
The Vietnam War was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. North Vietnam was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist allies; South Vietnam was supported by the United States and other anti-communist allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975.
Yankee Station was a fixed coordinate off the coast of Vietnam where U.S. Navy aircraft carriers and support ships operated in open waters over a nine-year period during the Vietnam War. The location was used primarily by aircraft carriers of Task Force 77 to launch strikes over North Vietnam. While the coordinate's official designation was "Point Yankee", it was universally referred to as Yankee Station. Carriers conducting air operations at Yankee Station were said to be "on the line" and statistical summaries were based on days on the line. Yankee Station was initially located at 16° 00′ N, 110° 00′ E, however with a massive increase in operations over North Vietnam in 1966 the station was moved about 145 miles (230 km) northwest to 17° 30′ N, 108° 30′ E, placing it about 90 miles (145 km) from the North Vietnamese shore.

Operation Rolling Thunder was the title of a gradual and sustained aerial bombardment campaign conducted by the United States (U.S.) 2nd Air Division, U.S. Navy, and Republic of Vietnam Air Force (RVNAF) against the Democratic Republic of Vietnam from 2 March 1965 until 2 November 1968, during the Vietnam War.

Vietnamization was a policy of the Richard Nixon administration to end U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War through a program to "expand, equip, and train South Vietnamese forces and assign to them an ever-increasing combat role, at the same time steadily reducing the number of U.S. combat troops". Brought on by the Viet Cong's Tet Offensive, the policy referred to U.S. combat troops specifically in the ground combat role, but did not reject combat by the U.S. Air Force, as well as the support to South Vietnam, consistent with the policies of U.S. foreign military assistance organizations. U.S. citizens' mistrust of their government that had begun after the offensive worsened with the release of news about U.S. soldiers massacring civilians at My Lai (1968), the invasion of Cambodia (1970), and the leaking of the Pentagon Papers (1971).

Operation Linebacker II was an aerial bombing campaign conducted by U.S. Seventh Air Force and U.S. Navy Task Force 77 against targets in the Democratic Republic of Vietnam during the final period of U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War. The operation was conducted from 18 to 29 December 1972, leading to several informal names such as "The December Raids" and "The Christmas Bombings". In Vietnam, it is just simply called "12 days and nights" and "Operation Dien Bien Phu in the air" or just simply Dien Bien Phu in the air. Unlike the Operation Rolling Thunder and Operation Linebacker interdiction operations, Linebacker II was designed to be a "maximum effort" bombing campaign to "destroy major target complexes in the Hanoi and Haiphong areas, which could only be accomplished by B-52s". It saw the largest heavy bomber strikes launched by the U.S. Air Force since World War II.
During the Vietnam War, the U.S. Joint Chiefs of Staff considered and rejected some additions to strategic bombing campaigns that would include targeting a series of dikes and dams along Vietnam's Red River delta. A classified 1965 USAF report suggested that the Red River flood control system could probably not be destroyed by conventional aerial bombing.

Operation Commando Hunt was a covert U.S. Seventh Air Force and U.S. Navy Task Force 77 aerial interdiction campaign that took place during the Vietnam War. The operation began on 15 November 1968 and ended on 29 March 1972. The objective of the campaign was to prevent the transit of People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) personnel and supplies on the logistical corridor known as the Ho Chi Minh Trail that ran from the southwestern Democratic Republic of Vietnam through the southeastern portion of the Kingdom of Laos and into the Republic of Vietnam.

The Easter Offensive, also known as the 1972 spring–summer offensive by North Vietnam, or the red fiery summer as romanticized in South Vietnamese literature, was a military campaign conducted by the People's Army of Vietnam against the Army of the Republic of Vietnam and the United States military between 30 March and 22 October 1972, during the Vietnam War. This conventional invasion was a radical departure from previous North Vietnamese offensives. The offensive was designed to achieve a decisive victory, which even if it did not lead to the collapse of South Vietnam, would greatly improve the North's negotiating position at the Paris Peace Accords.

