Related Research Articles

Haroutune Krikor Daghlian Jr. was an American physicist with the Manhattan Project, which designed and produced the atomic bombs that were used in World War II. He accidentally irradiated himself on August 21, 1945, during a critical mass experiment at the remote Omega Site of the Los Alamos Laboratory in New Mexico and died 25 days later from the resultant radiation poisoning.
Radiation hardening is the process of making electronic components and circuits resistant to damage or malfunction caused by high levels of ionizing radiation, especially for environments in outer space, around nuclear reactors and particle accelerators, or during nuclear accidents or nuclear warfare.
Turkish Sign Language is the language used by the deaf community in Turkey. As with other sign languages, TİD has a unique grammar that is different from the oral languages used in the region.
Wood River Junction is a small village in the town of Richmond, Rhode Island, Washington County, Rhode Island, in the United States. It is home to the Chariho school district's main campus and is otherwise largely turf farms, which were potato farms before the nuclear accident in 1964.

Ketazolam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.
Dag og Tid is a national weekly newspaper in Norway that uses the Nynorsk standard of the Norwegian language.
TID or tid may refer to:

Remogliflozin etabonate (INN/USAN) is a drug of the gliflozin class for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis ("NASH") and type 2 diabetes. Remogliflozin was discovered by the Japanese company Kissei Pharmaceutical and is currently being developed by BHV Pharma, a wholly owned subsidiary of North Carolina, US-based Avolynt, and Glenmark Pharmaceuticals through a collaboration with BHV. In 2002, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) received a license to use it. From 2002 to 2009, GSK carried out a significant clinical development program for the treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus in various nations across the world and obesity in the UK. Remogliflozin etabonate's pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and clinical dose regimens were characterized in 18 Phase I and 2 Phase II investigations. Due to financial concerns, GSK stopped working on remogliflozin and sergliflozin, two further SGLT2 inhibitors that were licensed to the company, in 2009. Remogliflozin was commercially launched first in India by Glenmark in May 2019.

Albert Stevens (1887–1966), also known as patient CAL-1 and most radioactive human ever, was a house painter from Ohio who was subjected to an involuntary human radiation experiment and survived the highest known accumulated radiation dose in any human. On May 14, 1945, he was injected with 131 kBq of plutonium without his knowledge because it was erroneously believed that he had a terminal disease.

Johan Cullberg was a Swedish professor in psychiatry and psychology, researcher, psychoanalyst, and author of a number of internationally recognised textbooks.
"Wilson" is the tenth episode of the sixth season of House. It aired on Fox on November 30, 2009. In contrast to the usual storylines focused on Gregory House, this episode is centered on James Wilson and a day in his life.
Acotiamide, sold under the brand name Acofide, is a medication manufactured and approved in Japan for the treatment of postprandial fullness, upper abdominal bloating, and early satiation due to functional dyspepsia. It acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.
Tourism Improvement Districts (TIDs) are a type of business improvement district in the United States. The aim of TIDs is increasing the number of overnight visitors using business and services in that area. TIDs are formed through a public–private partnership between the local government and the businesses in a district. TID funds are usually managed by a nonprofit corporation, generally a Convention and Visitors' Bureau, hotel association, or similar destination marketing organization. Typical TID services include marketing programs to raise awareness of the destination, sponsorship of special events that attract overnight visitors, and sales programs to bring in large-group business. Synonymous terms for TIDs include: tourism marketing district, hotel improvement district, and tourism business improvement district.

Gemigliptin (rINN), sold under the brand name Zemiglo, is an oral anti-hyperglycemic agent of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor class of drugs. Glucose lowering effects of DPP-4 inhibitors are mainly mediated by GLP-1 and gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) incretin hormones which are inactivated by DPP-4.
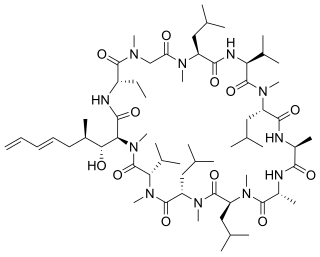
Voclosporin, sold under the brand name Lupkynis, is a calcineurin inhibitor used as an immunosuppressant medication for the treatment of lupus nephritis. It is an analog of ciclosporin that has enhanced action against calcineurin and greater metabolic stability.

Events from the year 1713 in Sweden

BIA 10-2474 is an experimental fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor developed by the Portuguese pharmaceutical company Bial-Portela & Ca. SA. It interacts with the human endocannabinoid system. The drug was in development for the treatment of a range of different medical conditions from anxiety disorder to Parkinson's disease, also for the treatment of chronic pain of multiple sclerosis, cancer, hypertension or the treatment of obesity. A clinical trial with this drug was underway in Rennes, France, in January 2016, in which serious adverse events occurred affecting five participants, including the death of one man. The underlying mechanism that caused the acute neurotoxicity of this molecule remains unknown.

COVID-19 vaccination in Switzerland is an ongoing immunization campaign against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), in response to the ongoing pandemic in the country.
On 29 January 2021, Algeria launched a COVID-19 vaccination campaign, a day after receiving its first shipment of 50,000 doses of the Russia's Sputnik V vaccine. As of 6 June 2021, around 2.5 million doses have been administered. Algeria is currently vaccinating its population with both Sputnik V and Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccines.
The COVID-19 vaccination campaign in Quebec was a provincial effort to distribute and administer vaccines against COVID-19.
References
- ↑ "Dosing: BID, TID". Global Antibiotic Research & Development Partnership.
Depending on the drug class and its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties, different dosing regimens may be optimal, including once a day (omne in die, OD), twice a day (bis in die, BID) or three times a day (ter in die, TID).