Related Research Articles

DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms may specifically repair double-strand breaks. Single-strand breaks are repaired by DNA ligase using the complementary strand of the double helix as a template, with DNA ligase creating the final phosphodiester bond to fully repair the DNA.
DNA primase is an enzyme involved in the replication of DNA and is a type of RNA polymerase. Primase catalyzes the synthesis of a short RNA segment called a primer complementary to a ssDNA template. After this elongation, the RNA piece is removed by a 5' to 3' exonuclease and refilled with DNA.

A nuclease is an enzyme capable of cleaving the phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides of nucleic acids. Nucleases variously affect single and double stranded breaks in their target molecules. In living organisms, they are essential machinery for many aspects of DNA repair. Defects in certain nucleases can cause genetic instability or immunodeficiency. Nucleases are also extensively used in molecular cloning.

DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages. This can eventually lead to malignant tumors, or cancer as per the two hit hypothesis.
RecQ helicase is a family of helicase enzymes initially found in Escherichia coli that has been shown to be important in genome maintenance. They function through catalyzing the reaction ATP + H2O → ADP + P and thus driving the unwinding of paired DNA and translocating in the 3' to 5' direction. These enzymes can also drive the reaction NTP + H2O → NDP + P to drive the unwinding of either DNA or RNA.

Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) is a pathway that repairs double-strand breaks in DNA. NHEJ is referred to as "non-homologous" because the break ends are directly ligated without the need for a homologous template, in contrast to homology directed repair, which requires a homologous sequence to guide repair. The term "non-homologous end joining" was coined in 1996 by Moore and Haber.

Mycobacterium smegmatis is an acid-fast bacterial species in the phylum Actinobacteria and the genus Mycobacterium. It is 3.0 to 5.0 µm long with a bacillus shape and can be stained by Ziehl–Neelsen method and the auramine-rhodamine fluorescent method. It was first reported in November 1884 by Lustgarten, who found a bacillus with the staining appearance of tubercle bacilli in syphilitic chancres. Subsequent to this, Alvarez and Tavel found organisms similar to that described by Lustgarten also in normal genital secretions (smegma). This organism was later named M. smegmatis.

Ku is a dimeric protein complex that binds to DNA double-strand break ends and is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair. Ku is evolutionarily conserved from bacteria to humans. The ancestral bacterial Ku is a homodimer. Eukaryotic Ku is a heterodimer of two polypeptides, Ku70 (XRCC6) and Ku80 (XRCC5), so named because the molecular weight of the human Ku proteins is around 70 kDa and 80 kDa. The two Ku subunits form a basket-shaped structure that threads onto the DNA end. Once bound, Ku can slide down the DNA strand, allowing more Ku molecules to thread onto the end. In higher eukaryotes, Ku forms a complex with the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) to form the full DNA-dependent protein kinase, DNA-PK. Ku is thought to function as a molecular scaffold to which other proteins involved in NHEJ can bind, orienting the double-strand break for ligation.
Zinc-finger nucleases (ZFNs) are artificial restriction enzymes generated by fusing a zinc finger DNA-binding domain to a DNA-cleavage domain. Zinc finger domains can be engineered to target specific desired DNA sequences and this enables zinc-finger nucleases to target unique sequences within complex genomes. By taking advantage of endogenous DNA repair machinery, these reagents can be used to precisely alter the genomes of higher organisms. Alongside CRISPR/Cas9 and TALEN, ZFN is a prominent tool in the field of genome editing.

DNA repair protein XRCC4 also known as X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 4 or XRCC4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the XRCC4 gene. In addition to humans, the XRCC4 protein is also expressed in many other metazoans, fungi and in plants. The X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 4 is one of several core proteins involved in the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway to repair DNA double strand breaks (DSBs).

Double-strand break repair protein MRE11 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MRE11 gene. The gene has been designated MRE11A to distinguish it from the pseudogene MRE11B that is nowadays named MRE11P1.

DNA ligase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the LIG4 gene.
DNA polymerase lambda, also known as Pol λ, is an enzyme found in all eukaryotes. In humans, it is encoded by the POLL gene.