The Paris Peace Accords, officially titled the Agreement on Ending the War and Restoring Peace in Vietnam, was a peace treaty signed on January 27, 1973, to establish peace in Vietnam and end the Vietnam War. The treaty included the governments of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, the Republic of Vietnam, and the United States, as well as the Republic of South Vietnam (PRG) that represented South Vietnamese communists. US ground forces up to that point had been sidelined with deteriorating morale and gradually withdrawn to coastal regions, not taking part in offensive operations or much direct combat for the preceding two-year period. The Paris Agreement Treaty would in effect remove all remaining US Forces, including air and naval forces in exchange. Direct U.S. military intervention was ended, and fighting between the three remaining powers temporarily stopped for less than a day. The agreement was not ratified by the United States Senate.
The Vietnam Service Medal is a military award of the United States Armed Forces established on 8 July 1965 by order of President Lyndon B. Johnson. The medal is awarded to recognize service during the Vietnam War by all members of the U.S. Armed Forces provided they meet the award requirements.
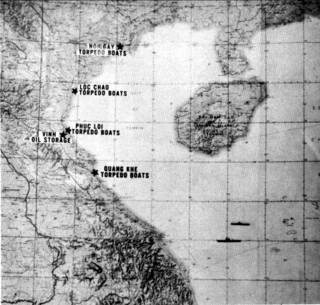
Operation Pierce Arrow was a U.S. bombing campaign at the beginning of the Vietnam War.

Operation Linebacker was the codename of a U.S. Seventh Air Force and U.S. Navy Task Force 77 air interdiction campaign conducted against North Vietnam from 9 May to 23 October 1972, during the Vietnam War.

Military Assistance Command, Vietnam – Studies and Observations Group (MACV-SOG) was a highly classified, multi-service United States special operations unit which conducted covert unconventional warfare operations prior to and during the Vietnam War.

The Cambodian campaign was a brief series of military operations conducted in eastern Cambodia in 1970 by South Vietnam and the United States as an extension of the Vietnam War and the Cambodian Civil War. Thirteen major operations were conducted by the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) between 29 April and 22 July and by U.S. forces between 1 May and 30 June 1970.
Operation Barrel Roll was a covert U.S. Air Force 2nd Air Division and U.S. Navy Task Force 77, interdiction and close air support campaign conducted in the Kingdom of Laos between 14 December 1964 and 29 March 1973 concurrent with the Vietnam War.
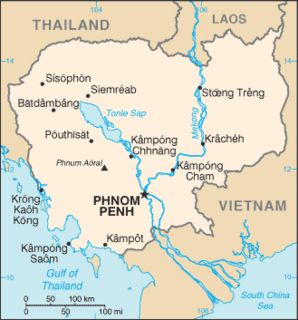
The Sihanouk Trail was a logistical supply system in Cambodia used by the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) and its Viet Cong (VC) guerillas during the Vietnam War (1960–1975). Between 1966 and 1970, this system operated in the same manner and served the same purposes as the much better known Ho Chi Minh trail which ran through the southeastern portion of the Kingdom of Laos. The name is of American derivation, since the North Vietnamese considered the system integral to the supply route mentioned above. U.S. attempts to interdict this system began in 1969.

The United States in the Vietnam War began shortly after the end of World War II in an extremely limited capacity and over a period of 20-years escalated peaking in April 1969 with 543,000 American combat troops stationed in Vietnam. By the conclusion of the United States's involvement in Vietnam, over 3.1 million Americans had been stationed in Vietnam. At home this involvement played a key role in sparking the Civil Rights Movement, hippie culture and wide ranging changes in popular culture.
Operation 34A was a highly classified United States program of covert actions against the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, consisting of agent team insertions, aerial reconnaissance missions and naval sabotage operations.

The Vietnam People's Army Air Defence - Air Force, commonly referred as the Vietnam People's Air Force or the Vietnam/Vietnamese Air Force, is the aerial warfare service branch of Vietnam. It is the successor of the former North Vietnamese Air Force and absorbed the Republic of Vietnam Air Force following the reunification of Vietnam in 1975 and being one of three main branches of the Vietnam People's Army, which is under the management of the Ministry of National Defence. The main mission of the VPAF is the defence of Vietnamese airspace and the provision of air cover for operations of the People's Army of Vietnam.
The following major military operations have sometimes been unofficially referred as Eleven Days War or Eleven Day War:













