This article needs additional citations for verification .(March 2025) |
Reports from these coastal stations and automatic weather logging stations in the British Isles are included in the extended Shipping Forecasts on BBC Radio 4 at 0048 and 0520 local time each day. [1] [2] The coastal stations are part of the Met Office station network. [3]
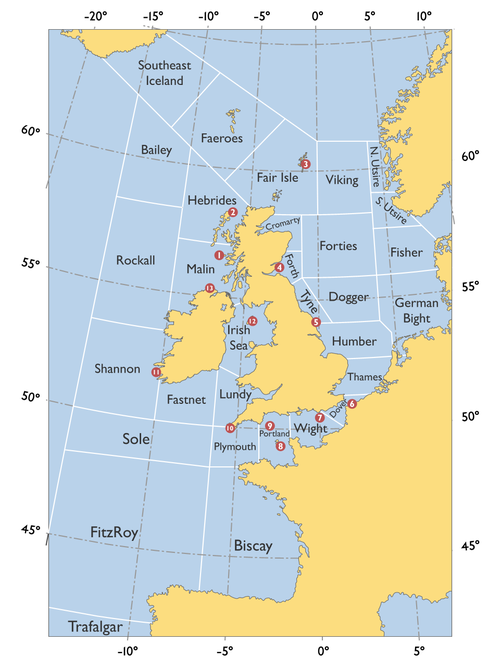
The stations are listed in the order they are read in the forecast, the numbers in brackets refer to the map on the right. Weather reports included in the forecasts are issued at 2300 local time for the late broadcast and 0400 for the early one, although reports issued at other times may be included if for some reason, the most recent weather report did not arrive.
The report from each station is read in the following format: wind direction and speed, visibility in nautical miles, air pressure and pressure trend (steady, rising, or falling with rate of change).
- Tiree Automatic (1)
- Stornoway (2)
- Lerwick (3)
- Wick Automatic (0048 only)
- Aberdeen (0048 only)
- Leuchars (4)
- Boulmer (0048 only)
- Bridlington (5)
- Sandettie Light Vessel Automatic (6)
- Greenwich Light Vessel Automatic (7)
- St. Catherine's Point Automatic (0048 only)
- Jersey (8)
- Channel Light Vessel Automatic (9)
- Scilly Automatic (10)
- Milford Haven (0048 only)
- Aberporth (0048 only)
- Valley (0048 only)
- Liverpool Crosby (0048 only)
- Valentia (11)
- Ronaldsway (12)
- Malin Head (13)
- Machrihanish Automatic (0048 only)