
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference and identifiable chemical change. These reactions involve electrons moving via an electronically-conducting phase between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte.

In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from naturally occurring sources such as ores using an electrolytic cell. The voltage that is needed for electrolysis to occur is called the decomposition potential. The word "lysis" means to separate or break, so in terms, electrolysis would mean "breakdown via electricity".

In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be a reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon dissolving, the substance separates into cations and anions, which disperse uniformly throughout the solvent. Solid-state electrolytes also exist. In medicine and sometimes in chemistry, the term electrolyte refers to the substance that is dissolved.

Electroplating, also known as electrochemical deposition or electrodeposition, is a process for producing a metal coating on a solid substrate through the reduction of cations of that metal by means of a direct electric current. The part to be coated acts as the cathode of an electrolytic cell; the electrolyte is a solution of a salt of the metal to be coated; and the anode is usually either a block of that metal, or of some inert conductive material. The current is provided by an external power supply.

A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The reverse operation is performed by an inverter.

An electrolytic capacitor is a polarized capacitor whose anode or positive plate is made of a metal that forms an insulating oxide layer through anodization. This oxide layer acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. A solid, liquid, or gel electrolyte covers the surface of this oxide layer, serving as the cathode or negative plate of the capacitor. Because of their very thin dielectric oxide layer and enlarged anode surface, electrolytic capacitors have a much higher capacitance-voltage (CV) product per unit volume than ceramic capacitors or film capacitors, and so can have large capacitance values. There are three families of electrolytic capacitor: aluminium electrolytic capacitors, tantalum electrolytic capacitors, and niobium electrolytic capacitors.

Single-wire earth return (SWER) or single-wire ground return is a single-wire transmission line which supplies single-phase electric power from an electrical grid to remote areas at lowest cost. Its distinguishing feature is that the earth is used as the return path for the current, to avoid the need for a second wire to act as a return path.
Capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated, to a very good degree of approximation, as being ideal capacitors and inductors in series with a resistance; this resistance is defined as the equivalent series resistance (ESR). If not otherwise specified, the ESR is always an AC resistance, which means it is measured at specified frequencies, 100 kHz for switched-mode power supply components, 120 Hz for linear power-supply components, and at its self-resonant frequency for general-application components. Additionally, audio components may report a "Q factor", incorporating ESR among other things, at 1000 Hz.

A current transformer (CT) is a type of transformer that is used to reduce or multiply an alternating current (AC). It produces a current in its secondary which is proportional to the current in its primary.
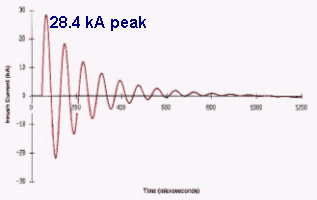
Inrush current, input surge current, or switch-on surge is the maximal instantaneous input current drawn by an electrical device when first turned on. Alternating-current electric motors and transformers may draw several times their normal full-load current when first energized, for a few cycles of the input waveform. Power converters also often have inrush currents much higher than their steady-state currents, due to the charging current of the input capacitance. The selection of over-current-protection devices such as fuses and circuit breakers is made more complicated when high inrush currents must be tolerated. The over-current protection must react quickly to overload or short-circuit faults but must not interrupt the circuit when the inrush current flows.

An electronic component is any basic discrete electronic device or physical entity part of an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not to be confused with electrical elements, which are conceptual abstractions representing idealized electronic components and elements. A datasheet for an electronic component is a technical document that provides detailed information about the component's specifications, characteristics, and performance.
An earthing system or grounding system (US) connects specific parts of an electric power system with the ground, typically the Earth's conductive surface, for safety and functional purposes. The choice of earthing system can affect the safety and electromagnetic compatibility of the installation. Regulations for earthing systems vary among countries, though most follow the recommendations of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Regulations may identify special cases for earthing in mines, in patient care areas, or in hazardous areas of industrial plants.

Capacitors are manufactured in many styles, forms, dimensions, and from a large variety of materials. They all contain at least two electrical conductors, called plates, separated by an insulating layer (dielectric). Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices.

Molten-salt batteries are a class of battery that uses molten salts as an electrolyte and offers both a high energy density and a high power density. Traditional non-rechargeable thermal batteries can be stored in their solid state at room temperature for long periods of time before being activated by heating. Rechargeable liquid-metal batteries are used for industrial power backup, special electric vehicles and for grid energy storage, to balance out intermittent renewable power sources such as solar panels and wind turbines.

An electrical conductivity meter measures the electrical conductivity in a solution. It has multiple applications in research and engineering, with common usage in hydroponics, aquaculture, aquaponics, and freshwater systems to monitor the amount of nutrients, salts or impurities in the water.
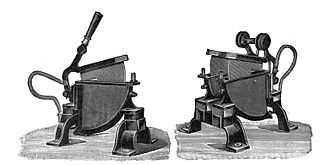
A liquid rheostat or water rheostat or salt water rheostat is a type of variable resistor. This may be used as a dummy load or as a starting resistor for large slip ring motors.

Electronic components have a wide range of failure modes. These can be classified in various ways, such as by time or cause. Failures can be caused by excess temperature, excess current or voltage, ionizing radiation, mechanical shock, stress or impact, and many other causes. In semiconductor devices, problems in the device package may cause failures due to contamination, mechanical stress of the device, or open or short circuits.

Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are polarized electrolytic capacitors whose anode electrode (+) is made of a pure aluminum foil with an etched surface. The aluminum forms a very thin insulating layer of aluminum oxide by anodization that acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. A non-solid electrolyte covers the rough surface of the oxide layer, serving in principle as the second electrode (cathode) (-) of the capacitor. A second aluminum foil called "cathode foil" contacts the electrolyte and serves as the electrical connection to the negative terminal of the capacitor.
This glossary of electrical and electronics engineering is a list of definitions of terms and concepts related specifically to electrical engineering and electronics engineering. For terms related to engineering in general, see Glossary of engineering.
















