
An aircraft pilot or aviator is a person who controls the flight of an aircraft by operating its directional flight controls. Some other aircrew members, such as navigators or flight engineers, are also considered aviators, because they are involved in operating the aircraft's navigation and engine systems. Other aircrew members, such as flight attendants, mechanics and ground crew, are not classified as aviators.
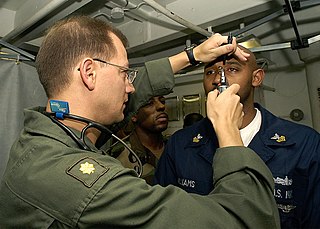
Aviation medicine, also called flight medicine or aerospace medicine, is a preventive or occupational medicine in which the patients/subjects are pilots, aircrews, or astronauts. The specialty strives to treat or prevent conditions to which aircrews are particularly susceptible, applies medical knowledge to the human factors in aviation and is thus a critical component of aviation safety. A military practitioner of aviation medicine may be called a flight surgeon and a civilian practitioner is an aviation medical examiner. One of the biggest differences between the military and civilian flight doctors is the military flight surgeon's requirement to log flight hours.
In aviation, groundcrew or ground staff are the support personnel that service aircraft on the ground – as opposed to aircrew, who operate an aircraft while in flight. The term groundcrew is used by both airlines and military aviation.
Life support is a set of therapies for preserving a patient's life when essential body systems are not functioning sufficiently to sustain life.
The Aircrew Badge, commonly known as Wings, is a qualification badge of the United States military that is awarded by all five branches of armed services to personnel who serve as aircrew members on board military aircraft. The badge is intended to recognize the training and qualifications required by aircrew of military aircraft. In order to qualify as an aircrew member and receive the Aircrew Badge, such personnel typically undergo advanced training in aircraft in-flight support roles.

Naval Air Station Oceana or NAS Oceana is a military airport located in Virginia Beach, Virginia, and is a United States Navy master jet base. It is also known as Apollo Soucek Field, named after Lieutenant Apollo Soucek, a Navy Test Pilot who set the global altitude record in 1930 by flying a Curtiss "Hawk" biplane to an altitude of 43,166 feet. NAS Oceana is the only Master Jet Base on the East Coast.

The Naval Aviation Warfighting Development Center was formerly known as the Naval Strike and Air Warfare Center at Naval Air Station Fallon located in the city of Fallon in western Nevada. It is the center of excellence for naval aviation training and tactics development. NAWDC provides service to aircrews, squadrons and air wings throughout the United States Navy through flight training, academic instructional classes, and direct operational and intelligence support. The name was changed from NSAWC to NAWDC to align with the naming convention of the Navy's other Warfare Development Centers (including Naval Surface and Mine Warfare Development Center SMWDC and the Undersea Warfare Development Center UWDC

The 1st Aviation Regiment is one of the Australian Army's three Army Aviation regiments and provides aerial reconnaissance and fire support to the Australian Army. The 1st Aviation Regiment, equipped with Eurocopter Tiger attack helicopters, forms part of the 16th Aviation Brigade and is based at Gaza Lines, Robertson Barracks, Darwin.
The Aircrew Survival Egress Knife or ASEK is a U.S. Army aircrew survival knife, designed and initially manufactured by the Ontario Knife Company, and entered service in 2003.

Marine Fighter Attack Training Squadron 101 (VMFAT-101) is a United States Marine Corps F/A-18 Hornet training squadron. The squadron is based at Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, California and falls under the command of Marine Aircraft Group 11 (MAG-11) and the 3rd Marine Aircraft Wing.

The Naval Aircrewman rating is an enlisted rating of the US Navy. It was previously designated as aviation anti-submarine warfare operator. However, under the CNO-directed "Helicopter Master Plan", all 78XX and 94XX aircrewmen were re-designated as "aviation warfare systems operators". The description of the Naval Aircrew Rate (AW) on this page define only the "Active Duty" aspects of the AW rate, fleets (aircraft), positions, and duties that are manned by aircrew in today's Navy. The Full Time Support (FTS) and Selected Reserves (SELRES) components of the U.S. Naval Reserves make up the largest number of Aircrew in today's Navy. Many technologically advanced navies have a similar trade.
In the field of aviation medicine, the 1 percent rule is a risk threshold that is applied to the medical fitness of pilots. The 1 percent rule states that a 1% per annum risk of medical incapacitation is the threshold between acceptable and unacceptable. In other words:
Applying this 1 percent rule would result in an airline pilot being denied a medical certificate if their risk of a medical incapacitation was determined as being greater than 1% during the year.
In aviation, a preflight checklist is a list of tasks that should be performed by pilots and aircrew prior to takeoff. Its purpose is to improve flight safety by ensuring that no important tasks are forgotten. Failure to correctly conduct a preflight check using a checklist is a major contributing factor to aircraft accidents.
Air Warrior (AW) is a modular, integrated, rapidly reconfigurable combat aircrew ensemble designed for U.S. Army aircrews. Previous aviation life support equipment consisted of a non-integrated assemblage of protective and survival gear. AW uses a systems approach to equipping the aircrew and closes the capability gap between human and machine. Fielded incrementally in blocks to rapidly provide enhanced capabilities to the warfighter, AW leverages and integrates clothing and equipment, such as the Army Aircrew Combat Uniform and ballistic protection, from other product managers. As of April 2010, more than 18,000 AW systems had been fielded in support of OIF and OEF.
Mike Monroney Aeronautical Center is administered as one of the FAA Regional Offices.
Program Executive Office Soldier is an American governmental organization responsible for rapid prototyping, procurement, and fielding of equipment for its soldiers.
Federal Office for Transport is a government agency of Austria. Its head office is Vienna. It is subordinate to the Ministry for Transport, Innovation and Technology.

VP-93, nicknamed the Executioners, was a Patrol Squadron of the U.S. Navy Reserve. It was the second squadron to be assigned the VP-93 designation. The squadron was established on 1 July 1976 and disestablished 18 years later, on 30 September 1994. It flew the Lockheed P-3 Orion, and was based at NAF Detroit during its entire life. Units of the squadron made 17 major overseas deployments.
The Royal Australian Air Force Institute of Aviation Medicine (AVMED) ensures the effectiveness and safety of Australian Defence Forces (ADF) air operations by conducting research and training ADF aircrew to understand and manage the physiological challenges of flight. AVMED is currently staffed by a mixture of uniformed and civilian personnel bringing with them diverse skills in aviation medicine, human factors, and life support.










