Related Research Articles

The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium and France. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north. It is more than 970 kilometres (600 mi) long and 580 kilometres (360 mi) wide, covering 570,000 square kilometres (220,000 sq mi).

An oil platform is a large structure with facilities to extract and process petroleum and natural gas that lie in rock formations beneath the seabed. Many oil platforms will also have facilities to accommodate the workers, although it is also common to have a separate accommodation platform linked by bridge to the production platform. Most commonly, oil platforms engage in activities on the continental shelf, though they can also be used in lakes, inshore waters, and inland seas. Depending on the circumstances, the platform may be fixed to the ocean floor, consist of an artificial island, or float. In some arrangements the main facility may have storage facilities for the processed oil. Remote subsea wells may also be connected to a platform by flow lines and by umbilical connections. These sub-sea facilities may include one or more subsea wells or manifold centres for multiple wells.

The Timor Sea is a relatively shallow sea in the Indian Ocean bounded to the north by the island of Timor with Timor-Leste to the north, Indonesia to the northwest, Arafura Sea to the east, and to the south by Australia. The Sunda Trench marks the deepest point of the Timor Sea with a depth of more than 3300 metres, separating the continents of Oceania in the southeast and Asia to the northwest and north. The Timor sea is prone to earthquakes and tsunamis north of the Sunda Trench, due to its location on the Ring of Fire as well as volcanic activity and can experience major cyclones, due to the proximity from the Equator.

North Sea oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons, comprising liquid petroleum and natural gas, produced from petroleum reservoirs beneath the North Sea.
Ørsted A/S is a Danish multinational energy company. Headquartered in Fredericia, Denmark, Ørsted is the largest energy company in Denmark. The company adopted its current name on 6 November 2017. It was previously known as DONG.

China Petroleum and Chemical Corporation, or Sinopec, is a Chinese oil and gas enterprise based in Beijing. It is listed in Hong Kong and also trades in Shanghai.

Eni S.p.A. is an Italian multinational energy company headquartered in Rome. It is considered one of the "supermajor" oil companies in the world, with a market capitalization of €50 billion, as of 31 December 2023. The Italian government owns a 30.33% golden share in the company, 4.37% held through the Ministry of Economy and Finance and 25.96% through the Cassa Depositi e Prestiti. The company is a component of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index.
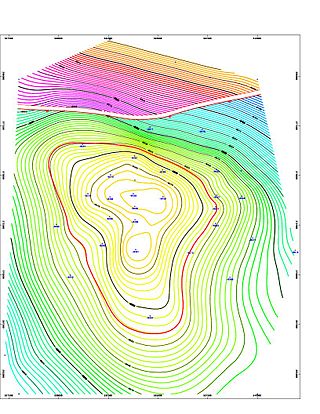
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations. Such reservoirs form when kerogen is created in surrounding rock by the presence of high heat and pressure in the Earth's crust.

Asaluyeh is a city in the Central District of Asaluyeh County, Bushehr province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. It also serves as the administrative center for Asaluyeh Rural District.
Nord Stream is a pair of offshore natural gas pipelines in Europe that run under the Baltic Sea from Russia to Germany. It comprises the Nord Stream 1 (NS1) pipeline running from Vyborg in northwestern Russia, near Finland, and the Nord Stream 2 (NS2) pipeline running from Ust-Luga in northwestern Russia near Estonia. Both pipelines run to Lubmin in the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Each pipeline comprises two pipes, denoted A and B; each of the four pipes is approximately 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) long and with approximate diameters of 1,220 millimetres (48 in). The combined capacity of the four pipes is 110 billion cubic metres per annum of natural gas.
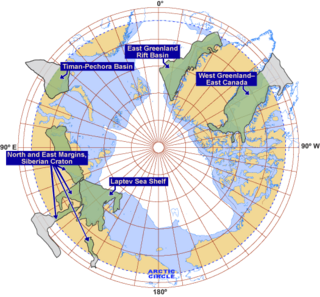
Exploration for petroleum in the Arctic is expensive and challenging both technically and logistically. In the offshore, sea ice can be a major factor. There have been many discoveries of oil and gas in the several Arctic basins that have seen extensive exploration over past decades but distance from existing infrastructure has often deterred development. Development and production operations in the Arctic offshore as a result of exploration have been limited, with the exception of the Barents and Norwegian seas. In Alaska, exploration subsequent to the discovery of the Prudhoe Bay oilfield has focussed on the onshore and shallow coastal waters.
As of 2017, Azerbaijan produced a range of metals and industrial minerals, including aluminum, bentonite, copper, gold, iodine, limestone, silver, and steel.

