
A watermark is an identifying image or pattern in paper that appears as various shades of lightness/darkness when viewed by transmitted light, caused by thickness or density variations in the paper. Watermarks have been used on postage stamps, currency, and other government documents to discourage counterfeiting. There are two main ways of producing watermarks in paper; the dandy roll process, and the more complex cylinder mould process.

Brown is a composite color. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is made by combining red, black, and yellow, or red, yellow, and blue. In the RGB color model used to project colors onto television screens and computer monitors, brown is made by combining red and green, in specific proportions. In painting, brown is generally made by adding black to orange.

Papermaking is the manufacture of paper and cardboard, which are used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes. Today almost all paper is made using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a specialized craft and a medium for artistic expression.

Chiaroscuro, in art, is the use of strong contrasts between light and dark, usually bold contrasts affecting a whole composition. It is also a technical term used by artists and art historians for the use of contrasts of light to achieve a sense of volume in modelling three-dimensional objects and figures. Similar effects in cinema and photography also are called chiaroscuro.

Photographic paper is a paper coated with a light-sensitive chemical formula, like photographic film, used for making photographic prints. When photographic paper is exposed to light, it captures a latent image that is then developed to form a visible image; with most papers the image density from exposure can be sufficient to not require further development, aside from fixing and clearing, though latent exposure is also usually present. The light-sensitive layer of the paper is called the emulsion. The most common chemistry was based on Silver halide but other alternatives have also been used.

Shading refers to the depiction of depth perception in 3D models or illustrations by varying the level of darkness. Shading tries to approximate local behavior of light on the object's surface and is not to be confused with techniques of adding shadows, such as shadow mapping or shadow volumes, which fall under global behavior of light.

Security printing is the field of the printing industry that deals with the printing of items such as banknotes, cheques, passports, tamper-evident labels, security tapes, product authentication, stock certificates, postage stamps and identity cards. The main goal of security printing is to prevent forgery, tampering, or counterfeiting. More recently many of the techniques used to protect these high-value documents have become more available to commercial printers, whether they are using the more traditional offset and flexographic presses or the newer digital platforms. Businesses are protecting their lesser-value documents such as transcripts, coupons and prescription pads by incorporating some of the features listed below to ensure that they cannot be forged or that alteration of the data cannot occur undetected.
The contrast ratio (CR) is a property of a display system, defined as the ratio of the luminance of the brightest shade (white) to that of the darkest shade (black) that the system is capable of producing.. A high contrast ratio is a desired aspect of any display. It has similarities with dynamic range.

The Fjord horse or Norwegian Fjord Horse is a relatively small but very strong horse breed from the mountainous regions of western Norway. It is an agile breed of light draught horse build. All Fjord horses are dun in colour, with five variations in shade recognised in the breed standard. One of the world's oldest breeds, it has been used for hundreds of years as a farm horse in Norway, and in modern times is popular for its generally good temperament. It is used both as a harness horse and under saddle.

High-dynamic-range rendering, also known as high-dynamic-range lighting, is the rendering of computer graphics scenes by using lighting calculations done in high dynamic range (HDR). This allows preservation of details that may be lost due to limiting contrast ratios. Video games and computer-generated movies and special effects benefit from this as it creates more realistic scenes than with the more simplistic lighting models used.

A lampshade is a fixture that covers the lightbulb on a lamp to diffuse the light it emits. Lampshades can be made out of a wide variety of materials like paper, glass, fabric or stone. Usually conical or cylindrical in shape, lampshades can be found on floor, desk, tabletop, or suspended lamps. The term can also apply to the glass hung under many designs of ceiling lamp. Beyond its practical purpose, significant emphasis is also usually given to decorative and aesthetic features. A lamp shade also serves to "shade" human eyes from the direct glare of the light bulbs used to illuminate the lamp. Some lamp shades are also lined with a hard-backed opaque lining, often white or gold, to reflect as much light as possible through the top and bottom of the shade while blocking light from emitting through the walls of the shade itself. In other cases, the shade material is deliberately decorative so that upon illumination it may emphasize a display of color and light emitting through the shade surface itself.
Visual design elements and principles describe fundamental ideas about the practice of visual design.
"The best designers sometimes disregard the principles of design. When they do so, however, there is usually some compensating merit attained at the cost of the violation. Unless you are certain of doing as well, it is best to abide by the principles."

Line engraving is a term for engraved images printed on paper to be used as prints or illustrations. The term is mainly used in connection with 18th or 19th century commercial illustrations for magazines and books or reproductions of paintings. It is not a technical term in printmaking, and can cover a variety of techniques, giving similar results.

Laid paper is a type of paper having a ribbed texture imparted by the manufacturing process. In the pre-mechanical period of European papermaking, laid paper was the predominant kind of paper produced. Its use, however, diminished in the 19th century, when it was largely supplanted by wove paper. Laid paper is still commonly used by artists as a support for charcoal drawings.
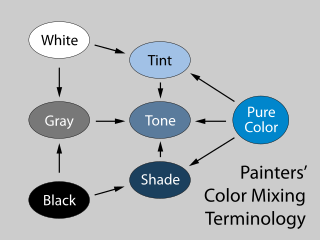
In color theory, a tint is a mixture of a color with white, which increases lightness, while a shade is a mixture with black, which increases darkness. Both processes affect the resulting color mixture's relative saturation. A tone is produced either by mixing a color with grey, or by both tinting and shading. Mixing a color with any neutral color reduces the chroma, or colorfulness, while the hue remains unchanged.

Postage stamp paper is the foundation or substrate of the postage stamp to which the ink for the stamp's design is applied to one side and the adhesive is applied to the other. The paper is not only the foundation of the stamp but it has also been incorporated into the stamp's design, has provided security against fraud and has aided in the automation of the postal delivery system.

Shades of brown can be produced by combining red, yellow, and black pigments, or by a combination of orange and black—as can be seen in the color box at right. In the RGB color model used to create all the colors on computer and television screens, brown is made by combining red and green light at different intensities. Brown color names are often not very precise, and some shades, such as beige, can refer to a wide variety of colors, including shades of yellow or red. Browns are usually described as light or dark, reddish, yellowish, or gray-brown. There are no standardized names for shades of brown; the same shade may have different names on different color lists, and sometimes the one name can refer to several very different colors. The X11 color list of web colors lists seventeen different shades of brown, but the complete list of browns is much longer.

The Three Crosses is a print in etching and drypoint by the Dutch artist Rembrandt van Rijn, which depicts the crucifixion of Jesus Christ. Most of his prints are mainly in etching and this one is a drypoint with burin adjustments from the third state onwards. It is considered "one of the most dynamic prints ever made".

The conservation and restoration of woodblock prints, is the process of caring for and repairing images made from a specific printing process involving using wooden reliefs to stamp or imprint an image onto paper. The process of creating woodblock prints as Asian examples are known, or woodcuts as Western examples are called, has been known for many centuries, and many older prints have experienced aging and deterioration of the paper and colorants used.

Low-key photography is a genre of photography consisting of shooting dark-colored scenes, and emphasizing natural or artificial light only on specific areas in the frame. This photographic style is usually used to create a mysterious atmosphere, that only suggests various shapes, often graphic, letting the viewer experience the photograph through subjective interpretation and often implies painting objects or the human body with black non-toxic dyes or pigments.





















