Related Research Articles

A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat, may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements, or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity.

A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is dependent on temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word is a combination of thermal and resistor. Thermistors are widely used as inrush current limiters, temperature sensors, self-resetting overcurrent protectors, and self-regulating heating elements.
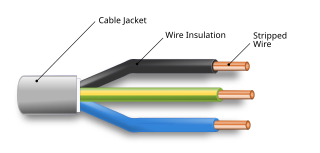
An electrical cable is an assembly of one or more wires running side by side or bundled, which is used to carry electric current.

In electronics and electromagnetism, the electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. The inverse quantity is electrical conductance, and is the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the notion of mechanical friction. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (Ω), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S).
Practical capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated, to a very good degree of approximation, as being ideal capacitors and inductors in series with a resistance; this resistance is defined as the equivalent series resistance (ESR). If not otherwise specified, the ESR is always an AC resistance, which means it is measured at specified frequencies, 100 kHz for switched-mode power supply components, 120 Hz for linear power-supply components, and at its self-resonant frequency for general-application components. Additionally, audio components may report a "Q factor", incorporating ESR among other things, at 1000 Hz.

The National Electrical Code (NEC), or NFPA 70, is a regionally adoptable standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment in the United States. It is part of the National Fire Code series published by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), a private trade association. Despite the use of the term "national", it is not a federal law. It is typically adopted by states and municipalities in an effort to standardize their enforcement of safe electrical practices. In some cases, the NEC is amended, altered and may even be rejected in lieu of regional regulations as voted on by local governing bodies.
Joule heating, also known as resistive, resistance, or Ohmic heating, is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor produces heat.

In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, thereby stopping or interrupting the current. It is a sacrificial device; once a fuse has operated it is an open circuit, it must be replaced or rewired, depending on type.
In electrical signalling an analog current loop is used where a device must be monitored or controlled remotely over a pair of conductors. Only one current level can be present at any time.
Resistance thermometers, also called resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), are sensors used to measure temperature. Many RTD elements consist of a length of fine wire wrapped around a ceramic or glass core but other constructions are also used. The RTD wire is a pure material, typically platinum, nickel, or copper. The material has an accurate resistance/temperature relationship which is used to provide an indication of temperature. As RTD elements are fragile, they are often housed in protective probes.

A security alarm is a system designed to detect intrusion – unauthorized entry – into a building or other area such as a home or school. Security alarms are used in residential, commercial, industrial, and military properties for protection against burglary (theft) or property damage, as well as personal protection against intruders. Security alarms in residential areas show a correlation with decreased theft. Car alarms likewise help protect vehicles and their contents. Prisons also use security systems for control of inmates.

A heating element converts electrical energy into heat through the process of Joule heating. Electric current through the element encounters resistance, resulting in heating of the element. Unlike the Peltier effect, this process is independent of the direction of current.
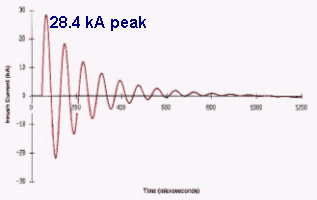
Inrush current, input surge current, or switch-on surge is the maximal instantaneous input current drawn by an electrical device when first turned on. Alternating-current electric motors and transformers may draw several times their normal full-load current when first energized, for a few cycles of the input waveform. Power converters also often have inrush currents much higher than their steady-state currents, due to the charging current of the input capacitance. The selection of over-current-protection devices such as fuses and circuit breakers is made more complicated when high inrush currents must be tolerated. The over-current protection must react quickly to overload or short-circuit faults but must not interrupt the circuit when the inrush current flows.

A load cell is a type of transducer, specifically a force transducer. It converts a force such as tension, compression, pressure, or torque into an electrical signal that can be measured and standardized. As the force applied to the load cell increases, the electrical signal changes proportionally. The most common types of load cell used are hydraulic, pneumatic, and strain gauge.

Mineral-insulated copper-clad cable is a variety of electrical cable made from copper conductors inside a copper sheath, insulated by inorganic magnesium oxide powder. The name is often abbreviated to MICC or MI cable, and colloquially known as pyro. A similar product sheathed with metals other than copper is called mineral insulated metal sheathed (MIMS) cable.

A test probe is a physical device used to connect electronic test equipment to a device under test (DUT). Test probes range from very simple, robust devices to complex probes that are sophisticated, expensive, and fragile. Specific types include test prods, oscilloscope probes and current probes. A test probe is often supplied as a test lead, which includes the probe, cable and terminating connector.
In an electric power system, a fault or fault current is any abnormal electric current. For example, a short circuit is a fault in which current bypasses the normal load. An open-circuit fault occurs if a circuit is interrupted by some failure. In three-phase systems, a fault may involve one or more phases and ground, or may occur only between phases. In a "ground fault" or "earth fault", current flows into the earth. The prospective short-circuit current of a predictable fault can be calculated for most situations. In power systems, protective devices can detect fault conditions and operate circuit breakers and other devices to limit the loss of service due to a failure.
Dual-loop is a method of electrical circuit termination used in electronic security applications, particularly modern intruder alarms. It is called 'dual-loop' because two circuits are combined into one using resistors. Its use became widespread in the early 21st century, replacing the basic closed-circuit system, mainly because of changes in international standards and practices.
The Kelvin-Varley voltage divider, named after its inventors William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin and Cromwell Fleetwood Varley, is an electronic circuit used to generate an output voltage as a precision ratio of an input voltage, with several decades of resolution. In effect, the Kelvin–Varley divider is an electromechanical precision digital-to-analog converter.

Overheating is a phenomenon of rising of temperature in an electric circuit. Overheating causes potential damage to the circuit components, and can cause fire, explosion, or injury. Damage caused by overheating is commonly irreversible; i.e. the only way to repair is to replace some components.
References
- 1 2 3 "Linear Heat Detection cable information" (PDF). Retrieved 26 April 2014.
- ↑ "Safe Fire Detection, LHD Information". Safe Fire Detection. Retrieved 26 April 2014.