The 740s decade ran from January 1, 740, to December 31, 749.

Year 741 (DCCXLI) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 741 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 744 (DCCXLIV) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 744 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 643 (DCXLIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 643 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

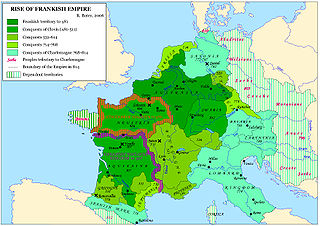
Austrasia was the northeastern kingdom within the core of the Frankish Empire during the Early Middle Ages, centring on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers. It included the original Frankish-ruled territories within what had been the northernmost part of Roman Gaul, and cities such as Cologne, Trier and Metz. It also stretched beyond the old Roman borders on the Rhine into Frankish areas which had never been formally under Roman rule. It came into being as a part of the Frankish Empire founded by Clovis I (481–511). At the same time, the initial powerbase of Clovis himself was the more Romanized part of northern Gaul, lying southwest of Austrasia, which came to be known as Neustria.

The House of Hanover is a European royal house with roots tracing back to the 17th century. Its members, known as Hanoverians, ruled Hanover, Great Britain, Ireland, and the British Empire at various times during the 17th to 20th centuries. Originating as a cadet branch of the House of Welf in 1635, also known then as the House of Brunswick-Lüneburg, the Hanoverians ascended to prominence with Hanover's elevation to an Electorate in 1692. In 1714 George I, prince-elector of Hanover and a descendant of King James VI and I, assumed the throne of Great Britain and Ireland, marking the beginning of Hanoverian rule over the British Empire. At the end of his line, Queen Victoria's death in 1901, the throne of the United Kingdom passed to her eldest son Edward VII, a member of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, through his father Albert, Prince Consort. The last reigning members of the House of Hanover lost the Duchy of Brunswick in 1918 when Germany became a republic and abolished royalty and nobility.

The Duchy of Aquitaine was a historical fiefdom located in the western, central and southern areas of present-day France, south of the river Loire. Although the full extent of the duchy, as well as its name, fluctuated greatly over the centuries and at times comprised much of what is now southwestern (Gascony) and central France.
The Duchy of Savoy was a territorial entity of the Savoyard state that existed from 1416 until 1847 and was a possession of the House of Savoy.

Alamannia, or Alemania, was the kingdom established and inhabited by the Alemanni, a Germanic tribal confederation that had broken through the Roman limes in 213.

Segorbe is a municipality in the mountainous coastal province of Castelló, autonomous community of Valencia, Spain. The former Palace of the Dukes of Medinaceli now houses the city's mayor. Segorbe's bull-running week in September attracts 200,000 visitors each year.

The Duchy of Bavaria was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (duces) under Frankish overlordship. A new duchy was created from this area during the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the late ninth century. It became one of the stem duchies of the East Frankish realm, which evolved as the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire.

Tassilo III was the duke of Bavaria from 748 to 788, the last of the house of the Agilolfings. He was the son of Duke Odilo of Bavaria and Hitrud, daughter of Charles Martel.

The Duchy of Swabia was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German Kingdom. It arose in the 10th century in the southwestern area that had been settled by Alemanni tribes in Late Antiquity.
Lanfredus was duke of Alamannia under Frankish sovereignty from 709 until his death. He was the son of duke Cotefredus. Lanfredus's brother was Theudebald.
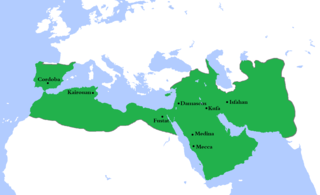
The title Duke(and Prince)of the Franks (Latin: dux(et princeps)Francorum) has been used for three different offices, always with "duke" implying military command and "prince" implying something approaching sovereign or regalian rights. The term "Franks" may refer to an ethnic group or to the inhabitants of a territory called Francia.

The Kingdom of the Lombards, also known as the Lombard Kingdom and later as the Kingdom of all Italy, was an early medieval state established by the Lombards, a Germanic people, on the Italian Peninsula in the latter part of the 6th century. The king was traditionally elected by the very highest-ranking aristocrats, the dukes, as several attempts to establish a hereditary dynasty failed. The kingdom was subdivided into a varying number of duchies, ruled by semi-autonomous dukes, which were in turn subdivided into gastaldates at the municipal level. The capital of the kingdom and the center of its political life was Pavia in the modern northern Italian region of Lombardy.

The Duchy of Gascony or Duchy of Vasconia was a duchy located in present-day southwestern France and northeastern Spain, an area encompassing the modern region of Gascony. The Duchy of Gascony, then known as Wasconia, was originally a Frankish march formed to hold sway over the Basques. However, the duchy went through different periods, from its early years with its distinctively Basque element to the merger in personal union with the Duchy of Aquitaine to the later period as a dependency of the Plantagenet kings of England.
Leuthard II may refer to:
The Duchy of Thuringia was an eastern frontier march of the Merovingian kingdom of Austrasia, established about 631 by King Dagobert I after his troops had been defeated by the forces of the Slavic confederation of Samo at the Battle of Wogastisburg. It was recreated in the Carolingian Empire and its dukes were appointed by the king until it was absorbed by the Saxon dukes in 908. From about 1111/12 the territory was ruled by the Landgraves of Thuringia as Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. When Frederick IV, the last independent ruler of Thuringia died in 1440, the territory passed to his nephew, the Saxon elector Frederick II.














