
The lesser spotted woodpecker is a member of the woodpecker family Picidae. It was formerly assigned to the genus Dendrocopos. Some taxonomic authorities continue to list the species there.

Asterias is a genus of the Asteriidae family of sea stars. It includes several of the best-known species of sea stars, including the (Atlantic) common starfish, Asterias rubens, and the northern Pacific seastar, Asterias amurensis. The genus contains a total of eight species in all. All species have five arms and are native to shallow oceanic areas of cold to temperate parts of the Holarctic. These starfish have planktonic larvae. Asterias amurensis is an invasive species in Australia and can in some years become a pest in the Japanese mariculture industry.

Beneficial insects are any of a number of species of insects that perform valued services like pollination and pest control. The concept of beneficial is subjective and only arises in light of desired outcomes from a human perspective. In agriculture, where the goal is to raise selected crops, insects that hinder the production process are classified as pests, while insects that assist production are considered beneficial. In horticulture and gardening, beneficial insects are often considered those that contribute to pest control and native habitat integration.

Pentatomidae is a family of insects belonging to the order Hemiptera, generally called shield bugs or stink bugs. Pentatomidae is the largest family in the superfamily Pentatomoidea, and contains around 900 genera and over 4700 species. As hemipterans, the pentatomids have piercing sucking mouthparts, and most are phytophagous, including several species which are severe pests on agricultural crops. However, some species, particularly in the subfamily Asopinae, are predatory and may be considered beneficial.
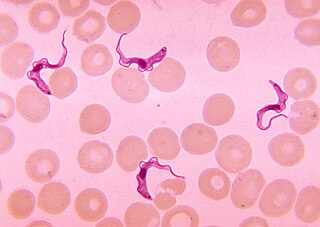
Trypanosoma is a genus of kinetoplastids, a monophyletic group of unicellular parasitic flagellate protozoa. Trypanosoma is part of the phylum Sarcomastigophora. The name is derived from the Greek trypano- (borer) and soma (body) because of their corkscrew-like motion. Most trypanosomes are heteroxenous and most are transmitted via a vector. The majority of species are transmitted by blood-feeding invertebrates, but there are different mechanisms among the varying species. Some, such as Trypanosoma equiperdum, are spread by direct contact. In an invertebrate host they are generally found in the intestine, but normally occupy the bloodstream or an intracellular environment in the vertebrate host.

Scutelleridae is a family of true bugs. They are commonly known as jewel bugs or metallic shield bugs due to their often brilliant coloration. They are also known as shield-backed bugs due to the enlargement of the thoracic scutellum into a continuous shield over the abdomen and wings. This latter characteristic distinguishes them from most other families within Heteroptera, and may lead to misidentification as a beetle rather than a bug. These insects feed on plant juices from a variety of different species, including some commercial crops. Closely related to stink bugs, they may also produce an offensive odour when disturbed. There are around 450 species worldwide.

The Miridae are a large and diverse insect family at one time known by the taxonomic synonym Capsidae. Species in the family may be referred to as capsid bugs or "mirid bugs". Common names include plant bugs, leaf bugs, and grass bugs. It is the largest family of true bugs belonging to the suborder Heteroptera; it includes over 10,000 known species, and new ones are being described constantly. Most widely known mirids are species that are notorious agricultural pests that pierce plant tissues, feed on the sap, and sometimes transmit viral plant diseases. Some species however, are predatory.

Belostomatidae is a family of freshwater hemipteran insects known as giant water bugs or colloquially as toe-biters, Indian toe-biters, electric-light bugs, alligator ticks, or alligator fleas. They are the largest insects in the order Hemiptera. There are about 170 species found in freshwater habitats worldwide, with more than 110 in the Neotropics, more than 20 in Africa, almost as many in the Nearctic, and far fewer elsewhere. These predators are typically encountered in freshwater ponds, marshes and slow-flowing streams. Most species are at least 2 cm (0.8 in) long, although smaller species, down to 0.9 cm (0.35 in), also exist. The largest are members of the genus Lethocerus, which can exceed 12 cm (4.5 in) and nearly reach the length of some of the largest beetles in the world. Giant water bugs are a popular food in parts of Asia.

The Amur falcon is a small raptor of the falcon family. It breeds in south-eastern Siberia and Northern China before migrating in large flocks across India and over the Arabian Sea to winter in Southern and East Africa.

Rana amurensis is a species of true frog found in northern Asia. It ranges across western Siberia, as well as northeastern China, northeastern Mongolia, and on the northern Korean Peninsula and on Sakhalin. Rana coreana was previously included in this species as a subspecies. Found at latitudes up to 71° N, it is the northernmost wild amphibian species.
Entomological warfare (EW) is a type of biological warfare that uses insects to interrupt supply lines by damaging crops, or direct harm to enemy combatants and civilian populations. There have been several programs which have attempted to institute this methodology; however, there has been limited application of entomological warfare against military or civilian targets, Japan being the only state known to have verifiably implemented the method against another state, namely the Chinese during World War II. However, EW was used more widely in antiquity, in order to repel sieges or cause economic harm to states. Research into EW was conducted during both World War II and the Cold War by numerous states such as the Soviet Union, United States, Germany and Canada. There have also been suggestions that it could be implemented by non-state actors in a form of bioterrorism. Under the Biological and Toxic Weapons Convention of 1972, use of insects to administer agents or toxins for hostile purposes is deemed to be against international law.

The Korean brown frog is a species of frog in the genus Rana. It is native to the Korean Peninsula and Shandong, China.
In the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, Carl Linnaeus classified the arthropods, including insects, arachnids and crustaceans, among his class "Insecta". True bugs and thrips were brought together under the name Hemiptera.

Carpocoris purpureipennis is a species of shield bug of the family Pentatomidae, subfamily Pentatominae.

Syneta is a genus of leaf beetles in the subfamily Synetinae. There are about 11 described species in Syneta. The genus is entirely holarctic in distribution, with species appearing in North America, Siberia, East Asia and Northern Europe.

Oebalus pugnax, the rice stink bug, is a flying insect in the shield bug family Pentatomidae native to North America that has become a major agricultural pest in the Southern United States. It has been a known pest since at least the time of Johan Christian Fabricius, who described the species in 1775.

The forest shield bug is a species of shield bugs endemic to New Zealand. Forest shield bug nymphs prefer feeding on grasses, while adults will eat a variety of New Zealand plants including "hard-leaved" plants like rimu. O. vittatus was one of the first insects from New Zealand to be described by a European scientist.



















