
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia.

A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies, and autoimmune disorders.

Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others.
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness, a mental health condition, or a psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. A mental disorder is also characterized by a clinically significant disturbance in an individual's cognition, emotional regulation, or behavior, often in a social context. Such disturbances may occur as single episodes, may be persistent, or may be relapsing–remitting. There are many different types of mental disorders, with signs and symptoms that vary widely between specific disorders. A mental disorder is one aspect of mental health.

Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms.

The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has six regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide.

The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH, is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late 1880s and is now part of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. Many NIH facilities are located in Bethesda, Maryland, and other nearby suburbs of the Washington metropolitan area, with other primary facilities in the Research Triangle Park in North Carolina and smaller satellite facilities located around the United States. The NIH conducts its own scientific research through the NIH Intramural Research Program (IRP) and provides major biomedical research funding to non-NIH research facilities through its Extramural Research Program.

The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of the U.S. people and providing essential human services. Its motto is "Improving the health, safety, and well-being of America". Before the separate federal Department of Education was created in 1979, it was called the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare (HEW).
Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. Health can be promoted by encouraging healthful activities, such as regular physical exercise and adequate sleep, and by reducing or avoiding unhealthful activities or situations, such as smoking or excessive stress. Some factors affecting health are due to individual choices, such as whether to engage in a high-risk behavior, while others are due to structural causes, such as whether the society is arranged in a way that makes it easier or harder for people to get necessary healthcare services. Still, other factors are beyond both individual and group choices, such as genetic disorders.

MSN is a American web portal and related collection of Internet services and apps for Windows and mobile devices, provided by Microsoft and launched on August 24, 1995, alongside the release of Windows 95.

Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professionals and allied health fields. Medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, midwifery, nursing, optometry, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy, physical therapy, athletic training, and other health professions all constitute health care. The term includes work done in providing primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care, as well as in public health.

Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the determinants of health of a population and the threats it faces is the basis for public health. The public can be as small as a handful of people or as large as a village or an entire city; in the case of a pandemic it may encompass several continents. The concept of health takes into account physical, psychological, and social well-being.

Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. According to World Health Organization (WHO), it is a "state of well-being in which the individual realizes his or her abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and can contribute to his or her community". It likewise determines how an individual handles stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making. Mental health includes subjective well-being, perceived self-efficacy, autonomy, competence, intergenerational dependence, and self-actualization of one's intellectual and emotional potential, among others. From the perspectives of positive psychology or holism, mental health may include an individual's ability to enjoy life and to create a balance between life activities and efforts to achieve psychological resilience. Cultural differences, personal philosophy, subjective assessments, and competing professional theories all affect how one defines "mental health". Some early signs related to mental health difficulties are sleep irritation, lack of energy, lack of appetite, thinking of harming oneself or others, self-isolating, and frequently zoning out.

Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances called pollutants in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. It is also the contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment either by chemical, physical, or biological agents that alters the natural features of the atmosphere. There are many different types of air pollutants, such as gases, particulates, and biological molecules. Air pollution can cause diseases, allergies, and even death to humans; it can also cause harm to other living organisms such as animals and crops, and may damage the natural environment or built environment. Air pollution can be caused by both human activities and natural phenomena.

Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses can be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialties with differing levels of prescription authority. Nurses comprise the largest component of most healthcare environments; but there is evidence of international shortages of qualified nurses. Nurses collaborate with other healthcare providers such as physicians, nurse practitioners, physical therapists, and psychologists. There is a distinction between nurses and nurse practitioners; in the U.S., the latter are nurses with a graduate degree in advanced practice nursing, and are permitted to prescribe medications unlike the former. They practice independently in a variety of settings in more than half of the United States. Since the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.

The Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) and colloquially known as Obamacare, is a landmark U.S. federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama on March 23, 2010. Together with the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 amendment, it represents the U.S. healthcare system's most significant regulatory overhaul and expansion of coverage since the enactment of Medicare and Medicaid in 1965.

Occupational safety and health (OSH) or occupational health and safety (OHS), also known simply as occupational health or occupational safety, is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the safety, health, and welfare of people at work. These terms also refer to the goals of this field, so their use in the sense of this article was originally an abbreviation of occupational safety and health program/department etc. OSH is related to the fields of occupational medicine and occupational hygiene.
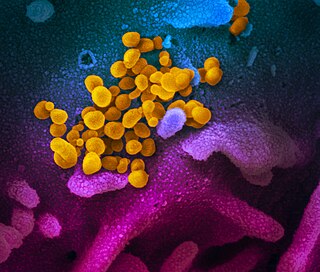
Disease X is a placeholder name that was adopted by the World Health Organization (WHO) in February 2018 on their shortlist of blueprint priority diseases to represent a hypothetical, unknown pathogen that could cause a future epidemic. The WHO adopted the placeholder name to ensure that their planning was sufficiently flexible to adapt to an unknown pathogen. Director of the US National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Anthony Fauci stated that the concept of Disease X would encourage WHO projects to focus their research efforts on entire classes of viruses, instead of just individual strains, thus improving WHO capability to respond to unforeseen strains. In 2020, experts, including some of the WHO's own expert advisors, speculated that COVID-19, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus strain, met the requirements to be the first Disease X.

The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is a global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified in an outbreak in the Chinese city of Wuhan in December 2019, and spread to other areas of Asia and then worldwide in early 2020. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) on 30 January 2020. The WHO ended its PHEIC declaration on 5 May 2023. As of 30 January 2024, the pandemic has caused 774,367,797 cases and 7,020,337 confirmed deaths, ranking it fifth in the list of the deadliest epidemics and pandemics in history.





























