
An altarpiece is an work of art in painting, sculpture or relief representing a religious subject made for placing at the back of or behind the altar of a Christian church. Though most commonly used for a single work of art such as a painting or sculpture, or a set of them, the word can also be used of the whole ensemble behind an altar, otherwise known as a reredos, including what is often an elaborate frame for the central image or images. Altarpieces were one of the most important products of Christian art especially from the late Middle Ages to the era of Baroque painting.

Lorenzo Lotto was an Italian painter, draughtsman, and illustrator, traditionally placed in the Venetian school, though much of his career was spent in other north Italian cities. He painted mainly altarpieces, religious subjects and portraits. He was active during the High Renaissance and the first half of the Mannerist period, but his work maintained a generally similar High Renaissance style throughout his career, although his nervous and eccentric posings and distortions represented a transitional stage to the Florentine and Roman Mannerists.

Pinturicchio, or Pintoricchio, also known as Benetto di Biagio or Sordicchio, was an Italian painter during the Renaissance. He acquired his nickname because of his small stature and he used it to sign some of his artworks that were created during the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries.

Carlo Crivelli was an Italian Renaissance painter of conservative Late Gothic decorative sensibility, who spent his early years in the Veneto, where he absorbed influences from the Vivarini, Squarcione, and Mantegna. He left the Veneto by 1458 and spent most of the remainder of his career in the March of Ancona, where he developed a distinctive personal style that contrasts with that of his Venetian contemporary Giovanni Bellini.

For the village near Livorno, see Sassetta, Tuscany

Giovanni di Paolo di Grazia was an Italian painter, working primarily in Siena, becoming a prolific painter and illustrator of manuscripts, including Dante's texts. He was one of the most important painters of the 15th century Sienese School. His early works show the influence of earlier Sienese masters, but his later style was more individual, characterized by cold, harsh colours and elongated forms. His style also took on the influence of International Gothic artists such as Gentile da Fabriano. Many of his works have an unusual dreamlike atmosphere, such as the surrealistic Miracle of St. Nicholas of Tolentino painted about 1455 and now housed in the Philadelphia Museum of Art, while his last works, particularly Last Judgment, Heaven, and Hell from about 1465 and Assumption painted in 1475, both at Pinacoteca Nazionale (Siena), are grotesque treatments of their lofty subjects. Giovanni's reputation declined after his death but was revived in the 20th century.

The Oddi altarpiece, or more correctly the degli Oddi altarpiece, is an altarpiece of the Coronation of the Virgin painted in 1502-1504 by the Italian Renaissance master Raphael for the altar of the Oddi family chapel in the church of San Francesco al Prato in Perugia, Italy, now in the Vatican Pinacoteca. The altarpiece was commissioned for the Oddi family chapel in San Francesco al Prato in Perugia, was taken to Paris in 1797 and in 1815 brought back to Italy, not to Perugia but to the Vatican Pinacoteca.

Bernardo Daddi was an early Italian Renaissance painter and the leading painter of Florence of his generation. He was one of the artists who contributed to the revolutionary art of the Renaissance, which broke away from the conventions of the preceding generation of Gothic artists, by creating compositions which aimed to achieve a more realistic representation of reality. He was particularly successful with his small-scale works and contributed to the development of the portable altarpiece, a format that subsequently gained great popularity.
Sano di Pietro or Ansano di Pietro di Mencio (1405–1481) was an Italian painter of the Sienese school of painting. He was active for about half a century during the Quattrocento period, and his contemporaries included Giovanni di Paolo and Sassetta.

The Baronci Altarpiece was a painting by the Italian High Renaissance artist Raphael. His first recorded commission, it was made for Andrea Baronci's chapel in the church of Sant'Agostino in Città di Castello, near Urbino. The altarpiece was seriously damaged during an earthquake in 1789, and since 1849 fragments of the original painting have been part of different collections.

Jacopo di Cione was an Italian Gothic period painter in the Republic of Florence.

Lippo Memmi was an Italian painter from Siena. He was the foremost follower of Simone Martini, who was his brother-in-law.

Biagio d’Antonio Tucci was an Italian Renaissance painter active in Florence, Faenza and Rome.

The Master of the Osservanza Triptych, also known as the Osservanza Master and as the Master of Osservanza, is the name given to an Italian painter of the Sienese School active about 1430 to 1450.

The Stefaneschi Altarpiece is a triptych by the Italian painter Giotto, from c. 1320. It was commissioned by Cardinal Giacomo Gaetani Stefaneschi to serve as an altarpiece for one of the altars of Old St. Peter's Basilica in Rome. It is now at the Pinacoteca Vaticana, in Rome.

The Averoldi Polyptych, also known as the Averoldi Altarpiece, is a painting by the Italian Renaissance painter Titian, dating to 1520–1522, in the basilica church of Santi Nazaro e Celso in Brescia, northern Italy.

Mariotto di Nardo di Cione was a Florentine painter in the Florentine Gothic style. He worked at the Duomo of Florence, the church of Santa Maria Maggiore, and the Orsanmichele. He created both frescoes and panel paintings, and was also active as a manuscript illuminator.

The San Pietro Polyptych is a polyptych by Italian Renaissance master Perugino, painted around 1496–1500. The panels are now in different locations: the lunette and the central panel, depicting the Ascension of Christ, are in the Museum of Fine Arts of Lyon, France.
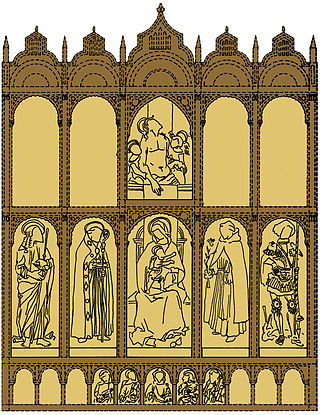
The 1472 Altarpiece was a tempera and oil on panel altarpiece by Carlo Crivelli, dated 1472 on the central panel. Also known as the Fesch Altarpiece or the Eckinson Altarpiece, it is now divided up between a number of galleries in the United States and Europe.

The Purification of the Virgin is a painting in tempera on panel from an altarpiece by Benozzo Gozzoli and once owned by the Compagnia di Santa Maria della Purificazione e di San Zanobi of Florence, Italy. The painting is on display in the Philadelphia Museum of Art in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States of America.



















