Related Research Articles
Fibre Channel (FC) is a high-speed data transfer protocol providing in-order, lossless delivery of raw block data. Fibre Channel is primarily used to connect computer data storage to servers in storage area networks (SAN) in commercial data centers.

Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. The term "NAS" can refer to both the technology and systems involved, or a specialized device built for such functionality.

The Symmetrix system was an EMC's enterprise storage array. It combined dozens of hard drives into a single virtual device that was then directly attached to a computer or I/O channel, or shared on a storage area network or a local area network. It was the flagship product of EMC in the 1990s and 2000s.
A World Wide Name (WWN) or World Wide Identifier (WWID) is a unique identifier used in storage technologies including Fibre Channel, Parallel ATA, Serial ATA, SCSI and Serial Attached SCSI (SAS).
NetApp, Inc. is an American data infrastructure company that provides unified data storage, integrated data services, and cloud operations (CloudOps) solutions to enterprise customers. The company is based in Cork City, Ireland. It has ranked in the Fortune 500 from 2012 to 2021. Founded in 1992 with an initial public offering in 1995, NetApp offers cloud data services for management of applications and data both online and physically.

In the computer storage field, a Fibre Channel switch is a network switch compatible with the Fibre Channel (FC) protocol. It allows the creation of a Fibre Channel fabric, that is the core component of a storage area network (SAN). The fabric is a network of Fibre Channel devices which allows many-to-many communication, device name lookup, security, and redundancy. FC switches implement zoning, a mechanism that disables unwanted traffic between certain fabric nodes.
FICON is the IBM proprietary name for the ANSI FC-SB-3 Single-Byte Command Code Sets-3 Mapping Protocol for Fibre Channel (FC) protocol. It is a FC layer 4 protocol used to map both IBM's antecedent channel-to-control-unit cabling infrastructure and protocol onto standard FC services and infrastructure. The topology is fabric utilizing FC switches or directors. Valid rates include 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32 Gigabit per second data rates at distances up to 100 km.
In storage area networking, Fabric OS (FOS) is the firmware for Brocade Communications Systems's Fibre Channel switches and Fibre Channel directors.
Brocade Communications Systems, Inc., was an American technology company specializing in storage networking products, now a subsidiary of Broadcom Inc. The company is known for its Fibre Channel storage networking products and technology. Prior to the acquisition, the company expanded into adjacent markets including a wide range of IP/Ethernet hardware and software products. Offerings included routers and network switches for data center, campus and carrier environments, IP storage network fabrics; Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) and software-defined networking (SDN) markets such as a commercial edition of the OpenDaylight Project controller; and network management software that spans physical and virtual devices.
Connectrix is the family name for EMC Corporation's brand of storage area network (SAN) switches. EMC does not manufacture any of these devices, instead they rebadge several other brands.
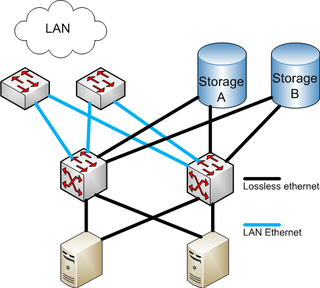
Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is a computer network technology that encapsulates Fibre Channel frames over Ethernet networks. This allows Fibre Channel to use 10 Gigabit Ethernet networks while preserving the Fibre Channel protocol. The specification was part of the International Committee for Information Technology Standards T11 FC-BB-5 standard published in 2009. FCoE did not see widespread adoption.

A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage. A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN).
Data center bridging (DCB) is a set of enhancements to the Ethernet local area network communication protocol for use in data center environments, in particular for use with clustering and storage area networks.

Fabric computing or unified computing involves constructing a computing fabric consisting of interconnected nodes that look like a weave or a fabric when seen collectively from a distance.
EMC VPLEX is a virtual computer data storage product introduced by EMC Corporation in May 2010. VPLEX implements a distributed "virtualization" layer within and across geographically disparate Fibre Channel storage area networks and data centers.
Virtual Cluster Switching (VCS) fabric technology is a Layer 2 proprietary Ethernet technology from Brocade Communications Systems, later acquired by Extreme Networks. It is designed to improve network utilization, maximize application availability, increase scalability, and simplify the network architecture in virtualized data centers.
Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) is a data center server computer product line composed of server hardware, virtualization support, switching fabric, and management software, introduced in 2009 by Cisco Systems. The products are marketed for scalability by integrating many components of a data center that can be managed as a single unit.
RecoverPoint is a continuous data protection product offered by Dell EMC which supports asynchronous and synchronous data replication of block-based storage. RecoverPoint was originally created by a company called Kashya, which was bought by EMC in 2006.
Object storage is a computer data storage approach that manages data as "blobs" or "objects", as opposed to other storage architectures like file systems, which manage data as a file hierarchy, and block storage, which manages data as blocks within sectors and tracks. Each object is typically associated with a variable amount of metadata, and a globally unique identifier. Object storage can be implemented at multiple levels, including the device level, the system level, and the interface level. In each case, object storage seeks to enable capabilities not addressed by other storage architectures, like interfaces that are directly programmable by the application, a namespace that can span multiple instances of physical hardware, and data-management functions like data replication and data distribution at object-level granularity.

Nexenta by DDN, Inc., is a subsidiary of DataDirect Networks that sells computer data storage and backup software. It is headquartered in San Jose, California. Nexenta developed NexentaStor, NexentaCloud, NexentaFusion, and NexentaEdge. It was founded as Nexenta Systems, Inc., in 2005.
References
- ↑ "Brocade Network Advisor". docs.vistanet.jp. Retrieved 2025-01-21.