Contents
This is list of archives in Iceland.
This is list of archives in Iceland.

Iceland is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which is home to over 65% of the population. Iceland is the only part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that rises above sea level, and its central volcanic plateau is erupting almost constantly. The interior consists of a plateau characterised by sand and lava fields, mountains, and glaciers, and many glacial rivers flow to the sea through the lowlands. Iceland is warmed by the Gulf Stream and has a temperate climate, despite a high latitude just outside the Arctic Circle. Its high latitude and marine influence keep summers chilly, and most of its islands have a polar climate.

Reykjavík is the capital and largest city of Iceland. It is located in southwestern Iceland, on the southern shore of Faxaflói bay. Its latitude is 64°08' N, making it the world's northernmost capital of a sovereign state. With a population of around 131,136, it is the centre of Iceland's cultural, economic and governmental activity, and is a popular tourist destination.

Iceland is an island country at the confluence of the North Atlantic and Arctic oceans, east of Greenland and immediately south of the Arctic Circle, atop the constructive boundary of the northern Mid-Atlantic Ridge about 860 km (530 mi) from Scotland and 4,200 km (2,600 mi) from New York City. One of the world's most sparsely populated countries, Iceland's boundaries are almost the same as the main island – the world's 18th largest in area and possessing almost all of the country's area and population and also it is world's 9th largest island country. It is the westernmost European country and has more land covered by glaciers than in all of continental Europe. The total size is 103,125 km2 (39,817 sq mi). It has an exclusive economic zone of 751,345 km2 (290,096 sq mi).

The economy of Iceland is small and subject to high volatility. In 2011, gross domestic product was US$12 billion, but by 2018 it had increased to a nominal GDP of US$27 billion. With a population of 350,000, this is $55,000 per capita, based on purchasing power parity (PPP) estimates. The financial crisis of 2007–2010 produced a decline in GDP and employment that has since been reversed entirely by a recovery aided by a tourism boom starting in 2010. Tourism accounted for more than 10% of Iceland's GDP in 2017. After a period of robust growth, Iceland's economy is slowing down according to an economic outlook for the years 2018–2020 published by Arion Research in April 2018.

Iceland's defences consist of the Icelandic Coast Guard, which patrols Icelandic waters and monitors its airspace, and other services such as the National Commissioner's National Security and Special Forces Units. Iceland is however the only NATO member which maintains no standing army.

Iceland took control of its foreign affairs in 1918 when it became a sovereign country, the Kingdom of Iceland, in a personal union with the King of Denmark. As a fully independent state, Iceland could have joined the League of Nations in 1918, but chose not to do so for cost reasons. It negotiated with Denmark to initially carry out most of its foreign relations, while maintaining full control. Denmark appointed a diplomatic envoy (Ambassador) to Iceland in 1919 and Iceland reciprocated in 1920, opening an Embassy in Copenhagen. Iceland established its own Foreign Service in April 1940 when Denmark became occupied by Nazi Germany and ties between the two countries were severed. The Republic of Iceland was founded in 1944. The Icelandic foreign service grew slowly in the post-WWII period, but increased rapidly after the mid-1990s. Iceland's closest relations are with the Nordic states, the European Union and the United States. Iceland has been a member of the United Nations since 1946. Iceland was a founding member of the World Bank in 1946 and NATO in 1949. In terms of European integration, Iceland was a founding member of the OEEC in 1948 and the Nordic Council in 1952, it joined EFTA in 1970, was a founding member of the CSCE in 1973 and the EEA in 1992 and joined Schengen in 1996.

Akureyri is a town in northern Iceland. It is Iceland's fourth-largest municipality, after Reykjavík, Hafnarfjörður, and Kópavogur, and the largest town outside Iceland's more populated southwest corner.

The Alþingi is the supreme national parliament of Iceland. It is the oldest surviving parliament in the world. The Althing was founded in 930 at Þingvellir, situated approximately 45 kilometres (28 mi) east of what later became the country's capital, Reykjavík. Even after Iceland's union with Norway in 1262, the Althing still held its sessions at Þingvellir until 1800, when it was discontinued. It was restored in 1844 by royal decree and moved to Reykjavík. The restored unicameral legislature first came together in 1845 and after 1874 operated in two chambers with an additional third chamber taking on a greater role as the decades passed until 1991 when Althing became once again unicameral. The present parliament building, the Alþingishús, was built in 1881, made of hewn Icelandic stone. The unicameral parliament has 63 members, and is elected every four years based on party-list proportional representation. The current speaker of the Althing is Birgir Ármannsson.

Nasdaq Nordic is the common name for the subsidiaries of Nasdaq, Inc. that provide financial services and operate marketplaces for securities in the Nordic and Baltic regions of Europe.

Icelandic names are names used by people from Iceland. Icelandic surnames are different from most other naming systems in the modern Western world by being patronymic or occasionally matronymic: they indicate the father of the child and not the historic family lineage. Iceland shares a common cultural heritage with the Scandinavian countries of Denmark, the Faroe Islands, Norway, and Sweden. Unlike other Nordics, Icelanders have continued to use their traditional name system, which was formerly used by all Nordic countries except partly Finland. The Icelandic system is thus not based on family names. Generally, with few exceptions, a person's last name indicates the first name of their father (patronymic) or in some cases mother (matronymic) in the genitive, followed by -son ("son") or -dóttir ("daughter").

Morgunblaðið is an Icelandic newspaper. Morgunblaðið's website, mbl.is, is the most popular website in Iceland.
The Nasdaq Iceland, formerly known as the Iceland Stock Exchange (XICE), is a stock exchange located in Iceland. It was established in 1985 as a joint venture of several banks and brokerage firms on the initiative of the central bank. Trading began in 1986 in Icelandic government bonds, and trading in equities began in 1991. Equities trading increased rapidly thereafter. A wide variety of firms are currently listed on the exchange, including firms in retail, fishing, transportation, banks, insurance and numerous other areas. Because of the small size of the Icelandic economy and the low cost of public listing, many of the companies traded on the XICE are relatively small and are relatively illiquid.

Icelanders are a North Germanic ethnic group and nation who are native to the island country of Iceland and speak Icelandic.

The Iceland national football team represents Iceland in men's international football. The team is controlled by the Football Association of Iceland, and have been a FIFA member since 1947 and an UEFA member since 1957. The team's nickname is Strákarnir okkar, which means Our Boys in Icelandic.
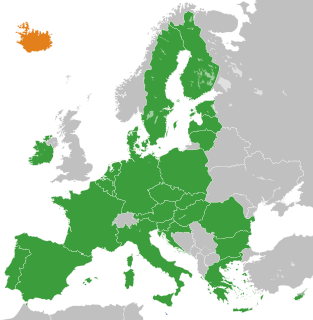
Iceland is heavily integrated into the European Union via the Agreement on the European Economic Area and the Schengen Agreement, despite its status as a non-EU member state. Iceland applied for membership in 2009 but the application was controversial and the Icelandic government withdrew it in 2015.
Elections in Iceland gives information on election and election results in Iceland.
The Besta-deild karla is the highest men's football league in Iceland. It has been played since 1912. Because of the harsh winters in Iceland, it is generally played in the spring and summer. It is governed by the Football Association of Iceland (KSI) and has 12 teams. By end of season 2015–2016, UEFA ranked the league No. 35 in Europe.

Athletes from Iceland first participated at the Olympic Games in 1908.

Jóhanna Sigurðardóttir is an Icelandic politician, who served as prime minister of Iceland from 2009 to 2013. She became active in the trade union movement, serving as an officer.