Related Research Articles

The Battle of Abensberg took place on 20 April 1809 between a Franco-German force under the command of Emperor Napoleon I of France and a reinforced Austrian corps led by Feldmarschall-Leutnant Archduke Louis of Austria. As the day wore on, Feldmarschall-Leutnant Johann von Hiller arrived with reinforcements to take command of the three corps that formed the Austrian left wing. The action ended in a complete Franco-German victory. The battlefield was southeast of Abensberg and included clashes at Offenstetten, Biburg-Siegenburg, Rohr in Niederbayern, and Rottenburg an der Laaber. On the same day, the French garrison of Regensburg capitulated.

The Battle of Charleroi or the Battle of the Sambre, was fought on 21 August 1914, by the French Fifth Army and the German 2nd and 3rd armies, during the Battle of the Frontiers. The French were planning an attack across the Sambre River, when the Germans attacked first, forced back the French from the river and nearly cut off the French retreat by crossing the Meuse River around Dinant and getting behind the French right flank. The French were saved by a counter-attack at Dinant and the re-direction of the 3rd Army to the north-west in support of the 2nd Army, rather than south-west.

The Battle of Teugen-Hausen or the Battle of Thann was an engagement that occurred during the War of the Fifth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle was fought on 19 April 1809 between the French III Corps led by Marshal Louis-Nicolas Davout and the Austrian III Armeekorps commanded by Prince Friedrich Franz Xaver of Hohenzollern-Hechingen. When the Austrians withdrew that evening, the French won a hard-fought victory over their opponents. The site of the battle is a wooded height approximately halfway between the villages of Teugn and Hausen in Lower Bavaria, part of modern-day Germany.

The IV Army Corps / IV AK was a corps level command of the Prussian and then the Imperial German Armies from the 19th Century to World War I.

The Imperial German Army (1871–1919), officially referred to as the German Army, was the unified ground and air force of the German Empire. It was established in 1871 with the political unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia, and was dissolved in 1919, after the defeat of the German Empire in World War I (1914–1918). In the Federal Republic of Germany, the term Deutsches Heer refers to the German Army, the land component of the Bundeswehr.

The XVIII Army Corps / XVIII AK was a corps level command of the German Army before and during World War I.
This is an order of battle of the French and German Armies at the beginning of the Franco-Prussian War in 1870.

The XIII Army Corps / XIII AK was a corps of the Imperial German Army. It was, effectively, also the army of the Kingdom of Württemberg, which had been integrated in 1871 into the Prussian Army command structure, as had the armies of most German states. The corps was originally established as the Württemberg Corps Command (Korpskommando) in 1817. It became the XIII Army Corps when it was integrated into the Prussian numbering system on December 18, 1871, shortly after the Franco-Prussian War.

The XIV Army Corps / XIV AK was a corps level command of the German Army before and during World War I. It was, effectively, also the army of the Grand Duchy of Baden, which, in 1871, had been integrated into the Prussian Army command structure, as had the armies of most German states. Both divisions and the bulk of the corps' support units were from the grand duchy. The corps was established in 1870, after the Siege of Strasbourg.

The Royal Saxon Army was the military force of the Electorate (1682–1807) and later the Kingdom of Saxony (1807–1918). A regular Saxon army was first established in 1682 and it continued to exist until the abolition of the German monarchies in 1918. With the formation of the Confederation of the Rhine by Napoleon the Royal Saxon Army joined the French "Grande Armée" along with 37 other German states.
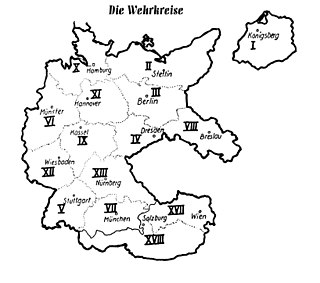
The military districts, also known in some English-language publications by their German name as Wehrkreise, were administrative territorial units in Nazi Germany before and during World War II. The task of military districts was the organization and the handling of reinforcements and resupplies for local military units. The Replacement Army (Ersatzheer) managed the districts. Responsibilities such as training, conscription, supply, and equipment were entrusted to the Ersatzheer.

The Bavarian Army was the army of the Electorate (1682–1806) and then Kingdom (1806–1918) of Bavaria. It existed from 1682 as the standing army of Bavaria until the merger of the military sovereignty of Bavaria into that of the German State in 1919. The Bavarian Army was never comparable to the armies of the Great Powers of the 19th century, but it did provide the Wittelsbach dynasty with sufficient scope of action, in the context of effective alliance politics, to transform Bavaria from a territorially-disjointed small state to the second-largest state of the German Empire after Prussia.

The XVI Army Corps / XVI AK was a corps level command of the German Army before and during World War I.
The Battle of Linz-Urfahr on 17 May 1809 saw soldiers from the Austrian Empire fighting against troops from two of Emperor Napoleon's allies, the Kingdom of Württemberg and the Kingdom of Saxony. An Austrian corps led by Feldzeugmeister Johann Kollowrat attacked General of Division Dominique Vandamme's Württembergers who held a fortified bridgehead on the north bank of the Danube opposite the city of Linz. As the combat got underway, Saxons led by Marshal Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte began reinforcing the defenders. This prompted Kollowrat to order a retreat, which was followed up by Napoleon's German allies.
The history of the German Cavalry in World War I is one of an arm in decline.

The North Army was an army level command of the German Army that existed briefly at the outbreak of World War I.

The II Royal Bavarian Army Corps / II Bavarian AK was a corps level command of the Royal Bavarian Army, part of the Imperial German Army, before and during World War I.

The XVII Army Corps / XVII AK was a corps level command of the German Army before and during World War I.

The VII Army Corps / VII AK was a corps level command of the Prussian and then the Imperial German Armies from the 19th Century to World War I.
References
- ↑ van Wyngarden, G. (2006). Early German Aces of World War I. Osprey Publishing Ltd. ISBN 1-84176-997-5.