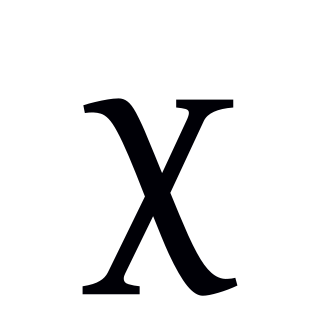Evolutionary linguistics or Darwinian linguistics is a sociobiological approach to the study of language. Evolutionary linguists consider linguistics as a subfield of sociobiology and evolutionary psychology. The approach is also closely linked with evolutionary anthropology, cognitive linguistics and biolinguistics. Studying languages as the products of nature, it is interested in the biological origin and development of language. Evolutionary linguistics is contrasted with humanistic approaches, especially structural linguistics.
Semantic properties or meaning properties are those aspects of a linguistic unit, such as a morpheme, word, or sentence, that contribute to the meaning of that unit. Basic semantic properties include being meaningful or meaningless – for example, whether a given word is part of a language's lexicon with a generally understood meaning; polysemy, having multiple, typically related, meanings; ambiguity, having meanings which aren't necessarily related; and anomaly, where the elements of a unit are semantically incompatible with each other, although possibly grammatically sound. Beyond the expression itself, there are higher-level semantic relations that describe the relationship between units: these include synonymy, antonymy, and hyponymy.

Canadian raising is an allophonic rule of phonology in many varieties of North American English that changes the pronunciation of diphthongs with open-vowel starting points. Most commonly, the shift affects or, or both, when they are pronounced before voiceless consonants. In North American English, and usually begin in an open vowel [~], but through raising they shift to (listen), (listen) or (listen). Canadian English often has raising in words with both and, while a number of American English varieties have this feature in but not. It is thought to have originated in Canada in the late 19th century.
Glottochronology is the part of lexicostatistics which involves comparative linguistics and deals with the chronological relationship between languages.
An infix is an affix inserted inside a word stem. It contrasts with adfix, a rare term for an affix attached to the outside of a stem, such as a prefix or suffix.
Lexicostatistics is a method of comparative linguistics that involves comparing the percentage of lexical cognates between languages to determine their relationship. Lexicostatistics is related to the comparative method but does not reconstruct a proto-language. It is to be distinguished from glottochronology, which attempts to use lexicostatistical methods to estimate the length of time since two or more languages diverged from a common earlier proto-language. This is merely one application of lexicostatistics, however; other applications of it may not share the assumption of a constant rate of change for basic lexical items.
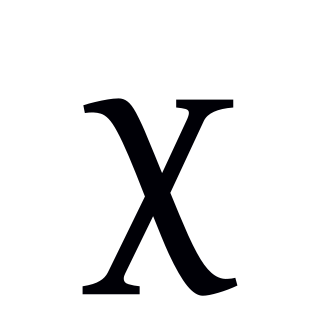
The voiceless uvular fricative is a type of consonantal sound that is used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨χ⟩, the Greek chi. The sound is represented by ⟨x̣⟩ in Americanist phonetic notation. It is sometimes transcribed with ⟨x⟩ in broad transcription.

The near-open front unrounded vowel, or near-low front unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨æ⟩, a lowercase of the ⟨Æ⟩ ligature. Both the symbol and the sound are commonly referred to as "ash".
In linguistics, a semantic field is a lexical set of words grouped semantically that refers to a specific subject. The term is also used in anthropology, computational semiotics, and technical exegesis.
Donkey sentences are sentences that contain a pronoun with clear meaning but whose syntactical role in the sentence poses challenges to grammarians. Such sentences defy straightforward attempts to generate their formal language equivalents. The difficulty is with understanding how English speakers parse such sentences.
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The modern-day scientific study of linguistics takes all aspects of language into account: cognitive, social, cultural, psychological, environmental, biological, literary, grammatical, paleographical, as well as structural aspects. Linguistics is based on the theoretical as well as descriptive study of language, and is also interlinked with the applied fields of language studies and language learning, which entails the study of specific languages. Before the 20th century, linguistics evolved in an informal manner that did not employ scientific methods.
Eloise Jelinek was an American linguist specializing in the study of syntax. Her 1981 doctoral dissertation at the University of Arizona was titled "On Defining Categories: AUX and PREDICATE in Colloquial Egyptian Arabic". She was a member of the faculty of the University of Arizona from 1981 to 1992.
David Michael Benjamin Denison is a British linguist whose work focuses on the history of the English language.
Noel Burton-Roberts is a British linguist and Emeritus Professor of English Language and Linguistics at Newcastle University. He is known for work ranging over general and English linguistics: architecture of language, semantics, pragmatics, philosophy of language, and English grammar.
Introducing Phonology is a 1984 book by Peter Hawkins designed for an introductory course in phonology for both graduates and undergraduates.
The Study of Language is a textbook by George Yule in which the author provides an introduction to linguistics. It is described as a "highly influential and widely used introductory text on linguistics."
Language: Introductory Readings is a textbook edited by Paul Eschholz, Alfred Rosa and Virginia Clark in which the authors provide an introduction to linguistics. It is described as a well-known introductory text in linguistics.

Contemporary Linguistics: An Introduction is a 1987 textbook edited by William O'Grady, Francis Katamba, John Archibald, Mark Aronoff, Janie Rees-Miller, Michael Dobrovolsky in which the authors provide an introduction to linguistics.
Language, Meaning and Context is a 1981 book by Sir John Lyons in which the author tries to outline the state of play in semantics.
Alan Stewart Kaye (1944-2007) was an American linguist and professor at California State University, Fullerton. He is best known for his works on Semitic and other language families. He died of cancer on May 31, 2007.