Related Research Articles
Protein engineering is the process of developing useful or valuable proteins through the design and production of unnatural polypeptides, often by altering amino acid sequences found in nature. It is a young discipline, with much research taking place into the understanding of protein folding and recognition for protein design principles. It has been used to improve the function of many enzymes for industrial catalysis. It is also a product and services market, with an estimated value of $168 billion by 2017.

A cloning vector is a small piece of DNA that can be stably maintained in an organism, and into which a foreign DNA fragment can be inserted for cloning purposes. The cloning vector may be DNA taken from a virus, the cell of a higher organism, or it may be the plasmid of a bacterium. The vector contains features that allow for the convenient insertion of a DNA fragment into the vector or its removal from the vector, for example through the presence of restriction sites. The vector and the foreign DNA may be treated with a restriction enzyme that cuts the DNA, and DNA fragments thus generated contain either blunt ends or overhangs known as sticky ends, and vector DNA and foreign DNA with compatible ends can then be joined by molecular ligation. After a DNA fragment has been cloned into a cloning vector, it may be further subcloned into another vector designed for more specific use.
A DNA construct is an artificially-designed segment of DNA borne on a vector that can be used to incorporate genetic material into a target tissue or cell. A DNA construct contains a DNA insert, called a transgene, delivered via a transformation vector which allows the insert sequence to be replicated and/or expressed in the target cell. This gene can be cloned from a naturally occurring gene, or synthetically constructed. The vector can be delivered using physical, chemical or viral methods. Typically, the vectors used in DNA constructs contain an origin of replication, a multiple cloning site, and a selectable marker. Certain vectors can carry additional regulatory elements based on the expression system involved.

In molecular biology, subcloning is a technique used to move a particular DNA sequence from a parent vector to a destination vector.
The overlap extension polymerase chain reaction is a variant of PCR. It is also referred to as Splicing by overlap extension / Splicing by overhang extension (SOE) PCR. It is used assemble multiple smaller double stranded DNA fragments into a larger DNA sequence. OE-PCR is widely used to insert mutations at specific points in a sequence or to assemble custom DNA sequence from smaller DNA fragments into a larger polynucleotide.

DNA shuffling, also known as molecular breeding, is an in vitro random recombination method to generate mutant genes for directed evolution and to enable a rapid increase in DNA library size. Three procedures for accomplishing DNA shuffling are molecular breeding which relies on homologous recombination or the similarity of the DNA sequences, restriction enzymes which rely on common restriction sites, and nonhomologous random recombination which requires the use of hairpins. In all of these techniques, the parent genes are fragmented and then recombined.

BioBrick parts are DNA sequences which conform to a restriction-enzyme assembly standard. These building blocks are used to design and assemble larger synthetic biological circuits from individual parts and combinations of parts with defined functions, which would then be incorporated into living cells such as Escherichia coli cells to construct new biological systems. Examples of BioBrick parts include promoters, ribosomal binding sites (RBS), coding sequences and terminators.
Artificial gene synthesis, or simply gene synthesis, refers to a group of methods that are used in synthetic biology to construct and assemble genes from nucleotides de novo. Unlike DNA synthesis in living cells, artificial gene synthesis does not require template DNA, allowing virtually any DNA sequence to be synthesized in the laboratory. It comprises two main steps, the first of which is solid-phase DNA synthesis, sometimes known as DNA printing. This produces oligonucleotide fragments that are generally under 200 base pairs. The second step then involves connecting these oligonucleotide fragments using various DNA assembly methods. Because artificial gene synthesis does not require template DNA, it is theoretically possible to make a completely synthetic DNA molecule with no limits on the nucleotide sequence or size.

