This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(September 2018) |
This is a list of short wave transmitters in Europe.
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(September 2018) |
This is a list of short wave transmitters in Europe.
Those are former prominent SW transmitters:
The above radio stations broadcast in the wavebands of 75, 60, 49, 41, 31, 25, 22, 19, 16 and/or 11 meters.

Shortwave radio is radio transmission using radio frequencies in the shortwave bands (SW). There is no official definition of the band range, but it always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz ; above the medium frequency band (MF), to the bottom of the VHF band.

In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna with the purpose of signal transmission up to a radio receiver. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves.

BBC Radio 4 is a British national radio station owned and operated by the BBC. The station replaced the BBC Home Service on 30 September 1967 and broadcasts a wide variety of spoken-word programmes from the BBC's headquarters at Broadcasting House, London. Since 2019, the station controller has been Mohit Bakaya. He replaced Gwyneth Williams, who had been the station controller since 2010.

Medium wave (MW) is a part of the medium frequency (MF) radio band used mainly for AM radio broadcasting. The spectrum provides about 120 channels with more limited sound quality than FM stations on the FM broadcast band. During the daytime, reception is usually limited to more local stations, though this is dependent on the signal conditions and quality of radio receiver used. Improved signal propagation at night allows the reception of much longer distance signals. This can cause increased interference because on most channels multiple transmitters operate simultaneously worldwide. In addition, amplitude modulation (AM) is often more prone to interference by various electronic devices, especially power supplies and computers. Strong transmitters cover larger areas than on the FM broadcast band but require more energy and longer antennas. Digital modes are possible but have not reached momentum yet.

In radio, longwave, long wave or long-wave, and commonly abbreviated LW, refers to parts of the radio spectrum with wavelengths longer than what was originally called the medium-wave broadcasting band. The term is historic, dating from the early 20th century, when the radio spectrum was considered to consist of longwave (LW), medium-wave (MW), and short-wave (SW) radio bands. Most modern radio systems and devices use wavelengths which would then have been considered 'ultra-short'.
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves as they travel, or are propagated, from one point to another in vacuum, or into various parts of the atmosphere. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio waves are affected by the phenomena of reflection, refraction, diffraction, absorption, polarization, and scattering. Understanding the effects of varying conditions on radio propagation has many practical applications, from choosing frequencies for amateur radio communications, international shortwave broadcasters, to designing reliable mobile telephone systems, to radio navigation, to operation of radar systems.
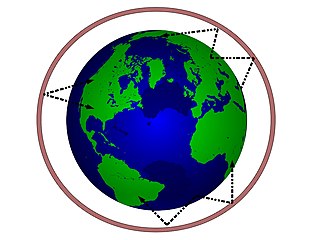
In radio communication, skywave or skip refers to the propagation of radio waves reflected or refracted back toward Earth from the ionosphere, an electrically charged layer of the upper atmosphere. Since it is not limited by the curvature of the Earth, skywave propagation can be used to communicate beyond the horizon, at intercontinental distances. It is mostly used in the shortwave frequency bands.
RTÉ Radio 1 is an Irish national radio station owned and operated by RTÉ and is the direct descendant of Dublin radio station 2RN, which began broadcasting on a regular basis on 1 January 1926.

RTL is a French commercial radio network owned by the RTL Group. Founded in 1933 as Radio Luxembourg, it broadcast from outside of France until 1981 because only public stations had been allowed until then. It is a general-interest, news, talk and music station, broadcasting nationally in France, Francophone Belgium, and Luxembourg. Until 2022, RTL was also broadcast on long wave frequency 234 kHz from Beidweiler which could be picked up in large parts of the continent. It has a sister station called Bel RTL tailored for the French Community of Belgium. As of 2018, RTL is France's most popular radio station with an average of 6.4 million daily listeners that year.

The Skelton Transmitting Station is a radio transmitter site at grid reference NY433376 near Skelton, Cumbria, England, about 5 miles (8 km) north-west of Penrith, run by Babcock International and owned by the Ministry of Defence. Since the Belmont Mast in Lincolnshire was shortened in 2010, the mast at Skelton has been the tallest structure in the United Kingdom.
Vatican Radio is the official broadcasting service of Vatican City.
A broadcast transmitter is an electronic device which radiates radio waves modulated with information content intended to be received by the general public. Examples are a radio broadcasting transmitter which transmits audio (sound) to broadcast radio receivers (radios) owned by the public, or a television transmitter, which transmits moving images (video) to television receivers (televisions). The term often includes the antenna which radiates the radio waves, and the building and facilities associated with the transmitter. A broadcasting station consists of a broadcast transmitter along with the production studio which originates the broadcasts. Broadcast transmitters must be licensed by governments, and are restricted to specific frequencies and power levels. Each transmitter is assigned a unique identifier consisting of a string of letters and numbers called a callsign, which must be used in all broadcasts.
Radio broadcasting in Sri Lanka dates to 1923. Radio broadcasting, like other forms of media in Sri Lanka, is generally divided along linguistic lines with state and private media operators providing services in Sinhala, Tamil, and English language.

ABC Radio Australia, also known as Radio Australia, is the international broadcasting and online service operated by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC), Australia's public broadcaster. Most programming is in English, with some in Tok Pisin.
A television station is a set of equipment managed by a business, organisation or other entity such as an amateur television (ATV) operator, that transmits video content and audio content via radio waves directly from a transmitter on the earth's surface to any number of tuned receivers simultaneously.

Deutschlandsender, abbreviated DLS or DS, was one of the longest-established radio broadcasting stations in Germany. The name was used between 1926 and 1993 to denote a number of powerful stations designed to achieve all-Germany coverage.

Radio Nacional de España is the national state-owned public service radio broadcaster in Spain.

The mass media in Ethiopia consist of radio, television and the Internet, which remain under the control of the Ethiopian government, as well as private newspapers and magazines. Ten radio broadcast stations, eight AM and two shortwave, are licensed to operate in Ethiopia. The major radio broadcasting stations include Radio Fana a private station, Radio Voice of One Free Ethiopia, and the Voice of the Revolution of Tigray. The only terrestrial (broadcast) television networks are government owned and include EBC and other regional stations. In keeping with government policy, radio broadcasts occur in a variety of languages including Amharic, Afaan Oromo, Tigrigna, and more. There are also many video sharing websites which are a popular way of getting information as well as entertainment in Ethiopia.

Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves. They are received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver. In addition to communication, radio is used for radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications.
W8XH was a Buffalo, New York radio station, authorized by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) as an "experimental audio station", which was owned by the Buffalo Evening News, and which operated from 1934 to 1939. It was the first apex band station, i.e. the first to transmit programming intended for the general public over what was then known as "ultra-high short-wave" frequencies. W8XH primarily simulcast programming originating from a co-owned AM radio station, WBEN, but it also aired some original programs. It ceased broadcasting in July 1939, after the newspaper began to focus on operation of an experimental facsimile broadcasting station, W8XA, which in turn shut down shortly prior to World War II and was succeeded after the war by the establishment of an FM station.