Lesotho's geographic location makes it extremely vulnerable to political and economic developments in South Africa. Its capital is the small city of Maseru. It is a member of many regional economic organizations including the Southern African Development Community (SADC) and the Southern African Customs Union (SACU). Lesotho also is active in the United Nations, the Organisation of African Unity, now the African Union, the Non-Aligned Movement, and many other international organizations. In addition to the Republic of Korea, the United States, South Africa, Ireland, People's Republic of China, Libya, and the European Union all currently retain resident diplomatic missions in Lesotho. Foreign relations of Lesotho are administered by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Relations.

Though the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MOFA) is the government agency responsible for the conduct of foreign relations of Nepal, historically, it is the Office of Prime Minister (PMO) that has exercised the authority to formulate and conduct policies related to Nepal's foreign affairs. As a landlocked country wedged between two larger and far stronger powers, Nepal has tried to maintain good relations with both of its neighbors, People's Republic of China and Republic of India. Nepal's relationship with China, India, and the USA has remained utmost priority for successive Nepali governments. The relationship between Nepal and India however was significantly hampered during the 2015 Nepal blockade by pro-Indian anti-Nepal protestors, where the Government of Nepal accused India of using "Russia-Ukraine" tactics to cause unrest along Nepal's southern border using ethnically Indian residents of Nepal. India strictly denied the allegation and said the unrest were solely due to Madheshi protesters. For the most part though, Nepal has traditionally maintained a non-aligned policy and enjoys friendly relations with its neighboring countries and almost all the major countries of the world.

The Islamic Republic of Pakistan maintains a large network of diplomatic relations across the world. Pakistan is the second largest Muslim-majority country in terms of population and is the only Muslim majority nation to have possession of nuclear weapons.

South Korea maintains diplomatic relations with 191 countries. The country has also been a member of the United Nations since 1991, when it became a member state at the same time as North Korea. South Korea has also hosted major international events such as the 1988 Summer Olympics and 2002 World Cup Soccer Tournament and the 2011 IAAF World Championships Daegu South Korea. Furthermore, South Korea had hosted the 2018 Winter Olympics which took place in Pyeongchang, South Korea from 9 to 25 February.

Foreign relations of Tajikistan are based on a desire to secure foreign investment and promote regional security while ensuring Tajikistan's independence. Sirodjidin Aslov is the current Foreign’s Minister of Tajikistan.
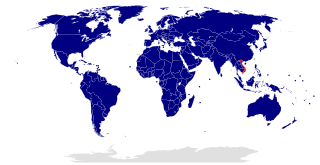
As of April 2022, Vietnam maintains diplomatic relationships with 189 nations throughout the world and the State of Palestine, including all UN member states and UN observer states other than (i) UN member states Malawi, Bahamas, Tonga and Tuvalu and (ii) the UN observer Holy See. In 2011 the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam, at the 11th National Congress of the Communist Party of Vietnam, released an official statement about Vietnam's foreign policy and a section of the statement stated: "Vietnam is a friend and reliable partner of all countries in the international community, actively taking part in international and regional cooperation processes. Deepen, stabilize and sustain established international relations. Develop relations with countries and territories in the world, as well as international organizations, while showing: respect for each other's independence; sovereignty and territorial integrity; non-interference in each other's international affairs; non-use or threat of force; settlement of disagreements and disputes by means of peaceful negotiations; mutual respect, equality and mutual benefit."

Uganda has formal diplomatic relations with many countries, some accredited. Since the colonial era and after independence Uganda has grown to be one of the most important African countries. Uganda has diplomatic relations with many countries throughout Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe and Oceania. Uganda is a member of the United Nations and the Commonwealth of Nations since 1962.

The foreign relations of the Islamic Republic of Mauritania have, since 1960, been dominated by the issues of the Spanish Sahara and the recognition of its independence by its neighbours, particularly Morocco. Mauritania's foreign relations are handled by the Minister for Foreign Affairs and Cooperation, who is currently Ismail Ould Cheikh Ahmed.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of China (Taiwan) is a ministry of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Governed as the cabinet level policy-making body under the Executive Yuan since 1928, the fundamental purpose of the ministry is to promote, expand, and conduct bilateral foreign affairs with other nations. Though the ministry was founded on 1 January 1912 when the Republic was founded, the ministry dates its origins on 11 March 1861 as the Office in Charge of Affairs Concerning All Nations in the Qing dynasty. The current Foreign Minister is Joseph Wu. The MOFA headquartered in Zhongzheng District in Taipei.
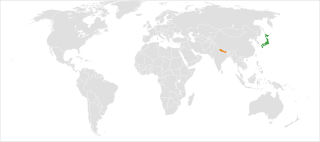
Japan–Nepal relations are foreign relations between Japan and Nepal. Diplomatic relations between the two countries were established on 28 September 1956. Japan has an embassy in Kathmandu. Nepal has an embassy in Tokyo.
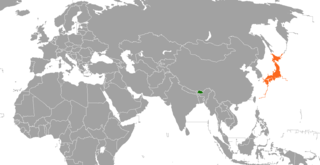
The Bhutan–Japan relations refers to the diplomatic relations between Bhutan and Japan. Diplomatic relations were established on March 28, 1986.
Diplomatic Academy of Vietnam, is a public research university located in Hanoi, Vietnam and an administrative unit under management of Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Vietnam. Founded in 1959, formerly known as "University of Foreign Affairs" or "Institute for International Relations", Diplomatic Academy of Vietnam is known as a prestigious institution providing in-depth training, strategic research and forecasts on a wide range of pressing regional and global issues to the country's government. It is regarded as an elite training ground for future diplomats, leaders, civil servants, journalists and business executives in Vietnam.

Algeria and Poland are members of the Union for the Mediterranean and the United Nations. Both nations established diplomatic relations in 1962.