
An airborne wind turbine is a design concept for a wind turbine with a rotor supported in the air without a tower, thus benefiting from the higher velocity and persistence of wind at high altitudes, while avoiding the expense of tower construction, or the need for slip rings or yaw mechanism. An electrical generator may be on the ground or airborne. Challenges include safely suspending and maintaining turbines hundreds of meters off the ground in high winds and storms, transferring the harvested and/or generated power back to earth, and interference with aviation.
Airborne wind energy (AWE) is the direct use or generation of wind energy by the use of aerodynamic or aerostatic lift devices. AWE technology is able to harvest high altitude winds, in contrast to wind turbines, which use a rotor mounted on a tower.

Unconventional wind turbines are those that differ significantly from the most common types in use.
Southwest Windpower (SWWP) was a wind turbine manufacturer established in 1987 based in Flagstaff, Arizona, United States. The company specialized in small, reliable battery charging wind generators that complement photovoltaics (solar energy or PV) in supplying energy to rural areas.
A laddermill kite system is an airborne wind turbine consisting of a long string or loop of power kites. The loop or string of kites would be launched in the air by the lifting force of the kites, until it is fully unrolled, and the top reaches a height determined by designers and operators; some designers have considered heights of about 30,000 feet, but the concept is not height-dependent. The laddermill method may use one endless loop, two endless loops, or more such loops.
SkySails Group GmbH is a Hamburg-based company that sells kite rigs to propel cargo ships, large yachts and fishing vessels by wind energy as well as airborne wind energy systems for electricity production from high-altitude winds.
Different types of flying kites have niche applications. In nature, some animals, such as spiders, also make use of kiting.

A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. As of 2020, hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, were generating over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. Wind turbines are an increasingly important source of intermittent renewable energy, and are used in many countries to lower energy costs and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. One study claimed that, as of 2009, wind had the "lowest relative greenhouse gas emissions, the least water consumption demands and the most favorable social impacts" compared to photovoltaic, hydro, geothermal, coal and gas energy sources.

SMA Solar Technology AG is a German solar energy equipment supplier founded in 1981 and headquartered in Niestetal, Northern Hesse, Germany. SMA is a producer and manufacturer of solar inverters for photovoltaics systems with grid connection, off-grid power supply and backup operations.

GE Wind is a division of GE Vernova. The company manufactures and sells wind turbines to the international market. In 2018, GE Wind was the fourth largest wind turbine manufacturer in the world. Vic Abate is the CEO of GE Vernova’s Wind businesses.
Squid Labs was an American independent research and development company founded by a group of four MIT graduates. In 2004, Colin Bulthaup, Dan Goldwater, Saul Griffith, and Eric Wilhelm moved from the East Coast to California to found the company known as Squid Labs. During its years of existence from 2004 to 2007, Squid Labs added three more members to its team: Geo Homsy, Corwin Hardham and Ryan McKinley. Working out of a warehouse in Emeryville, the group adopted the slogan "We're not a think tank, we're a do tank." and created a handful of patents and inventions including an electronically sensed rope, portable pull-cord generators, and a machine that could manufacture eyeglasses of any prescriptions at extremely low cost. Squid Labs was also the birthplace for many companies still running today, such as Makani Power and Howtoons. Although the company no longer exists, Squid Lab's co-founder, Saul Griffith created a similar company in San Francisco named Otherlab.

James G.P. Dehlsen is an American businessman, inventor, and entrepreneur. He is a pioneering figure in wind power and renewable energy development in the United States and holds 25 patents.
Makani Technologies LLC was an Alameda, California-based company that developed airborne wind turbines. Founded in 2006, Makani was acquired by Google in May 2013. In February 2020, Makani was shut down by Alphabet, Google's parent company.

X Development LLC, doing business as X, is an American semi-secret research and development facility and organization founded by Google in January 2010. X has its headquarters about a mile and a half from Alphabet's corporate headquarters, the Googleplex, in Mountain View, California.
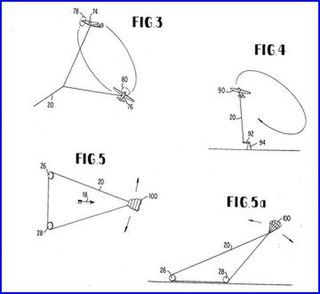
Crosswind kite power is power derived from airborne wind-energy conversion systems or crosswind kite power systems (CWKPS). The kite system is characterized by energy-harvesting parts flying transversely to the direction of the ambient wind, i.e., to crosswind mode; sometimes the entire wing set and tether set are flown in crosswind mode. From toy to power-grid-feeding sizes, these systems may be used as high-altitude wind power (HAWP) devices or low-altitude wind power (LAWP) devices without having to use towers. Flexible wings or rigid wings may be used in the kite system. A tethered wing, flying in crosswind at many times wind speed, harvests wind power from an area that exceeds the wing's total area by many times.
NTS Energie- und Transportsysteme GmbH was founded in 2006 in Berlin, Germany by Uwe Ahrens.The company is developing X-Wind technology. This technology combines two technologies - automatically steered kites and generators on a rail system - to produce electricity. A closed loop rail with cable-connected cars work in concert to pull the loop cable. Each railed car is pulled by a four-tethered kited wing; each wing is controlled by an autopilot or kite-steering unit.

Donald Lewis Montague is a Canadian-American watersport athlete and designer. He is President of Kai Concepts, co-founder of Makani Power, and the head of the Kiteboat Project in Alameda, California.

Ampyx Power was a Dutch company based in The Hague whose aim was to develop utility-scale airborne wind energy systems. The company was founded in 2008 by Bas Lansdorp and Dr. Richard Ruiterkamp.
Kitepower is a registered trademark of the Dutch company Enevate B.V. developing mobile airborne wind power systems. Kitepower was founded in 2016 by Johannes Peschel and Roland Schmehl as a university spin-off from the Delft University of Technology’s airborne wind energy research group established by the former astronaut Wubbo Ockels. The company is located in Delft, Netherlands, and currently comprises 18 employees (2018).









