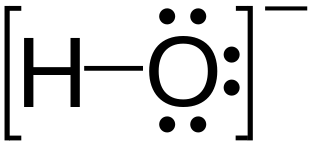
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile, and a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate in aqueous solution, liberating solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. The corresponding electrically neutral compound HO• is the hydroxyl radical. The corresponding covalently bound group –OH of atoms is the hydroxy group. Both the hydroxide ion and hydroxy group are nucleophiles and can act as catalysts in organic chemistry.

Infrared spectroscopy is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms. It can be used to characterize new materials or identify and verify known and unknown samples. The method or technique of infrared spectroscopy is conducted with an instrument called an infrared spectrometer which produces an infrared spectrum. An IR spectrum can be visualized in a graph of infrared light absorbance on the vertical axis vs. frequency, wavenumber or wavelength on the horizontal axis. Typical units of wavenumber used in IR spectra are reciprocal centimeters, with the symbol cm−1. Units of IR wavelength are commonly given in micrometers, symbol μm, which are related to the wavenumber in a reciprocal way. A common laboratory instrument that uses this technique is a Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometer. Two-dimensional IR is also possible as discussed below.
An intermolecular force (IMF) is the force that mediates interaction between molecules, including the electromagnetic forces of attraction or repulsion which act between atoms and other types of neighbouring particles, e.g. atoms or ions. Intermolecular forces are weak relative to intramolecular forces – the forces which hold a molecule together. For example, the covalent bond, involving sharing electron pairs between atoms, is much stronger than the forces present between neighboring molecules. Both sets of forces are essential parts of force fields frequently used in molecular mechanics.
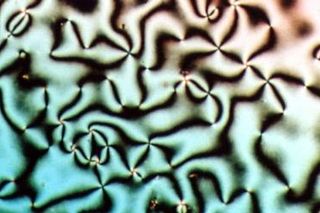
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter that has properties between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For instance, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many different types of liquid-crystal phases, which can be distinguished by their different optical properties. The contrasting areas in the textures correspond to domains where the liquid-crystal molecules are oriented in different directions. Within a domain, however, the molecules are well ordered. LC materials may not always be in a liquid-crystal state of matter.

X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information.

Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circular birefringence and circular dichroism are the manifestations of optical activity. Optical activity occurs only in chiral materials, those lacking microscopic mirror symmetry. Unlike other sources of birefringence which alter a beam's state of polarization, optical activity can be observed in fluids. This can include gases or solutions of chiral molecules such as sugars, molecules with helical secondary structure such as some proteins, and also chiral liquid crystals. It can also be observed in chiral solids such as certain crystals with a rotation between adjacent crystal planes or metamaterials.
In chemistry, hydronium (hydroxonium in traditional British English) is the common name for the aqueous cation H3O+, the type of oxonium ion produced by protonation of water. It is often viewed as the positive ion present when an Arrhenius acid is dissolved in water, as Arrhenius acid molecules in solution give up a proton (a positive hydrogen ion, H+) to the surrounding water molecules (H2O). In fact, acids must be surrounded by more than a single water molecule in order to ionize, yielding aqueous H+ and conjugate base. Three main structures for the aqueous proton have garnered experimental support: The Eigen cation, which is a tetrahydrate, H3O+(H2O)3; the Zundel cation, which is a symmetric dihydrate, H+(H2O)2; and the Stoyanov cation, an expanded Zundel cation, which is a hexahydrate: H+(H2O)2(H2O)4. Spectroscopic evidence from well-defined IR spectra overwhelmingly supports the Stoyanov cation as the predominant form. For this reason, it has been suggested that wherever possible, the symbol H+(aq) should be used instead of the hydronium ion.

Raman spectroscopy ; is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified.

Rotational spectroscopy is concerned with the measurement of the energies of transitions between quantized rotational states of molecules in the gas phase. The spectra of polar molecules can be measured in absorption or emission by microwave spectroscopy or by far infrared spectroscopy. The rotational spectra of non-polar molecules cannot be observed by those methods, but can be observed and measured by Raman spectroscopy. Rotational spectroscopy is sometimes referred to as pure rotational spectroscopy to distinguish it from rotational-vibrational spectroscopy where changes in rotational energy occur together with changes in vibrational energy, and also from ro-vibronic spectroscopy where rotational, vibrational and electronic energy changes occur simultaneously.
Raman scattering or the Raman effect is the inelastic scattering of photons by matter, meaning that there is both an exchange of energy and a change in the light's direction. Typically this effect involves vibrational energy being gained by a molecule as incident photons from a visible laser are shifted to lower energy. This is called normal Stokes Raman scattering. The effect is exploited by chemists and physicists to gain information about materials for a variety of purposes by performing various forms of Raman spectroscopy. Many other variants of Raman spectroscopy allow rotational energy to be examined and electronic energy levels may be examined if an X-ray source is used in addition to other possibilities. More complex techniques involving pulsed lasers, multiple laser beams and so on are known.

Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom.

Photosensitizers produce a physicochemical change in a neighboring molecule by either donating an electron to the substrate or by abstracting a hydrogen atom from the substrate. At the end of this process, the photosensitizer eventually returns to its ground state, where it remains chemically intact until the photosensitizer absorbs more light. This means that the photosensitizer remains unchanged before and after the energetic exchange, much like heterogeneous photocatalysis. One branch of chemistry which frequently utilizes photosensitizers is polymer chemistry, using photosensitizers in reactions such as photopolymerization, photocrosslinking, and photodegradation. Photosensitizers are also used to generate prolonged excited electronic states in organic molecules with uses in photocatalysis, photon upconversion and photodynamic therapy. Generally, photosensitizers absorb electromagnetic radiation consisting of infrared radiation, visible light radiation, and ultraviolet radiation and transfer absorbed energy into neighboring molecules. This absorption of light is made possible by photosensitizers' large de-localized π-systems, which lowers the energy of HOMO and LUMO orbitals to promote photoexcitation. While many photosensitizers are organic or organometallic compounds, there are also examples of using semiconductor quantum dots as photosensitizers.

A molecular solid is a solid consisting of discrete molecules. The cohesive forces that bind the molecules together are van der Waals forces, dipole-dipole interactions, quadrupole interactions, π-π interactions, hydrogen bonding, halogen bonding, London dispersion forces, and in some molecular solids, coulombic interactions. Van der Waals, dipole interactions, quadrupole interactions, π-π interactions, hydrogen bonding, and halogen bonding are typically much weaker than the forces holding together other solids: metallic, ionic, and network solids. Intermolecular interactions, typically do not involve delocalized electrons, unlike metallic and certain covalent bonds. Exceptions are charge-transfer complexes such as the tetrathiafulvane-tetracyanoquinodimethane (TTF-TCNQ), a radical ion salt. These differences in the strength of force and electronic characteristics from other types of solids give rise to the unique mechanical, electronic, and thermal properties of molecular solids.
A molecular vibration is a periodic motion of the atoms of a molecule relative to each other, such that the center of mass of the molecule remains unchanged. The typical vibrational frequencies range from less than 1013 Hz to approximately 1014 Hz, corresponding to wavenumbers of approximately 300 to 3000 cm−1 and wavelengths of approximately 30 to 3 µm.
Vibrational circular dichroism (VCD) is a spectroscopic technique which detects differences in attenuation of left and right circularly polarized light passing through a sample. It is the extension of circular dichroism spectroscopy into the infrared and near infrared ranges.

Water-in-water (W/W) emulsion is a system that consists of droplets of water-solvated molecules in another continuous aqueous solution; both the droplet and continuous phases contain different molecules that are entirely water-soluble. As such, when two entirely aqueous solutions containing different water-soluble molecules are mixed, water droplets containing predominantly one component are dispersed in water solution containing another component. Recently, such a water-in-water emulsion was demonstrated to exist and be stable from coalescence by the separation of different types of non-amphiphilic, but water-soluble molecular interactions. These molecular interactions include hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and salt bridging. This w/w emulsion was generated when the different water-solvated molecular functional groups get segregated in an aqueous mixture consisting of polymer and liquid crystal molecules.
In physics and chemistry, a degree of freedom is an independent physical parameter in the formal description of the state of a physical system. The set of all states of a system is known as the system's phase space, and the degrees of freedom of the system are the dimensions of the phase space.
Crystallization of polymers is a process associated with partial alignment of their molecular chains. These chains fold together and form ordered regions called lamellae, which compose larger spheroidal structures named spherulites. Polymers can crystallize upon cooling from melting, mechanical stretching or solvent evaporation. Crystallization affects optical, mechanical, thermal and chemical properties of the polymer. The degree of crystallinity is estimated by different analytical methods and it typically ranges between 10 and 80%, with crystallized polymers often called "semi-crystalline". The properties of semi-crystalline polymers are determined not only by the degree of crystallinity, but also by the size and orientation of the molecular chains.

Introduction - pure and doped Triglycine Sulfate

C70 fullerene is the fullerene molecule consisting of 70 carbon atoms. It is a cage-like fused-ring structure which resembles a rugby ball, made of 25 hexagons and 12 pentagons, with a carbon atom at the vertices of each polygon and a bond along each polygon edge. A related fullerene molecule, named buckminsterfullerene (C60 fullerene), consists of 60 carbon atoms.














