
Westphalia is a region in northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of 20,208 km2 (7,802 sq mi) and 7.9 million inhabitants.

Detmold is one of the five Regierungsbezirks of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, located in the north-east of the state. It is congruent with the administratively not existent area of Ostwestfalen-Lippe (OWL).
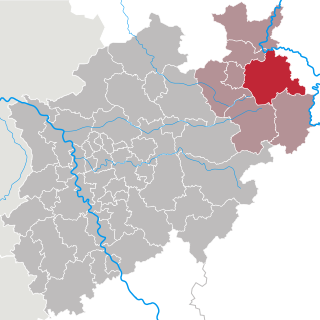
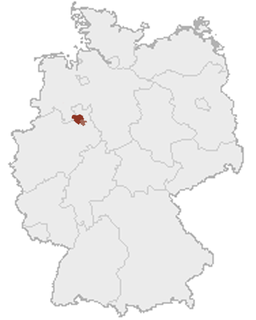
Lippe is a Kreis (district) in the east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Herford, Minden-Lübbecke, Höxter, Paderborn, Gütersloh, and district-free Bielefeld, which forms the region Ostwestfalen-Lippe.

Detmold is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, with a population of about 73,400 (2013). It was the capital of the small Principality of Lippe from 1468 until 1918 and then of the Free State of Lippe until 1947. Today it is the administrative center of the district of Lippe and of the Regierungsbezirk Detmold. The Church of Lippe has its central administration located in Detmold. The Reformed Redeemer Church is the preaching venue of the state superintendent of the Lippe church.

Alexander, Prince of Lippe was the penultimate sovereign of the Principality of Lippe. Succeeding to the throne in 1895, power was exercised by a regent throughout his reign on account of his mental illness.

Woldemar of Lippe was the sovereign of the Principality of Lippe, reigning from 1875 until his death.

Georg Friedrich Wilhelm Rosen was a German (Lippe/Prussian) orientalist and diplomat.

Lippe was a historical state in Germany, ruled by the House of Lippe. It was located between the Weser River and the southeast part of the Teutoburg forest.

The Free State of Lippe was a German state formed after the Principality of Lippe was abolished following the German Revolution of 1918.

The House of Lippe is the former reigning house of a number of small German states, two of which existed until the German Revolution of 1918–19. Princess Beatrix of the Netherlands, former Queen of the Netherlands, is an agnatic member of this house.

Lippe-Biesterfeld was a countly cadet line of the House of Lippe between 1762 and 1905. In 1916, a new, Princely, cadet line was created for the wife and sons of Prince Bernhard of Lippe. It also became a title of the Dutch Royal House created in 1937.
The Ravensberg Basin or Ravensberg Hills is a natural region in the governorate of Detmold (Ostwestfalen-Lippe) in the northeastern part of the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia; small elements also fall within the neighbouring state of Lower Saxony. It is part of the lower Weser Uplands and includes the hilly basin country between the Wiehen Hills in the north, Lippe Uplands in the east, Teutoburg Forest in the south and Osnabrück Hills in the west. The heart of the Ravensberg Basin is almost coincident with the cultural region of the Ravensberg Land.

The Detmold Open-air Museum is a museum at Detmold in the Ostwestfalen-Lippe region of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It was founded, together with the Hagen Open-air Museum, in 1960, and was first opened to the public in the early 1970s. The museum is run by the Landschaftsverband Westfalen-Lippe.

Pauline Christine Wilhelmine of Anhalt-Bernburg was a princess consort of Lippe, married in 1796 to Leopold I, Prince of Lippe. She served as the regent of Lippe during the minority of her son from 1802 to 1820. She is regarded as one of the most important rulers of Lippe. On 1 January 1809, she abolished serfdom by princely decree. She managed to keep the principality independent during the Napoleonic Wars. She wrote a constitution, in which the power of the estates was reduced. In the collective historical consciousness of the Lippe population, however, she is best remembered for her social goals. Influenced by French reformist writings, she founded the first day care center in Germany, a labor school for neglected children, a voluntary work camp for adult charity recipients and a health care institution with first aid center.

Simon August, Count of Lippe, ruled the Principality of Lippe-Detmold from 1734 until 1782.

Simon Henry Adolph, Count of Lippe-Detmold was a ruler of the county of Lippe.

Frederick Adolphus of Lippe-Detmold was a German nobleman and the Count of Lippe-Detmold from 1697 to 1718.
Simon Louis, Count of Lippe, was Count of Lippe-Detmold from 1627 until his death.

The Velmerstot is the northernmost and highest hill in the Eggegebirge ridge in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has two summits, the Prussian Velmerstot, which lies on the territory of Steinheim-Sandebeck in the county of Höxter, and the Lippe Velmerstot, which is located in the county of Lippe. The whole hill is part of the Teutoburg Forest / Egge Hills Nature Park.

















