These are lists of incumbents, including heads of states or of subnational entities.

The President of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces.

The president of the French Republic is the executive head of state of France in the French Fifth Republic. In French terms, the presidency is the supreme magistracy of the country.

The Cabinet of the United States is part of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States. The Cabinet's role, inferred from the language of the Opinion Clause of the Constitution, is to serve as an advisory body to the President of the United States. Additionally, the Twenty-fifth Amendment authorizes the Vice President, together with a majority of certain members of the Cabinet, to declare the president "unable to discharge the powers and duties of his office". Among the senior officers of the Cabinet are the Vice President and the heads of the federal executive departments, all of whom—if eligible—are in the line of succession. Members of the Cabinet serve at the pleasure of the President, who can dismiss them at will for no cause. All federal public officials, including Cabinet members, are also subject to impeachment by the House of Representatives and trial in the Senate for "treason, bribery, and other high crimes and misdemeanors".

The United States Attorney General (A.G.) is the chief lawyer of the Federal Government of the United States, head of the United States Department of Justice per 28 U.S.C. § 503, and oversees all governmental legal affairs.

The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). OMB's most prominent function is to produce the President's Budget, but OMB also measures the quality of agency programs, policies, and procedures to see if they comply with the president's policies and coordinates inter-agency policy initiatives.

The President of the Republic of China is the head of state of the Republic of China (ROC). Since 1996, the President is directly elected by plurality voting to a four-year term, with at most one re-election. The incumbent, Tsai Ing-wen, succeeded Ma Ying-jeou on 20 May 2016 as the first female president in the nation's history. Originally established in Nanking in 1912, the government and its president relocated to Taipei in 1949 after losing the Chinese Civil War.

The president of India is the ceremonial head of state of India and the commander-in-chief of the Indian Armed Forces.

Sonia Gandhipronunciation (help·info) is an Indian politician. She is a former president of the Indian National Congress, the secular and left-of-centre political party, which governed India for most of its post-independence history. She took over as the party leader in 1998, seven years after the assassination of her husband, Rajiv Gandhi, a former prime minister of India, and remained in office for nineteen years.
Emeritus, in its current usage, is an adjective used to designate a retired chairman, professor, pastor, bishop, pope, director, president, prime minister, rabbi, emperor, or other person.

The Rajya Sabha or Council of States is the upper house of the Parliament of India the other being Lok Sabha or House of the People. Membership of Rajya Sabha is limited by the Constitution to a maximum of 250 members and current laws have provision for 245 members. Most of the members of the House are indirectly elected by the members of States and union territories of India state and territorial legislatures using single transferable votes through Open Ballot, while the President can appoint 12 members for their contributions to art, literature, science, and social services. Members sit for staggered terms lasting six years, with a third of the members up for election every two years.

The President of Russia, officially the President of the Russian Federation, is the head of state of the Russian Federation, as well as holder of the highest office in Russia and commander-in-chief of the Russian Armed Forces.

The Parliament of India is the supreme legislative body of the Republic of India. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the President of India and the two houses: the Rajya Sabha and the Lok Sabha. The President in his role as head of legislature has full powers to summon and prorogue either house of Parliament or to dissolve Lok Sabha. The president can exercise these powers only upon the advice of the Prime Minister and his Union Council of Ministers.
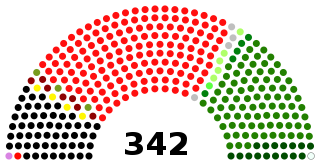
The National Assembly is the lower house of the bicameral Majlis-e-Shura, which also comprises the President of Pakistan and Senate of Pakistan. The National Assembly and the Senate both convene at Parliament House in Islamabad. The National Assembly is a democratically elected body consisting of a total of 336 members, before 25th amendment they used to be 342' who are referred to as Members of the National Assembly (MNAs), of which 272 are directly elected members and 70 reserved seats for women and religious minorities. A political party must secure 137 seats to obtain and preserve a majority.

Philippine elections are of several types. The president, vice-president, and the senators are elected for a six-year term, while the members of the House of Representatives, governors, vice-governors, members of the Sangguniang Panlalawigan, mayors, vice-mayors, members of the Sangguniang Panlungsod/members of the Sangguniang Bayan, barangay officials, and the members of the Sangguniang Kabataan are elected to serve for a three-year term.
A union territory is a type of administrative division in the Republic of India. Unlike the states of India, which have their own governments, union territories are federal territories ruled directly by the union government, hence the name "union territory"