DNA polymerase theta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLQ gene. This polymerase plays a key role in one of the three major double strand break repair pathways: theta-mediated end joining (TMEJ). Most double-strand breaks are repaired by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology directed repair (HDR). However, in some contexts, NHEJ and HR are insufficient and TMEJ is the only solution to repair the break. TMEJ is often described as alternative NHEJ, but differs in that it lacks a requirement for the Ku heterodimer, and it can only act on resected DNA ends. Following annealing of short regions on the DNA overhangs, DNA polymerase theta catalyzes template-dependent DNA synthesis across the broken ends, stabilizing the paired structure.

DNA polymerase mu is a polymerase enzyme found in eukaryotes. In humans, this protein is encoded by the POLM gene.
Non-homologous end-joining factor 1 (NHEJ1), also known as Cernunnos or XRCC4-like factor (XLF), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NHEJ1 gene. XLF was originally discovered as the protein mutated in five patients with growth retardation, microcephaly, and immunodeficiency. The protein is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair. Patients with XLF mutations also have immunodeficiency due to a defect in V(D)J recombination, which uses NHEJ to generate diversity in the antibody repertoire of the immune system. XLF interacts with DNA ligase IV and XRCC4 and is thought to be involved in the end-bridging or ligation steps of NHEJ. The yeast homolog of XLF is Nej1.
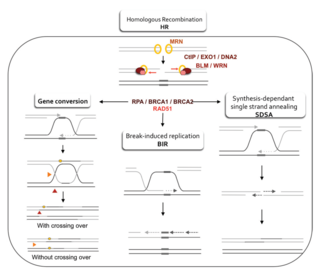
Homology directed repair (HDR) is a mechanism in cells to repair double-strand DNA lesions. The most common form of HDR is homologous recombination. The HDR mechanism can only be used by the cell when there is a homologous piece of DNA present in the nucleus, mostly in G2 and S phase of the cell cycle. Other examples of homology-directed repair include single-strand annealing and breakage-induced replication. When the homologous DNA is absent, another process called non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) takes place instead.
Microhomology-mediated end joining (MMEJ), also known as alternative nonhomologous end-joining (Alt-NHEJ) is one of the pathways for repairing double-strand breaks in DNA. As reviewed by McVey and Lee, the foremost distinguishing property of MMEJ is the use of microhomologous sequences during the alignment of broken ends before joining, thereby resulting in deletions flanking the original break. MMEJ is frequently associated with chromosome abnormalities such as deletions, translocations, inversions and other complex rearrangements.

DNA ligase 3 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the LIG3 gene. The human LIG3 gene encodes ATP-dependent DNA ligases that seal interruptions in the phosphodiester backbone of duplex DNA.
Streptomyces albidoflavus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from Poland. Streptomyces albidoflavus produces dibutyl phthalate and streptothricins.
References
- ↑ Della M, Palmbos PL, Tseng HM, et al. (October 2004). "Mycobacterial Ku and ligase proteins constitute a two-component NHEJ repair machine". Science. 306 (5696): 683–5. doi:10.1126/science.1099824. PMID 15499016.
- 1 2 Gong C, Bongiorno P, Martins A, et al. (April 2005). "Mechanism of nonhomologous end-joining in mycobacteria: a low-fidelity repair system driven by Ku, ligase D and ligase C". Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12 (4): 304–12. doi:10.1038/nsmb915. PMID 15778718.
- ↑ Pitcher RS, Green AJ, Brzostek A, Korycka-Machala M, Dziadek J, Doherty AJ (September 2007). "NHEJ protects mycobacteria in stationary phase against the harmful effects of desiccation" (PDF). DNA Repair (Amst.). 6 (9): 1271–6. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.02.009. PMID 17360246.
- ↑ Bartlett, EJ; Brissett, NC; Doherty, AJ (28 May 2013). "Ribonucleolytic resection is required for repair of strand displaced nonhomologous end-joining intermediates". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (22): E1984-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1302616110 . PMID 23671117.