
Micronesia is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Polynesia to the east, and Melanesia to the south—as well as with the wider community of Austronesian peoples.
Nauru, officially the Republic of Nauru and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in Micronesia, part of Oceania in the Central Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba of Kiribati, about 300 km (190 mi) to the east.

The history of human activity in Nauru, an island country in the Pacific Ocean, began roughly 3,000 years ago when clans settled the island.

The demographics of Nauru, an island country in the Pacific Ocean, are known through national censuses, which have been analysed by various statistical bureaus since the 1920s. The Nauru Bureau of Statistics have conducted this task since 1977—the first census since Nauru gained independence in 1968. The most recent census of Nauru was on 30 October 2021, when population had reached 11,680 people. The population density is 554 inhabitants per square kilometre, and the overall life expectancy is 63.9 years. The population rose steadily from the 1960s until 2006 when the Government of Nauru repatriated thousands of Tuvaluan and I-Kiribati workers from the country. Since 1992, Nauru's birth rate has exceeded its death rate; the natural growth rate is positive. In terms of age structure, the population is dominated by the 15–59-year-old segment (57%). The median age of the population is 21.6, and the estimated gender ratio of the population is 101.8 males per 100 females.

Yaren is a district of the Pacific island country of Nauru. It is the de facto capital of Nauru and is coextensive with Yaren Constituency.

Nauru, following independence from the United Kingdom, became a sovereign, independent republic on 31 January 1968. Nauru has established diplomatic relations with a number of nations, including most of its Pacific neighbors with which it maintains economic, cultural and administrative ties.

The president of Nauru is elected by Parliament from among its members, and is both the head of state and the head of government of Nauru. Nauru's unicameral Parliament has 19 members, with an electoral term of three years. Political parties only play a minor role in Nauru politics, and there have often been periods of instability in the Presidential office. Shifting allegiances among a small number of individuals can lead to frequent changes in the makeup of the government of the day, including the presidential position itself.

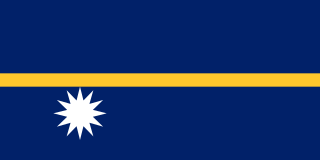
Following the independence of Nauru, the flag of Nauru was raised for the first time. The flag, chosen in a local design competition, was adopted on independence day, 31 January 1968. The design symbolically depicts Nauru's geographical position, with a star just south of the Equator.

The displacement of the traditional culture of Nauru by contemporary western influences is evident on the island. Little remains from the old customs. The traditions of arts and crafts are nearly lost.

Arthur Charles Hamilton-Gordon, 1st Baron Stanmore was a Scottish Liberal Party politician and colonial administrator. He had extensive contact with Prime Minister William Ewart Gladstone.

The Manusela or Wahai people has a population of over 10,100 centered in the Manusela mountains of North Seram, Maluku, Indonesia. They are also found along Teluti Bay in south Seram, which suggests their name of their tribe.

The first colonies of the British Empire on the continent of Australia were the penal colony of New South Wales, founded in 1788, and the Swan River Colony, founded in 1829. Over the next few decades, the colonies of New Zealand, Queensland, South Australia, Van Diemen's Land, and Victoria were created from New South Wales, as well as an aborted Colony of North Australia. On 1 January 1901, these colonies, excepting New Zealand, became states in the Commonwealth of Australia. Since federation, the internal borders have remained mostly stable, except for the creation of some territories with limited self-government: the Northern Territory from South Australia, to govern the vast, sparsely populated centre of the country; the split of the Northern Territory into Central Australia and North Australia, and then the quick merger of those back into the Northern Territory; and the Australian Capital Territory, a federal district ceded from New South Wales.

Christianity is the largest religion in Nauru, with Nauru Congregational Church being the largest denomination, encompassing 35.71% of the population as of the 2011 census.

Nauru–Russia relations are the bilateral relations between Nauru and Russia. Russia is represented in Nauru through its embassy in Canberra (Australia).

Visitors to Nauru must obtain a visa unless they come from one of the countries eligible for free visa on arrival. All visitors must hold a passport valid for 3 months. Transit visas are not required if the connecting flight leaves within three hours of arrival in Nauru. Business visitors must have a local sponsor.

India–Nauru relations are the international relations that exist between India and Nauru. These have been established since the island's independence in 1968.

Nauru-United States relations are the bilateral relations of Nauru and the United States The U.S. has no consular or diplomatic offices in Nauru. Officers of the American Embassy in Suva, Fiji, are concurrently accredited to Nauru and make periodic visits.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Nauru is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The virus was confirmed to have reached Nauru on 2 April 2022.

Russ Joseph Kun is a Nauruan politician who served as President of Nauru from being elected in the 2022 presidential election to October 2023. He has served as a member of parliament for Ubenide since 2013.