Related Research Articles

Elizabeth Garrett Anderson was an English physician and suffragist. She is known for being the first woman to qualify in Britain as a physician and surgeon and as a co-founder and dean of the London School of Medicine for Women, which was the first medical school in Britain to train women as doctors. She was the first female dean of a British medical school, the first woman in Britain to be elected to a school board and, as mayor of Aldeburgh, the first female mayor in Britain.
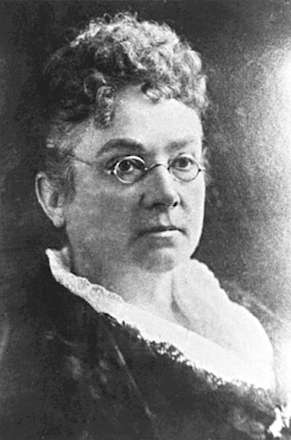
Emily Howard Stowe was a Canadian physician who was the first female physician to practise in Canada, the second licensed female physician in Canada and an activist for women's rights and suffrage. Stowe helped found the women's suffrage movement in Canada and campaigned for the country's first medical college for women.

Rebecca Lee Crumpler, born Rebecca Davis,, was an American physician, nurse and author. After studying at the New England Female Medical College, in 1864 she became the first African American woman to become a doctor of medicine in the United States. Crumpler was also one of the first female physician authors in the nineteenth century. In 1883, she published A Book of Medical Discourses. The book has two parts that cover the prevention and cure of infantile bowel complaints, and the life and growth of human beings. Dedicated to nurses and mothers, it focuses on maternal and pediatric medical care and was among the first publications written by an African American on the subject of medicine.

Elizabeth Blackwell was a British and American physician, notable as the first woman to earn a medical degree in the United States, and the first woman on the Medical Register of the General Medical Council for the United Kingdom. Blackwell played an important role in both the United States and the United Kingdom as a social reformer, and was a pioneer in promoting education for women in medicine. Her contributions remain celebrated with the Elizabeth Blackwell Medal, awarded annually to a woman who has made a significant contribution to the promotion of women in medicine.
The London School of Medicine for Women (LSMW) established in 1874 was the first medical school in Britain to train women as doctors. The patrons, vice-presidents, and members of the committee that supported and helped found the London School of Medicine for Women wanted to provide educated women with the necessary facilities for learning and practicing midwifery and other branches of medicine while also promoting their future employment in the fields of midwifery and other fields of treatment for women and children.

The presence of women in medicine, particularly in the practicing fields of surgery and as physicians, has been traced to the earliest of history. Women have historically had lower participation levels in medical fields compared to men with occupancy rates varying by race, socioeconomic status, and geography.
Martha Wollstein was an American physician. Wollstein was born in New York to a German Jewish family.

Kristine Munch was a Norwegian physician. She was among the first female physicians in Norway.

Nielsine Nielsen was the first female academic and physician in Denmark. She graduated in 1885 and in 1889 she established her own medical practice and worked as a general practitioner. She was active in the gender equality movement through her work in Danish Women's Society.
Susie O'Reilly was an Australian family doctor and obstetrician. She practiced on the North Shore in Sydney in the first half of the 20th century. Despite graduating fourth in her year from Medicine at the University of Sydney, her application for residency at Sydney Hospital in 1905 was rejected in favour of male applicants with a poorer academic record.

Catherine Chisholm was a British physician and the first female medical graduate of the University of Manchester. She was instrumental in founding the Manchester Babies Hospital, which was opened on 4 August 1914, contributing to her reputation as one of the founders of modern neonatology practice. She was appointed a CBE in 1935 and became the first female Honorary Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians in 1949.

Myra Adele Logan is known as the first African American female physician, surgeon, and anatomist to perform a successful open-heart surgery. Following this accomplishment, Logan focused her work on children's heart surgery and was involved in the development of the antibiotic Aureomycin which treated bacterial, viral, and rickettsial diseases with the majority of her medical practice done at the Harlem Hospital in New York. Logan attended medical school during the pre–Civil Rights era. The majority of black female physicians in this time period were forced to attend segregated schools. Earning a medical degree as an African American woman during this time period was extremely difficult.

Verina Harris Morton Jones was an American physician, suffragist and clubwoman. Following her graduation from the Woman's Medical College of Pennsylvania in 1888 she was the first woman licensed to practice medicine in Mississippi. She then moved to Brooklyn where she co-founded and led the Lincoln Settlement House. Jones was involved with numerous civic and activist organizations and was elected to the board of directors of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP).

Mary Amanda Dixon Jones was an American physician and surgeon in the field of obstetrics and gynecology, who was the first American physician to propose and perform a total hysterectomy to treat a tumor in the uterine muscle (myoma). Jones had a successful career until her work doing gynecological surgery at Woman's Hospital of Brooklyn drew the attention of the news media, and she was the subject of a 24-article investigative expose by the Brooklyn Eagle. As a result, she was charged with one count of murder, and one count of manslaughter. She was found not guilty, and sued the Eagle. She lost the libel case, and was forced to close her medical practice. Jones then spent the last years of her medical career researching the tissue pathology of gynecological conditions.

Edith Irby Jones was an American physician who was the first woman president of the National Medical Association and a founding member of the Association of Black Cardiologists. She was honored by many awards, including induction into both the University of Arkansas College of Medicine Hall of Fame and the inaugural group of women inducted into the Arkansas Women's Hall of Fame. She was the first African American to be accepted as a non-segregated student at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences and the first black student to attend racially mixed classes in the American South. She was the first African American to graduate from a southern medical school, first black intern in the state of Arkansas, and later first black intern at Baylor College of Medicine.
Barbara Ross-Lee, D.O. is an American physician, academic, and the first African-American woman to serve as dean of a U.S. medical school; she is also known as the sister of Diana Ross along with being the aunt of actress Tracee Ellis Ross, and singer-songwriters Rhonda Ross Kendrick and Evan Ross. She majored in biology and chemistry at Wayne State University, graduating in 1965. Then, in 1969, she entered Michigan State University's College of Osteopathic Medicine. Ross-Lee then went on to open her own private family practice, teach as a professor, and hold other positions within the medical community. In 1993, she was elected as the first woman dean of a medical school, at Ohio University's Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine. She has earned several awards and honors for her work and accomplishments.

Alida Avery (1833–1908) was an American physician and Vassar College faculty member. In Colorado, she was thought to be the first woman licensed to practice medicine in the state. She was also the Superintendent of Hygiene for Colorado. Avery was among the first women first admitted to the Denver Medical Society.

Tomasa Ester Casís was a Panamanian teacher and woman's rights activist. She founded the first women's cultural society in the country and pressed for women's equality. Supporting suffrage, she was one of the pioneering feminists of Panama and was honored as a commander in the Order of Vasco Núñez de Balboa for her educational contributions to the country.

Katherine C. Galbraith Manion (1867–1956) was an American physician and suffragist. She and three other women challenged the United States Army's ban on women doctors during World War I. She was elected president of the Medical Women's National Association in 1924.
References
- ↑ "Lidia Gertrudis Sogandares Rivera". EnCaribe (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 10 March 2015. Retrieved 2018-04-02.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ↑ "Encyclopedia of Arkansas". Encyclopedia of Arkansas. Retrieved 2024-05-10.
- ↑ "Encyclopedia of Arkansas". Encyclopedia of Arkansas. Retrieved 2024-06-19.