Related Research Articles

The Drosophilidae are a diverse, cosmopolitan family of flies, which includes species called fruit flies, although they are more accurately referred to as vinegar or pomace flies. Another distantly related family of flies, Tephritidae, are true fruit flies because they are frugivorous, and include apple maggot flies and many pests. The best known species of the Drosophilidae is Drosophila melanogaster, within the genus Drosophila, also called the "fruit fly." Drosophila melanogaster is used extensively for studies concerning genetics, development, physiology, ecology and behaviour. Many fundamental biological mechanisms were discovered first in D. melanogaster. The fruit fly is mostly composed of post-mitotic cells, has a very short lifespan, and shows gradual aging. As in other species, temperature influences the life history of the animal. Several genes have been identified that can be manipulated to extend the lifespan of these insects. Additionally, Drosophila subobscura, also within the genus Drosophila, has been reputed as a model organism for evolutionary-biological studies, along with D. sechellia for the evolution of host specialization on the toxic noni fruit and Scaptomyza flava for the evolution of herbivory and specialist on toxic mustard leaves.
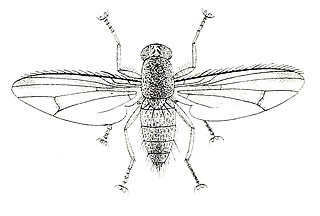
The Curtotonidae or quasimodo flies are a small family of small grey to dark brown humpbacked flies (Diptera) with a worldwide distribution, but with very few species in the Nearctic, Australasian/Oceanian, and Palaearctic regions. Most members of the family are found in tropical to subtropical latitudes in Africa and the Neotropics. Many remain undescribed in collections, since little work on the family has been done since the 1930s.

The Drosophila obscura species group belongs to the subgenus Sophophora and contains 6 subgroups: affinis, microlabis, obscura, pseudoobscura, subobscura, and sinobscura.

Hirtodrosophila is a genus of fruit flies from the family Drosophilidae. Originally Hirtodrosophila was a subgenus of the genus Drosophila. It was raised to the status of genus by Grimaldi in 1990.

The genus Zaprionus belongs to the family fruit fly Drosophilidae and is positioned within the paraphyletic genus Drosophila. All species are easily recognized by the white longitudinal stripes across the head and thorax. The genus is subdivided in two subgenera, based on the presence of an even or odd number of white stripes. The species of the genus can be found in Africa and Southern Asia. One species, Zaprionus indianus, has invaded the New World.
Rachispoda is a genus of flies belonging to the family Lesser Dung flies.

Chymomyza is a genus of vinegar flies.
Microdrosophila is a genus of vinegar flies, insects in the family Drosophilidae. There are at least 70 described species in Microdrosophila.

Stegana is a genus of vinegar flies, insects in the family Drosophilidae. There are at least 140 described species in Stegana. Seven species complexes have been established based on morphological data: S. biprotrusa, S. castanea, S. coleoptrata, S. nigrolimbata, S. ornatipes, S. shirozui and S. undulata.

Curtonotum is a genus of flies in the family Curtonotidae. There are more than 50 described species in Curtonotum.

Japanagromyza is a genus of leaf miner flies in the family Agromyzidae. There are more than 80 described species in Japanagromyza.

Lordiphosa is a genus of fly in the family Drosophilidae.

Amiota is a genus of flies belonging to the family Drosophilidae. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution.
References
- 1 2 "Mycodrosophila Report". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 2018-04-27.
- 1 2 "Browse Mycodrosophila". Catalogue of Life. Retrieved 2018-04-27.
- 1 2 "Mycodrosophila". GBIF. Retrieved 2018-04-27.
- 1 2 "Mycodrosophila Genus Information". BugGuide.net. Retrieved 2018-04-27.