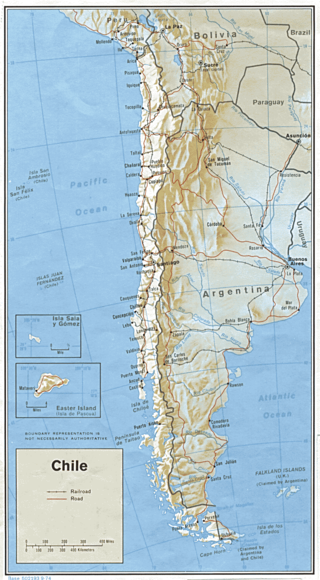
Transport in Chile is mostly by road. The far south of the country is not directly connected to central Chile by road, and water transport also plays a part there. The railways were historically important in Chile, but now play a relatively small part in the country's transport system. Because of the country's geography and long distances between major cities, aviation is also important.

Santiago, also known as Santiago de Chile, is the capital and largest city of Chile and one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is located in the country's central valley and is the center of the Santiago Metropolitan Region, which has a population of 7 million, representing 40% of Chile's total population. Most of the city is situated between 500–650 m (1,640–2,133 ft) above sea level.
The project of the Pan-American highway began approximately in or before 1923. The main idea was to create a network of wide roads that would connect major points of interest in North and South America with a single highway.

Santiago Province is one of the six provinces of the Santiago Metropolitan Region (RM) of central Chile. It encompasses the majority of the population of that region, including 31 of the 36 communities of Greater Santiago. The province spans 2,030.30 km (1,262 mi).

Lampa is a Chilean commune and city in the Chacabuco province, Santiago Metropolitan Region. Lampa is situated near the Chicauma mountain range, part of which was added to the La Campana National Park.

The Spanish motorway (highway) network is the third largest in the world, by length. As of 2019, there are 17,228 km (10,705 mi) of High Capacity Roads in the country. There are two main types of such roads, autopistas and autovías, which differed in the strictness of the standards they are held to.
DR-1 is a dual carriageway highway that forms part of the five designated national highways of the Dominican Republic. DR-1 provides a fast connection between Santo Domingo, the capital, on the southern coast, and the second city Santiago and the rest of the northerly Cibao region, one of the country's main regions.

As the third largest and second most populous country in Latin America, Mexico has developed an extensive transportation network to meet the needs of the economy. As with communications, transportation in Mexico is regulated by the Secretariat of Communications and Transportation, a federal executive cabinet branch.
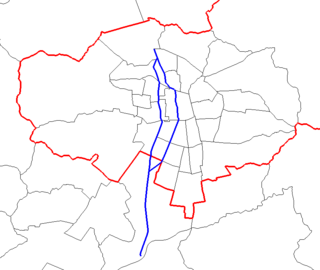
Autopista Central is a privatized, partially submerged highway in Chile forming part of the Ruta 5. It forms part of the urban highway network of Santiago, all of which incorporate a free flow toll system. Out of these highways it is the longest, with a length of 60.5 km (37.6 mi).

Chile Route 68 is a highway in central Chile. It runs 110.21 km (68.48 mi) from Santiago to Valparaíso.

Américo Vespucio Avenue is a 64.8-kilometre (40.3 mi) ring road in Santiago, Chile named after Renaissance cartographer Amerigo Vespucci. Two adjacent sections of the avenue are occupied by Vespucio Norte Express and Vespucio Sur free-flow tolling highways, which are under concession. Vespucio Avenue meets the two largest roundabouts in Santiago, namely Quilín and Grecia, which have circumferences of 793 m and 535 m respectively.
La Granja station is an embanked metro station located on Line 4A of the Santiago Metro in Santiago, Chile. It lies between the Santa Julia and Santa Rosa stations in the commune of the same name, La Granja, and is located along the Autopista Vespucio Sur highway at the junction with Coronel Street. The station was opened on 16 August 2006 as part of the inaugural section of the line between Vicuña Mackenna and La Cisterna.
Autopista San Antonio-Santiago is a toll highway that runs from Santiago, Santiago Metropolitan Region to San Antonio, Valparaíso Region, in central Chile. Its total length in Santiago Metropolitan Region is 85 km (53 mi).
Federal Highway 95D is a toll highway connecting Mexico City to Acapulco, Guerrero. Highway 95D is among the most important toll roads in the country, serving as a backbone for traffic out of Mexico City toward Morelos and tourist destinations in Guerrero.
Federal Highway 15D is the name for toll highways paralleling Federal Highway 15. The toll segments of Highway 15D include some of the most significant highways in the country along the Nogales-Mexico City corridor. The highway is the southern terminus of the CANAMEX Corridor, a trade corridor that stretches from Mexico north across the United States to the Canadian province of Alberta.
Federal Highway 40D is the designation for toll highways paralleling Mexican Federal Highway 40. Highway 40D connects Mazatlán, Sinaloa to Reynosa, Tamaulipas. It forms most of the highway corridor between Mazatlán and Matamoros, Tamaulipas, one of 14 major highway corridors in the country.

The northeastern zone of Santiago de Chile, known as “sector oriente”, refers to the name given to the communes to the east of the Santiago commune, where the majority of the population with the highest income in Chile live. It is made up of the communes of Lo Barnechea, Vitacura, Las Condes, Providencia, La Reina, and Ñuñoa. It had 929,158 inhabitants according to the Chilean census of 2017 added to a large floating population that travels daily to the sector for work, studies or services, especially to Providencia and Las Condes through Providencia Avenue and Apoquindo Avenue, which are the main commercial and transport axis of the city and the continuation of the Alameda from downtown. Together covering the 40% of total motorized journeys in the city. Likewise, in the communal limit of Las Condes, Providencia and Vitacura is located the financial sector of Sanhattan, which has experienced significant growth in high-rise buildings destined mainly for offices and trade.
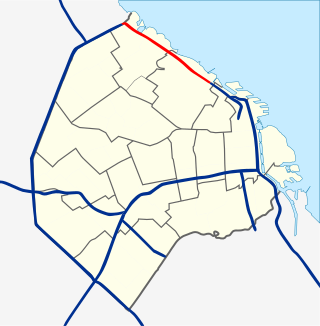
Avenida Leopoldo Lugones, and its southern continuation, Autopista Dr. Arturo Umberto Illia, is a freeway running from Avenida General Paz in the north, which continues to an interchange with National Route 9 and the Paseo del Bajo in the city center. It provides access to Downtown Buenos Aires from the northern suburbs, and from Rosario, Cordoba, and other northern destinations. Due to the lack of a complete bypass of the city, it also connects truck and bus traffic from La Plata to the north. It runs along the east shore of the city, providing access to Aeroparque Jorge Newbery.