The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake and sometimes referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau. It covers a surface area of 371,000 km2 (143,000 sq mi), an area approximately equal to that of Japan, with a volume of 78,200 km3 (19,000 cu mi). It has a salinity of approximately 1.2%, about a third of the salinity of average seawater. It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the southwest, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast.
The Tamar gas field is a natural gas field in the Mediterranean Sea off the coast of Israel. The field is located in Israel's exclusive economic zone, roughly 80 kilometres (50 mi) west of Haifa in waters 1,700 metres (5,600 ft) deep. The Tamar field is considered to have proven reserves of 200 billion cubic metres of natural gas, while the adjoining Tamar South field has 23 billion cubic metres. Together, they may have an additional 84 BCM of "probable" reserves and up to 49 BCM of "possible" reserves. At the time of discovery, Tamar was the largest find of gas or oil in the Levant basin of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea and the largest discovery by Noble Energy. Since Tamar's discovery, large gas discoveries have been made in other analogous geological formations dating back to the Oligocene–Miocene epoch in the Levant basin. Because Tamar was the first such discovery, these gas containing presalt formations have become collectively known as Tamar sands.

The oil and gas industry plays a central role in the economy of the United Kingdom. Oil and gas account for more than three-quarters of the UK's total primary energy needs. Oil provides 97 per cent of the fuel for transport, and gas is a key fuel for heating and electricity generation. Transport, heating and electricity each account for about one-third of the UK's primary energy needs. Oil and gas are also major feedstocks for the petrochemicals industries producing pharmaceuticals, plastics, cosmetics and domestic appliances.
The Leviathan gas field is a large natural gas field in the Mediterranean Sea off the coast of Israel, 47 kilometres (29 mi) south-west of the Tamar gas field. The gas field is roughly 130 kilometres (81 mi) west of Haifa in waters 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) deep in the Levantine basin, a rich hydrocarbon area in one of the largest offshore natural gas field finds. According to some commentators, the gas find has the potential to change Israel's foreign relations with neighboring countries, including Turkey, and Egypt. Together with the nearby Tamar gas field, the Leviathan field is seen as an opportunity for Israel to achieve energy independence in the Middle East.

China National Offshore Oil Corporation, or CNOOC Group, is the third-largest national oil company in China, after CNPC and China Petrochemical Corporation. The CNOOC Group focuses on the exploitation, exploration and development of crude oil and natural gas in offshore China, along with its subsidiary COOEC.

PetroSA is the national oil and gas company (NOC) of South Africa. Its main activities are the extraction of natural gas from offshore fields about 89 km from Mossel Bay, the production of synthetic fuels from this gas through a gas to liquids (GTL) process, and the extraction of crude oil from oil fields off the South Coast of South Africa. The GTL Refinery is located in Mossel Bay. Its capacity is about 45 000 bpd and processes both the gas and condensate to produce liquid fuels and chemicals. The company is also involved in the exploration for and development of new sources of oil and gas.
The oil industry in Poland began at Bóbrka Field in 1853, followed by the first refinery in 1854. Poland was the third most productive region in the world in 1900. It now has only a small, mostly state-owned component, with production from its Permian Basin in the west, small and very old fields in the Carpathians in the south, and offshore in the Baltic Sea. For natural gas the country is almost completely dependent on legacy pipelines from the former Soviet Union.
B8 is a major oil field in the Polish exclusive economic area of the Baltic Sea about 70 km north of Jastarnia. The field was discovered in 1983 and started producing oil in 2006. The field currently accounts for four per cent of Poland’s oil production.
References
- ↑ "The Paleozoic Hydrocarbon System in the Gotland Basin (Central Baltic Sea) Leaks" . Retrieved 9 December 2023.
- ↑ "Final Report on Prospective Sites for the Geological Storage of CO2 in the Southern Baltic Sea" (PDF). Retrieved 9 December 2023.
- ↑ "Kaliningrad region: Main directions and priorities of oil and gas complex development". 16 October 2017. Retrieved 9 December 2023.
- ↑ "Baltic Gas Project, Southern Baltic Sea" . Retrieved 9 December 2023.
- ↑ "The Baltic Sea: Europe's Forgotten $80 Billion Oil Play?" . Retrieved 9 December 2023.
- ↑ "Global Energy Monitor B21 gas field (Poland)" . Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ↑ Mihkel Veiderma (2005) ‘Natural gas in the Baltic region' given at the Assembly of the Baltic States, 26 November 2005