Related Research Articles

The four national languages of Switzerland are German, French, Italian and Romansh. All but Romansh maintain equal status as official languages at the national level within the Federal Administration of the Swiss Confederation. In some situations, Latin is used, particularly as a single language to denote the country.

The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to Switzerland.

Each of the 26 modern cantons of Switzerland has an official flag and a coat of arms. The history of development of these designs spans the 13th to the 20th centuries.

In contrast to centrally organised states, in the federally constituted Switzerland each canton is completely free to decide its own internal organisation. Therefore, there exists a variety of structures and terminology for the subnational entities between canton and municipality, loosely termed districts.

The Protestant Reformation in Switzerland was promoted initially by Huldrych Zwingli, who gained the support of the magistrate and population of Zürich in the 1520s. It led to significant changes in civil life and state matters in Zürich and spread to several other cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy. Seven cantons remained Roman Catholic, though, which led to inter-cantonal wars known as the Wars of Kappel. After the victory of the Catholic cantons in 1531, they proceeded to institute counter-reformatory policies in some regions. The schism and distrust between Catholic and Protestant cantons would define their interior politics and paralyse any common foreign policy until well into the 18th century.

The Swiss Plateau or Central Plateau is one of the three major landscapes in Switzerland, lying between the Jura Mountains and the Swiss Alps. It covers about 30% of the Swiss surface area, and is partly flat but mostly hilly. The average height is between 400 metres (0.25 mi) and 700 metres (0.43 mi) AMSL. It is by far the most densely populated region of Switzerland, the center of economy and important transportation.
The Swiss Confederation comprises the 26 cantons of Switzerland.
The Federation of Swiss Protestant Churches is a federation of 26 member churches — 24 cantonal churches and two free churches. The SEK-FEPS is not a church in a theological understanding, because every member is independent with their own theological and formal organisation. It serves as a legal umbrella before the federal government and represents the church in international relations. Except for the Evangelical-Methodist Church, which covers all of Switzerland, the member churches are restricted to a certain territory.

The Old Swiss Confederacy was a loose confederation of independent small states within the Holy Roman Empire. It is the precursor of the modern state of Switzerland.

Christianity is the predominant religion of Switzerland, its presence going back to the Roman era. Since the 16th century, Switzerland has been traditionally divided into Roman Catholic and Reformed confessions. However, adherence to Christian churches has declined considerably since the late 20th century, from close to 94% in 1980 to about 64% as of 2018.
The Green Liberal Party of Switzerland, abbreviated to glp, is a centrist green-liberal political party in Switzerland. Founded in 2007, the party holds sixteen seats in the Federal Assembly as of the October 2019 election.
The Swiss Mathematical Society, founded in Basel on September 4, 1910, is the national mathematical society of Switzerland and a member society of the European Mathematical Society. It is notably running the scholarly journal Commentarii Mathematici Helvetici and Elemente der Mathematik, both currently published by the European Mathematical Society.

Biel/Bienne railway station serves the bilingual municipality of Biel/Bienne, in the canton of Bern, Switzerland.

Neuchâtel railway station serves the municipality of Neuchâtel, the capital city of the canton of Neuchâtel, Switzerland. Opened in 1857, it is owned and operated by SBB-CFF-FFS.
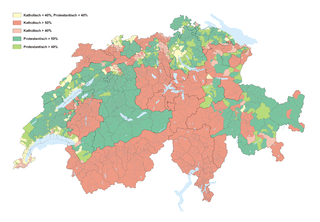
The Swiss Reformed Church is the Reformed branch of Protestantism in Switzerland started in Zürich in 1519 by Huldrych Zwingli (1484–1531). It spread within a few years to Basel, Bern, St. Gallen, to cities in southern Germany and via Alsace to France.
References
- ↑ "Geneva Conservatory and Botanical Garden of the city of Geneva". City of Geneva. Retrieved 2014-10-12.