Related Research Articles

The politics of Russia take place in the framework of the federal semi-presidential republic of Russia. According to the Constitution of Russia, the President of Russia is head of state, and of a multi-party system with executive power exercised by the government, headed by the Prime Minister, who is appointed by the President with the parliament's approval. Legislative power is vested in the two houses of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation, while the President and the government issue numerous legally binding by-laws. Since the collapse of the Soviet Union at the end of 1991, Russia has seen serious challenges in its efforts to forge a political system to follow nearly seventy-five years of Soviet governance. For instance, leading figures in the legislative and executive branches have put forth opposing views of Russia's political direction and the governmental instruments that should be used to follow it. That conflict reached a climax in September and October 1993, when President Boris Yeltsin used military force to dissolve the parliament and called for new legislative elections. This event marked the end of Russia's first constitutional period, which was defined by the much-amended constitution adopted by the Supreme Soviet of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic in 1978. A new constitution, creating a strong presidency, was approved by referendum in December 1993.
Primary elections, often abbreviated to primaries, are a process by which voters can indicate their preference for their party's candidate, or a candidate in general, in an upcoming general election, local election, or by-election. Depending on the country and administrative divisions within the country, voters might consist of the general public in what is called an open primary, or solely the members of a political party in what is called a closed primary. In addition to these, there are other variants on primaries that are used by many countries holding elections throughout the world.

The president of the Russian Federation, is the head of state of the Russian Federation, as well as the commander-in-chief of the Russian Armed Forces. It is the highest office in Russia.

The 2004 Russian presidential election was held on 14 March 2004. Incumbent President Vladimir Putin was seeking a second full four-year term. It was a landslide victory for Putin, who was re-elected with 71.9% of the vote.

The 2000 Russian presidential election was held on 26 March 2000. Incumbent Prime Minister and acting President Vladimir Putin, who had succeeded Boris Yeltsin on his resignation on 31 December 1999, was seeking a four-year term in his own right and won the elections in the first round.
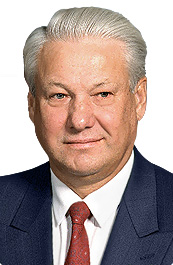
The 1996 Russian presidential election took place in Russia on 16 June 1996, with a second round being held on 3 July. It resulted in a victory for the incumbent President of Russia Boris Yeltsin, who ran as an independent politician. Yeltsin defeated Communist challenger Gennady Zyuganov in the run-off, receiving 54.4% of the vote. His inauguration ceremony took place on 9 August.

Viktor Andriyovych Yushchenko is a Ukrainian politician who was the third President of Ukraine from 23 January 2005 to 25 February 2010.

The president of the Republic of Belarus is the head of state and de facto head of government of Belarus. The office was created in 1994 with the passing of the Constitution of Belarus by the Supreme Soviet. This replaced the office of Chairman of the Supreme Soviet as the head of state. The tasks of the president include executing foreign and domestic policy, defending the rights and general welfare of citizens and residents, and upholding the Constitution. The president is mandated by the Constitution to serve as a leader in the social affairs of the country and to act as its main representative abroad. The duties, responsibilities and other transitional clauses dealing with the presidency are listed in Chapter Three, Articles 79 through 89, of the Constitution.

The 2008 Russian presidential election was held on 2 March 2008, and resulted in the election of Dmitry Medvedev as the third President of Russia. Medvedev was elected for a four-year term, whose candidacy was supported by incumbent president Vladimir Putin and five political parties, received 71% of the vote, and defeated Gennady Zyuganov of the Communist Party of the Russian Federation, and Vladimir Zhirinovsky of the Liberal Democratic Party of Russia.

Presidential elections were held in Ukraine on 17 January 2010. As no candidate received a majority of the vote, a run-off election was held between Prime Minister Yulia Tymoshenko and opposition leader Viktor Yanukovych on 7 February.

The president of Ukraine is the head of state of Ukraine. The president represents the nation in international relations, administers the foreign political activity of the state, conducts negotiations and concludes international treaties. The president is directly elected by the citizens of Ukraine for a five-year term of office, limited to two terms consecutively.

The 2016 United States presidential election was the 58th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. The Republican ticket of businessman Donald Trump and Indiana governor Mike Pence defeated the Democratic ticket of former secretary of state Hillary Clinton and U.S. senator from Virginia Tim Kaine, in what was considered one of the greatest upsets in American history. Trump took office as the 45th president, and Pence as the 48th vice president, on January 20, 2017. It was the fifth and most recent presidential election in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote.

Snap presidential elections were held in Ukraine on 25 May 2014, resulting in Petro Poroshenko being elected President of Ukraine. Originally scheduled to take place on 29 March 2015, the date was changed following the 2014 Ukrainian revolution. Poroshenko won the elections with 54.7% of the votes, enough to win in a single round. His closest competitor was Yulia Tymoshenko, who emerged with 12.81% of the votes. The Central Election Commission reported voter turnout at over 60% excluding those regions not under government control. Since Poroshenko obtained an absolute majority in the first round, a run-off second ballot was unnecessary.

The 2012 Russian presidential election was held on 4 March 2012. There were five officially registered candidates: four representatives of registered parties, and one nominal independent. These Russian presidential elections were the first after the constitutional amendments in 2008. In this election, the president was elected for the first time for six years, not four as before.

Anatoly Ilyich Bibilov is a Russian and South Ossetian military officer, currently serving as the 4th President of South Ossetia, a partially recognized, but de facto independent state, succeeding Leonid Tibilov as President on April 21, 2017, following his election victory.

Civic Platform is a conservative political party in Russia. The party was formed on 4 June 2012 by businessman and 2012 presidential candidate Mikhail Prokhorov.

The 2018 Russian presidential election was held on 18 March 2018. Incumbent Vladimir Putin won reelection for his second consecutive term in office with 77% of the vote. Vladimir Zhirinovsky from the Liberal Democratic Party was the perennial candidate, having unsuccessfully run in five previous presidential elections. Other candidates included Pavel Grudinin, Sergey Baburin, Ksenia Sobchak, Maxim Suraykin, Boris Titov and Grigory Yavlinsky (Yabloko). Anti-corruption activist Alexei Navalny announced his intent to run in December 2016 but was barred from doing so due to a prior criminal conviction, which is widely seen as politically motivated, for corruption. Consequently, Navalny called for a boycott of the election. He had previously organized several public rallies against corruption among members of Putin's government.

The 2019 Ukrainian presidential election was held on 31 March and 21 April in a two-round system.

Russian presidential elections determine who will serve as the President of Russia for the next six years.