Related Research Articles

A biome is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader term than habitat and can comprise a variety of habitats.

Norway is a country located in Northern Europe in the northern and western parts of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The majority of the country borders water, including the Skagerrak inlet to the south, the North Sea to the southwest, the North Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the Barents Sea to the north. It has a land border with Sweden to the east and a shorter border with Finland and an even shorter border with Russia to the northeast.
The Global 200 is the list of ecoregions identified by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the global conservation organization, as priorities for conservation. According to WWF, an ecoregion is defined as a "relatively large unit of land or water containing a characteristic set of natural communities that share a large majority of their species dynamics, and environmental conditions". For example, based on their levels of endemism, Madagascar gets multiple listings, ancient Lake Baikal gets one, and the North American Great Lakes get none.

The ecology of California can be understood by dividing the state into a number of ecoregions, which contain distinct ecological communities of plants and animals in a contiguous region. The ecoregions of California can be grouped into four major groups: desert ecoregions, Mediterranean ecoregions, forested mountains, and coastal forests.

The Scandinavian coastal conifer forests or Norwegian coastal conifer forest is a Palearctic ecoregion in the temperate coniferous forests biome, located along the coast of Norway. Within it are a number of small areas with botanical features and a local climate consistent with a temperate rainforest.

The Scandinavian montane birch forests and grasslands is defined by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) as a terrestrial tundra ecoregion in Norway, Sweden, and Finland.

A forest steppe is a temperate-climate ecotone and habitat type composed of grassland interspersed with areas of woodland or forest.

The Sarmatic mixed forests constitute an ecoregion within the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome, according to the World Wide Fund for Nature classification.

The Scandinavian and Russian taiga is an ecoregion within the taiga and boreal forests biome as defined by the WWF classification. It is situated in Northern Europe between tundra in the north and temperate mixed forests in the south and occupies about 2,156,900 km2 (832,800 sq mi) in Norway, Sweden, Finland and the northern part of European Russia, being the largest ecoregion in Europe. In Sweden the taiga is primarily associated with the Norrland terrain.

The Alaska Peninsula montane taiga is a taiga and boreal forests ecoregion, located in Alaska, and defined by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) categorization system.

Kandalaksha Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik' on the south shore of Kandalaksha Bay in the Murmansk and Karelia regions on the opening to the White Sea. The reserve also includes two small sectors on the northern coast of the Kola peninsula on the Barents Sea; notably, the warm Atlantic current causes the northern sectors on the Barents Sea to be warmer than the more southerly White Sea sectors. Over 550 islands are covered in the boundaries of the reserve. It is one of the oldest nature reserves in Russia, created in 1932 to protect the marine habitats and waterfowl of the region, particularly the eider. The reserve is situated in the Kandalakshsky District, Kolsky District, and Lovozersky District of Murmansk Oblast. The nearest city, Kandalaksha, is at the northwest entrance to the Kandalaksha Gulf, about 5 km from the nearest point in the reserve. Since 1976, the reserve has been part of the Ramsar wetland site of international importance "Kandalaksha Bay". It covers an area of 70,530 ha (272.3 sq mi).
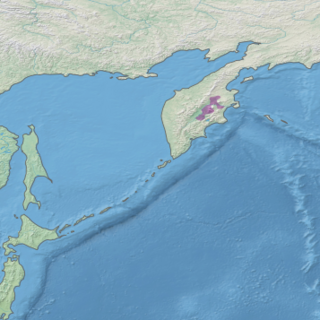
The Kamchatka–Kurile taiga ecoregion is a "conifer island" in the middle of the Kamchatka Peninsula, along the Kamchatka River. It is the easternmost example of Siberian taiga. The region has unusual ecological conditions, a "snow forest" that combines low temperatures, high humidity and boreal forest with heavy snowfall. The local ecology is also affected by volcanic activity. The region is about 300 km long (north-south), and averages about 100 km west-east. It is in the Palearctic realm, and mostly in the Boreal forests/taiga ecoregion with a humid continental climate, cool summer climate. It covers 147,064 km2 (56,782 sq mi).

The Urals montane tundra and taiga ecoregion covers the main ridge of the Ural Mountains - a 2,000 km (north-south) by 300 km (west-east) region. The region is on the divide between European and Asian ecoregions, and also the meeting point of tundra and taiga. It is in the Palearctic realm, and mostly in the Boreal forests/taiga ecoregion with a Humid continental climate, cool summer climate. It covers 174,565 km2 (67,400 sq mi).

The Kola Peninsula tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that covers the northeastern half of the Kola Peninsula, along the coast of the White Sea, a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. The maritime effects of the White Sea create a milder climate than would be expected for a region of this latitude. It is in the Palearctic realm, and the tundra biome. It has an area of 58,793 square kilometres (22,700 sq mi).

Khibiny National Park protects a mountainous region of taiga and tundra on the Khibiny Mountains and Lovozero Massif of the western Kola Peninsula in northwestern Russia. The mountains contain commercially important minerals, and the park's borders reflect the need to balance three uses - protection of the unique natural environment, recreation, and industrial mining. The park was officially created in 2018, and is located in the districts of Kirovsk and Olenegorsk in Murmansk Oblast.
References
- ↑ Hogan, C. Michael (November 19, 2012). McGinley, Mark (ed.). "Scandinavian and Russian taiga". Encyclopedia of the Earth. Retrieved 2018-12-27.
- ↑ "Scandinavian coastal conifer forest". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
- ↑ World Wildlife Fund, ed. (2001). "Scandinavian coastal conifer forest". WildWorld Ecoregion Profile. National Geographic Society. Archived from the original on 2010-03-08.
- ↑ "Sarmatic mixed forests". World Wildlife Federation. Retrieved October 21, 2020.
- ↑ "Kola Peninsula tundra". World Wildlife Federation. Retrieved November 20, 2018.
- ↑ "Scandinavian montane birch forest and grasslands". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
- ↑ "Arctic desert". World Wildlife Federation. Retrieved November 20, 2018.