its total length is 78 kilometres (48 mi).

Esch-sur-Alzette is a canton in southwestern Luxembourg. It is both the second most populous and second most densely populated canton after the canton of Luxembourg. It borders Belgium & France.

Pétange is a commune and town in south-western Luxembourg. It is part of the canton of Esch-sur-Alzette and is the fifth-most populous commune in Luxembourg, as well as the most populous without town status. Pétange lies at the borders with both Belgium and France.

The Société Nationale des Chemins de Fer Luxembourgeois is the national railway company of Luxembourg. In 2023, it carried approximately 28.7 million passengers. As of 2023, the company employs around 5,000 people, making CFL the country's largest corporate employer.
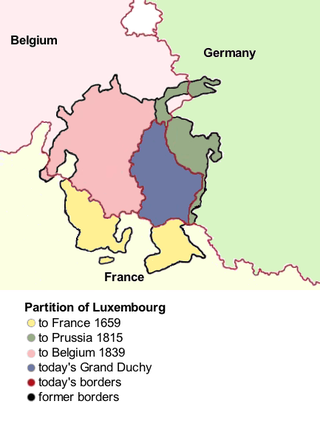
There were three Partitions of Luxembourg between 1659 and 1839. Together, the three partitions reduced the territory of the Duchy of Luxembourg from 10,700 km2 (4,100 sq mi) to the present-day area of 2,586 km2 (998 sq mi) over a period of 240 years. The remainder forms parts of modern-day Belgium, France, and Germany.

The Arrondissement of Arlon is one of the five administrative arrondissements in the Walloon province of Luxembourg, Belgium. It is an administrative arrondissement not to be confused with the exctint judicial arrondissement of Arlon, also comprising the municipalities of the Arrondissement of Virton.

The Greater Region, formerly also known as SaarLorLux, is a euroregion of eleven regional authorities located in four European states. The term has also been applied to cooperations of several of these authorities or of their subdivisions, administrations, organisations, clubs and people. Member regions represent different political structures: the Walloon region, comprising the French and German-speaking Communities of Belgium; the former Lorraine part of Grand Est, a region of France, including the French departments Meurthe-et-Moselle, Meuse, Moselle and Vosges; the German federated states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland; and the sovereign state of Luxembourg.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Luxembourg.

The German invasion of Luxembourg was part of Case Yellow, the German invasion of the Low Countries—Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands—and France during World War II. The battle began on 10 May 1940 and lasted just one day. Facing only light resistance, German troops quickly occupied Luxembourg. The Luxembourgish government, and Grand Duchess Charlotte, managed to escape the country and a government-in-exile was created in London.

The Schuster Line was a line of barriers and barricades erected by the Luxembourg government along its borders with Germany and France shortly before World War II. The line was named after Joseph Schuster, Luxembourg's chief engineer of bridges and highways, who was responsible for its construction.

Belgium–Luxembourg relations are the bilateral relations between the Kingdom of Belgium and Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.
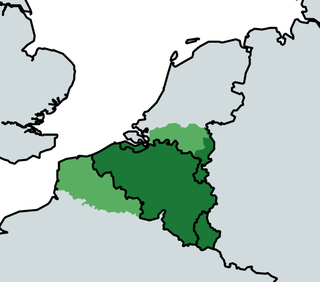
Greater Belgium is a Belgian irredentist concept which lays claim on territory nationalists deem as rightfully Belgian. It usually laid claim to: German territory historically belonging to the former Duchy of Limburg (Eupen-Malmedy), Dutch Limburg, Zeelandic Flanders, and the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. To a lesser degree, they also claimed the Dutch province of North Brabant and the French Netherlands (Nord-Pas-de-Calais). Shortly after the Belgian Revolution, some groups even proposed a Belgo-Rhine federation. Nowadays, belief in Belgian irredentism is very uncommon and overshadowed by talk of partitioning Belgium or the incorporation of Flanders into the Netherlands.





















