
The Grand Trunk Railway was a railway system that operated in the Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario and in the American states of Connecticut, Maine, Michigan, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont. The railway was operated from headquarters in Montreal, Quebec, with corporate headquarters in London, United Kingdom. It cost an estimated $160 million to build. The Grand Trunk, its subsidiaries, and the Canadian Government Railways were precursors of today's Canadian National Railway.
The Central Vermont Railway was a railroad that operated in the U.S. states of Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New York, and Vermont, as well as the Canadian province of Quebec.

The St. Lawrence and Atlantic Railroad, known as St-Laurent et Atlantique Quebec in Canada, is a short-line railway operating between Portland, Maine, on the Atlantic Ocean, and Montreal, Quebec, on the St. Lawrence River. It crosses the Canada–US border at Norton, Vermont, and Stanhope, Quebec, and is owned by short-line operator Genesee & Wyoming.

The Downeaster is a 145-mile (233 km) passenger train service operated by Amtrak and managed by the Northern New England Passenger Rail Authority (NNEPRA), an agency of the state of Maine. Named for the Down East region of Maine, the train operates five daily round trips between North Station in Boston, Massachusetts, and Brunswick, Maine, with 10 intermediate stops.

The Maine Central Railroad Company was a U. S. Class I railroad in central and southern Maine. It was chartered in 1856 and began operations in 1862. By 1884, Maine Central was the longest railroad in New England. Maine Central had expanded to 1,358 miles (2,185 km) when the United States Railroad Administration assumed control in 1917. The main line extended from South Portland, Maine, east to the Canada–United States border with New Brunswick, and a Mountain Division extended west from Portland to St. Johnsbury, Vermont, and north into Quebec. The main line was double track from South Portland to Royal Junction, where it split into a "lower road" through Brunswick and Augusta and a "back road" through Lewiston, which converged at Waterville into single track to Bangor and points east. Branch lines served the industrial center of Rumford, a resort hotel on Moosehead Lake and coastal communities from Bath to Eastport.

The International Railway of Maine was a historic railroad constructed by the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) between Lac-Mégantic, Quebec, and Mattawamkeag, Maine, closing a key gap in the railway's transcontinental main line to the port of Saint John, New Brunswick.
The European and North American Railway (E&NA) is the name for three historic Canadian and American railways which were built in New Brunswick and Maine.

The railroad history of Portland, Maine, began in 1842 with the arrival of the Portland, Saco & Portsmouth Railway (PS&P). Most of the rail activity in Portland revolved around agricultural goods bound for export and import freight from Europe. Yet Maine's largest city also enjoyed 125 years of continuous passenger rail service, from 1842 until 1967, and Amtrak began serving the city in 2001. For most of Portland's history, passenger train schedules were designed with intercity travel rather than daily commuting in mind; passenger activities were mostly confined to intercity travel from Portland to Boston, Montreal, Nova Scotia, and points west.

The Portland Company was established 10 November 1846 by John A. Poor and Norris Locomotive Works engineer Septimus Norris as a locomotive foundry to build railroad equipment for the adjacent Portland terminus of the Atlantic and St. Lawrence Railroad connection between Portland, Maine and Montreal. The shops opened for business in October, 1847. Its first locomotive, the Augusta, emerged from the shops in July 1848 for delivery to the Portland, Saco & Portsmouth. Over the next several decades, the Company produced in its Fore Street facilities over 600 steam locomotives as well as 160 merchant and naval vessels, railcars, construction equipment, Knox automobiles, and the like. Portland Company built the engines of the civil war side-wheel gunboats Agawam and Pontoosuc. Taking into account its other products, the Company could lay claim to being one of the leading medium-to-heavy steel manufacturers in New England. The company ceased production in 1978.
The Portland Terminal Company was a terminal railroad notable for its control of switching (shunting) activity for the Maine Central Railroad (MEC) and Boston & Maine (B&M) railroads in the Maine cities of Portland, South Portland, and Westbrook.

The Maine Central Railroad Rumford Branch is a railroad line in Maine now operated as part of the Pan Am Railways system. The Rumford Branch leaves the mainline at Leeds Junction and continues northwest up the Androscoggin River valley, passing through Livermore Falls and terminating at Rumford. The branch comprises the remaining trackage of three earlier branches:

The Grand Trunk station is a historic railroad station at 103 Lincoln Street in Lewiston, Maine. It was built in 1874 for a spur line connecting Lewiston and Auburn to the Grand Trunk Railway, to which it was leased. It is through this station that many of the area's French Canadian immigrants arrived to work in the area mills. The station was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1979.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Portland, Maine, USA.

The Maine Central Railroad Company main line extended from Portland, Maine, east to the Canada–US border with New Brunswick at the Saint Croix-Vanceboro Railway Bridge. It is the transportation artery linking Maine cities to the national railway network. Sections of the main line had been built by predecessor railroads consolidated as the Maine Central in 1862 and extended to the Canada–US border in 1882. Through the early 20th century, the main line was double track from South Portland to Royal Junction, where it split into a lower road through Brunswick and Augusta and a back road through Lewiston which converged at Waterville into single track to Bangor and points east. Westbound trains typically used the lower road with lighter grades, while eastbound trains of empty cars used the back road. This historical description does not include changes following purchase of the Maine Central Railroad by Guilford Transportation Industries in 1981 and subsequent operation as part of Pan Am Railways.

The Portland–Lewiston Interurban (PLI) was an electric railroad subsidiary of the Androscoggin Electric Company operating from 1914 to 1933 between Monument Square in Portland and Union Square in Lewiston, Maine. Hourly service was offered over the 40-mile (64 km) route between the two cities. Express trains stopping only at West Falmouth, Gray, New Gloucester, Upper Gloucester and Danville made the trip in 80 minutes, while trains making other local stops upon request required 20 minutes more. The line was considered the finest interurban railroad in the state of Maine.

The Grand Trunk station was a historic railroad station in Oxford, Maine. The station was built in 1883 by the Grand Trunk Railroad linking Oxford with Montreal and Portland, Maine. The village grew especially after the arrival of the St. Lawrence & Atlantic Railroad toward the end of 1840. The railroad opened the village to several business ventures between Portland and Montreal. The railroad passes through the midst of the town, in the same general line with the river, and has a station a short distance south of the centre.

Richmond railway station is a historic building located on rue Principale Nord in Richmond in the province of Quebec. The current building was constructed in 1912 by the Grand Trunk Railway (GTR) to replace the previous wood-frame structure which had been destroyed by fire.

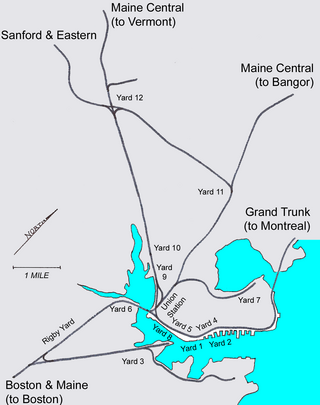
Union Station was a train station in Portland, Maine.

Railroads have played an important role in New England ever since the Granite Railway, America's first commercial railway, began operations in Massachusetts in 1826. As industrialization spread across the region, hundreds of railroads were built throughout the 19th century. Railroad mileage peaked around World War I, and from that point on mileage began to shrink. Despite this, railroads continue to be important for freight and passenger transportation in the region, with the New Haven Line holding the title of busiest railroad line in the entire United States.

















