
Alcaeus of Mytilene was a lyric poet from the Greek island of Lesbos who is credited with inventing the Alcaic stanza. He was included in the canonical list of nine lyric poets by the scholars of Hellenistic Alexandria. He was a contemporary of Sappho, with whom he may have exchanged poems. He was born into the aristocratic governing class of Mytilene, the main city of Lesbos, where he was involved in political disputes and feuds.

Longus, sometimes Longos, was the author of an ancient Greek novel or romance, Daphnis and Chloe. Nothing is known of his life; it is assumed that he lived on the isle of Lesbos during the 2nd century AD.
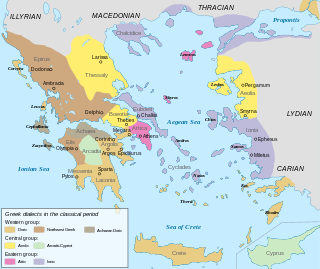
In linguistics, Aeolic Greek, also known as Aeolian, Lesbian or Lesbic dialect, is the set of dialects of Ancient Greek spoken mainly in Boeotia; in Thessaly; in the Aegean island of Lesbos; and in the Greek colonies of Aeolis in Anatolia and adjoining islands.
Megalochori may refer to the following places in Greece:

Mithymna is a town and former municipality on the island of Lesbos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2019 local government reform it is part of the municipality of West Lesbos, of which it is a municipal unit. Before 1919, its official name was Μόλυβος - Molyvos; that name dates back to the end of the Byzantine Era, but is still in common use today.
Lesbian language can refer to:

Lesbos or Lesvos is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of 1,633 km2 (631 sq mi), with approximately 400 kilometres of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece and the eighth largest in the Mediterranean. It is separated from Asia Minor by the narrow Mytilini Strait. On the southeastern coast is the island's capital and largest city, Mytilene (Μυτιλήνη), whose name is also used as a moniker for the whole island. Lesbos is a separate regional unit with the seat in Mytilene, which is also the capital of the larger North Aegean region. The region includes the islands of Lesbos, Chios, Ikaria, Lemnos, and Samos. The total population of the island is 83,068. A third of Lesbians live in the capital, while the remainder are concentrated in small towns and villages. The largest are Plomari, Kalloni, the Gera Villages, Agiassos, Eresos, and Molyvos.

Vampyros Lesbos is a 1971 West German-Spanish erotic horror film directed and co-written by Jesús Franco. The film stars Ewa Strömberg as Linda Westinghouse, an American who works in a Turkish legal firm. Westinghouse has a series of erotic dreams that involve a mysterious vampire woman who seduces her before feeding on her blood. When she travels to an island to settle an inheritance, Linda recognizes a woman as the vampire from her dreams.
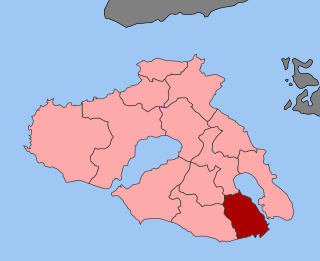
Gera or Yera is a town on the Aegean island of Lesbos in Greece. It once stood as one of the largest ports of the island. According to scholars the ancient name may have been Portus Hieraeus; Pliny the Elder mentions a Lesbian city called Hiera, which was abandoned before his time.

Kalloni is a town in the west-central part of the island of Lesbos, Greece. It is the seat of the West Lesbos municipality and the Kalloni municipal unit within it. Prior to 2011 the current municipal unit was a municipality. The name also existed in ancient times, though the conventional transcription of the classical name in English is "Callone".
In Greek mythology, Pyrrha was the daughter of Epimetheus and Pandora.

Lesbos wine is wine made on the Greek island of Lesbos in the Aegean Sea. The island has a long history of winemaking dating back to at least the 7th century BC when it was mentioned in the works of Homer. During this time the area competed with the wines of Chios for the Greek market. An apocryphal account details one of the brothers of the poet Sappho as a merchant trading Lesbos wine with the Greek colony of Naucratis in Egypt. The most noted Lesbos wine was known as Pramnian which draws similarities today to the Hungarian wine Eszencia. The popularity of Lesbos wine continued into Roman times where it was highly valued along with other Aegean wines of Chios, Thasos and Kos.

The influence of wine in ancient Greece helped ancient Greece trade with neighboring countries and regions. Many mannerisms and cultural aspects were associated with wine. It led to great change in Ancient Greece as well.
The peoples of the Mediterranean began to emerge from barbarism when they learned to cultivate the olive and the vine.

Chidira is a village on the Greek island of Lesbos, located at its western part and belonging to the municipal unit of Eresos-Antissa. Its population was 472 in 2011. Chidira borders with the villages Agra, Mesotopos, Eresos, Antissa, Revma, Pterounda and Vatousa.
In Greek mythology, Pylaeus, son of Lethus, son of Teutamides, descendant of Pelasgus. He was one of the allies to King Priam in the Trojan War; he commanded the Pelasgian contingent together with his brother Hippothous. Pylaeus is hardly ever mentioned separately from his brother; they are said to have fallen in battle together by Dictys Cretensis and to have been buried "in a garden" according to the late Latin poet Ausonius.
Melinno was a Greek lyric poet. She is known from a single surviving poem, known as the "Ode to Rome". The poem survives in a quotation by the fifth century AD author Stobaeus, who included it in a compilation of poems on manliness. It was apparently included in this collection by mistake, as Stobaeus misinterpreted the word ρώμα in the first line as meaning "strength", rather than being the Greek name for the city of Rome.
Pordoselene or Poroselene (Ποροσελήνη) was a town and polis (city-state) of ancient Aeolis. It was located on the chief island of the Hecatonnesi, a group of small islands lying between Lesbos and the coast of Asia Minor, which was also called Prodoselene. Strabo says that some, in order to avoid the dirty allusion presented by this name, as pordos means fart in Greek, called it Poroselene, which is the form employed by Ptolemy, Pliny the Elder, and Aelian. At a still later time the name was changed into Proselene, under which form the town appears as a bishop's see. Aristotle mentions the town in his History of Animals where it was on the extremity of a road that formed the border between an area of the island that contained weasels and another area that did not have them.
Lesbian tourism may refer to:

The Battle of Lesbos took place from 21 November – 21 December 1912 during the First Balkan War, resulting in the capture of the eastern Aegean island of Lesbos by the Kingdom of Greece.