Functional cloning is a molecular cloning technique that relies on prior knowledge of the encoded protein’s sequence or function for gene identification. In this assay, a genomic or cDNA library is screened to identify the genetic sequence of a protein of interest. Expression cDNA libraries may be screened with antibodies specific for the protein of interest or may rely on selection via the protein function. Historically, the amino acid sequence of a protein was used to prepare degenerate oligonucleotides which were then probed against the library to identify the gene encoding the protein of interest. Once candidate clones carrying the gene of interest are identified, they are sequenced and their identity is confirmed. This method of cloning allows researchers to screen entire genomes without prior knowledge of the location of the gene or the genetic sequence.
NdeI is an endonuclease isolated from Neisseria denitrificans.
The versatility of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has led to modifications of the basic protocol being used in a large number of variant techniques designed for various purposes. This article summarizes many of the most common variations currently or formerly used in molecular biology laboratories; familiarity with the fundamental premise by which PCR works and corresponding terms and concepts is necessary for understanding these variant techniques.
Topoisomerase-based cloning is a molecular biology technique in which DNA fragments are cloned into specific vectors without the requirement for DNA ligases. Taq polymerase has a nontemplate-dependent terminal transferase activity that adds a single deoxyadenosine (A) to the 3'-end of the PCR products. This characteristic is exploited in "sticky end" TOPO TA cloning. For "blunt end" TOPO cloning, the recipient vector does not have overhangs and blunt-ended DNA fragments can be cloned.
The Gateway cloning method, invented and commercialized by Invitrogen since the late 1990s, is the cloning method of the integration and excision recombination reactions that take place when bacteriophage lambda infects bacteria. This technology provides a fast and highly efficient way to transport DNA sequences into multi-vector systems for functional analysis and protein expression using Gateway att sites, and two proprietary enzyme mixes called BP Clonase and LR Clonase. In vivo, these recombination reactions are facilitated by the recombination of attachment sites from the lambda/phage chromosome (attP) and the bacteria (attB). As a result of recombination between the attP and attB sites, the phage integrates into the bacterial genome flanked by two new recombination sites. The removal of the phage from the bacterial chromosome and the regeneration of attP and attB sites can both result from the attL and attR sites recombining under specific circumstances.
TA cloning is a subcloning technique that avoids the use of restriction enzymes and is easier and quicker than traditional subcloning. The technique relies on the ability of adenine (A) and thymine (T) on different DNA fragments to hybridize and, in the presence of ligase, become ligated together. PCR products are usually amplified using Taq DNA polymerase which preferentially adds an adenine to the 3' end of the product. Such PCR amplified inserts are cloned into linearized vectors that have complementary 3' thymine overhangs.
Diversity Arrays Technology (DArT) is a high-throughput genetic marker technique that can detect allelic variations to provide comprehensive genome coverage without any DNA sequence information for genotyping and other genetic analysis. The general steps involve reducing the complexity of the genomic DNA with specific restriction enzymes, choosing diverse fragments to serve as representations for the parent genomes, amplify via polymerase chain reaction (PCR), inserting fragments into a vector to be placed as probes within a microarray, and then fluorescent targets from a reference sequence will be allowed to hybridize with probes and put through an imaging system. The objective is to identify and quantify various forms of DNA polymorphism within genomic DNA of sampled species.
Gibson assembly is a molecular cloning method that allows for the joining of multiple DNA fragments in a single, isothermal reaction. It is named after its creator, Daniel G. Gibson, who is the chief technology officer and co-founder of the synthetic biology company, Telesis Bio. The technology is more efficient than manual plasmid genetic recombination methods, but remains expensive as it is still under patent.

Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.
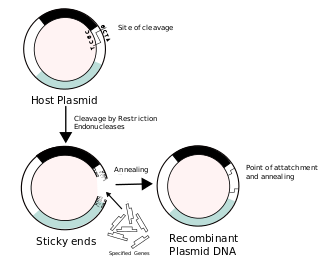
Recombinant DNA (rDNA), or molecular cloning, is the process by which a single gene, or segment of DNA, is isolated and amplified. Recombinant DNA is also known as in vitro recombination. A cloning vector is a DNA molecule that carries foreign DNA into a host cell, where it replicates, producing many copies of itself along with the foreign DNA. There are many types of cloning vectors such as plasmids and phages. In order to carry out recombination between vector and the foreign DNA, it is necessary the vector and DNA to be cloned by digestion, ligase the foreign DNA into the vector with the enzyme DNA ligase. And DNA is inserted by introducing the DNA into bacteria cells by transformation.

Ligation is the joining of two nucleic acid fragments through the action of an enzyme. It is an essential laboratory procedure in the molecular cloning of DNA, whereby DNA fragments are joined to create recombinant DNA molecules (such as when a foreign DNA fragment is inserted into a plasmid). The ends of DNA fragments are joined by the formation of phosphodiester bonds between the 3'-hydroxyl of one DNA terminus with the 5'-phosphoryl of another. RNA may also be ligated similarly. A co-factor is generally involved in the reaction, and this is usually ATP or NAD+. Eukaryotic cells ligases belong to ATP type, and NAD+ - dependent are found in bacteria (e.g. E. coli).

Golden Gate Cloning or Golden Gate assembly is a molecular cloning method that allows a researcher to simultaneously and directionally assemble multiple DNA fragments into a single piece using Type IIS restriction enzymes and T4 DNA ligase. This assembly is performed in vitro. Most commonly used Type IIS enzymes include BsaI, BsmBI, and BbsI.
References
- ↑ "Seamless Cloning | NEB". www.neb.com. Retrieved 2020-01-23.
- ↑ "Ligation Independent Cloning (LIC)". New England BioLabs (NEB). Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- ↑ "Get Your Clone 90% Of The Time with Ligation Independent Cloning". Bitesize Bio. Retrieved 2012-05-09.
- ↑ Haun, RS; Serventi, IM; Moss, J (1992). "Rapid, reliable ligation-independent cloning of PCR products using modified plasmid vectors". BioTechniques. 13 (4): 515–8. PMID 1362067.
- ↑ Snyder, Lori A. S. (2020). "Laboratory Techniques". Bacterial genetics and genomics. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 301. ISBN 9781000039191.