Related Research Articles

The Dytiscidae – based on the Greek dytikos (δυτικός), "able to dive" – are the predaceous diving beetles, a family of water beetles. They occur in virtually any freshwater habitat around the world, but a few species live among leaf litter. The adults of most are between 1 and 2.5 cm (0.4–1.0 in) long, though much variation is seen between species. The European Dytiscus latissimus and Brazilian Megadytes ducalis are the largest, reaching up to 4.5 cm (1.8 in) and 4.75 cm (1.9 in) respectively. In contrast, the smallest is likely the Australian Limbodessus atypicali of subterranean waters, which only is about 0.9 mm (0.035 in) long. Most are dark brown, blackish, or dark olive in color with golden highlights in some subfamilies. The larvae are commonly known as water tigers due to their voracious appetite. They have short, but sharp mandibles and immediately upon biting, they deliver digestive enzymes into prey to suck their liquefied remains. The family includes more than 4,000 described species in numerous genera.

Zopheridae is a family of beetles belonging to Tenebrionoidea. It has grown considerably in recent years as the members of two other families have been included within its circumscription; these former families are the Monommatidae and the Colydiidae, which are now both included in the Zopheridae as subfamilies or even as tribe of subfamily Zopherinae. Some authors accept up to six subfamilies here, while others merge all except the Colydiinae into the Zopherinae.

Acmaeodera is a genus of beetles in the family Buprestidae, a group of metallic wood-boring beetles favored by insect collectors. Whereas most beetles including most buprestids fly with their elytra held out and vibrating their hindwings to give lift and thrust, Acmaedodera, however, fly with their hind wings only — the elytra are fused down the center and form a shield over the insect's abdomen, even during flight. This fact, combined with the banding across the abdomen which is common in this family, gives many of them a distinct wasp-like appearance when in flight. Several are therefore considered hymenopteran mimics.

Mordellistena is a genus of beetles in the family Mordellidae, containing the following species:

Dryopidae is a family of beetles, commonly named long-toed water beetles, in the superfamily Byrrhoidea. It was described by Gustaf Johan Billberg in 1820.

Elminae is a subfamily of riffle beetles in the family Elmidae. There are at least 120 genera and more than 1,300 described species in Elminae.

Elmini is a tribe of riffle beetles in the family Elmidae. There are more than 90 genera and 1,200 described species in North America.

Aphodiini is a tribe of aphodiine dung beetles in the family Scarabaeidae. There are more than 250 genera and 2,200 described species in Aphodiini.
Hexacylloepus is a genus of riffle beetles in the family Elmidae. There are about 19 described species in Hexacylloepus.
Neoelmis is a genus of riffle beetles in the family Elmidae. There are more than 50 described species in Neoelmis.
Phanocerus is a genus of riffle beetles in the family Elmidae. There are about seven described species in Phanocerus.
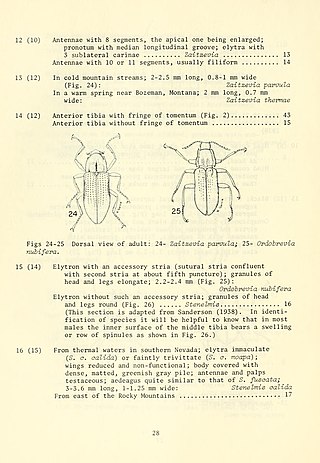
Zaitzevia is a genus of riffle beetles in the family Elmidae. There are about 19 described species in Zaitzevia. The genus is named after the Russian entomologist Filipp Zaitsev.
Grouvellinus is a genus of beetle in the family Elmidae. As of 2018, over forty species are recognized, including:

Macronychus is a genus of riffle beetles in the family Elmidae. There are about 11 described species in Macronychus.
Larainae is a subfamily of riffle beetles in the family Elmidae. There are more than 20 genera and 160 described species in Larainae.

Macronychini is a tribe of riffle beetles in the family Elmidae. There are more than 20 genera and 80 described species in Macronychini.
References
- ↑ "Elmidae Report". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 2019-06-22.
- ↑ "Elmidae". GBIF. Retrieved 2019-06-22.
- ↑ "Family Elmidae information". BugGuide.net. Retrieved 2019-06-22.