This glossary of climate change is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to climate change, global warming, and related topics.
RWE AG is a German multinational energy company headquartered in Essen. It generates and trades electricity in the Asia-Pacific region, Europe and the United States.

Palcacocha is a glacier lake in the Andes mountain range of South America in northwestern Peru located in the Ancash Region, Huaraz Province.
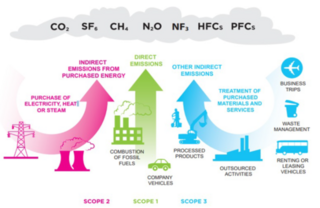
Carbon accounting is a framework of methods to measure and track how much greenhouse gas (GHG) an organization emits. It can also be used to track projects or actions to reduce emissions in sectors such as forestry or renewable energy. Corporations, cities and other groups use these techniques to help limit climate change. Organizations will often set an emissions baseline, create targets for reducing emissions, and track progress towards them. The accounting methods enable them to do this in a more consistent and transparent manner.
Massachusetts v. Environmental Protection Agency, 549 U.S. 497 (2007), is a 5–4 U.S. Supreme Court case in which Massachusetts, along with eleven other states and several cities of the United States, represented by James Milkey, brought suit against the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) represented by Gregory G. Garre to force the federal agency to regulate the emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases (GHGs) that pollute the environment and contribute to climate change.

Climate of Peru describes the diverse climates of this large South American country with an area of 1,285,216 km2 (496,225 sq mi). Peru is located entirely in the tropics but features desert and mountain climates as well as tropical rainforests. Elevations above sea level in the country range from −37 to 6,778 m and precipitation ranges from less than 20 mm (0.79 in) annually to more than 8,000 mm (310 in). There are three main climatic regions: the Pacific Ocean coast is one of the driest deserts in the world but with some unique features; the high Andes mountains have a variety of microclimates depending on elevation and exposure and with temperatures and precipitation from temperate to polar and wet to dry; and the Amazon basin has tropical climates, mostly with abundant precipitation, along with sub-tropical climates in elevations above 1,550 m (5,090 ft).
The Investor Network on Climate Risk (INCR) is a nonprofit organization of investors and financial institutions that promotes better understanding of the financial risks and investment opportunities posed by climate change. INCR is coordinated by Ceres, a coalition of investors and environmental groups working to advance sustainable prosperity.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person.

Kivalina v. ExxonMobil Corp., No. 4:08-cv-01138, is a lawsuit filed on February 26, 2008, in a United States district court. The suit, based on the common law theory of nuisance, claims monetary damages from the energy industry for the destruction of Kivalina, Alaska by flooding caused by climate change. The damage estimates made by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and the Government Accountability Office are placed between $95 million and $400 million. This lawsuit is an example of greenhouse gas emission liability.
American Electric Power Company v. Connecticut, 564 U.S. 410 (2011), was a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court, in an 8–0 decision, held that corporations cannot be sued for greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs) under federal common law, primarily because the Clean Air Act (CAA) delegates the management of carbon dioxide and other GHG emissions to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Brought to court in July 2004 in the Southern District of New York, this was the first global warming case based on a public nuisance claim.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) began regulating greenhouse gases (GHGs) under the Clean Air Act from mobile and stationary sources of air pollution for the first time on January 2, 2011. Standards for mobile sources have been established pursuant to Section 202 of the CAA, and GHGs from stationary sources are currently controlled under the authority of Part C of Title I of the Act. The basis for regulations was upheld in the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia in June 2012.

Climate change has resulted in an increase in temperature of 2.3 °C (4.14 °F) (2022) in Europe compared to pre-industrial levels. Europe is the fastest warming continent in the world. Europe's climate is getting warmer due to anthropogenic activity. According to international climate experts, global temperature rise should not exceed 2 °C to prevent the most dangerous consequences of climate change; without reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, this could happen before 2050. Climate change has implications for all regions of Europe, with the extent and nature of impacts varying across the continent.

Climate change in Pakistan is a major issue for the country. Pakistan is highly vulnerable to climate change. As with the changing climate in South Asia as a whole, the climate of Pakistan has changed over the past several decades, with significant impacts on the environment and people. In addition to increased heat, drought and extreme weather in parts of the country, the melting of glaciers in the Himalayas has impacted some of the important rivers of Pakistan. Between 1999 and 2018, Pakistan ranked 5th in the countries affected by extreme weather caused by climate change.

The California Global Warming Solutions Act of 2016: emissions limit, or SB-32, is a California Senate bill expanding upon AB-32 to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. The lead author is Senator Fran Pavley and the principal co-author is Assemblymember Eduardo Garcia. SB-32 was signed into law on September 8, 2016, by Governor Jerry Brown. SB-32 sets into law the mandated reduction target in GHG emissions as written into Executive Order B-30-15.
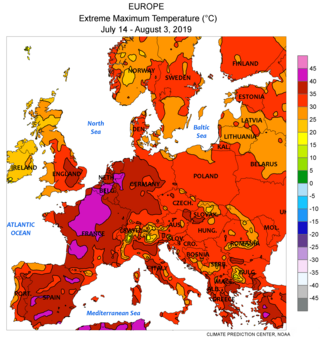
In France, climate change has caused some the greatest annual temperature increases registered in any country in Europe. The 2019 heat wave saw record temperatures of 46.0 °C. Heat waves and other extreme weather events are expected to increase with continued climate change. Other expected environmental impacts include increased floods due to both sea level rise and increased glacier melt. These environmental changes will lead to shifts in ecosystems and affect local organisms. Climate change will also cause economic losses in France, particularly in the agriculture and fisheries sectors.

Climate change litigation, also known as climate litigation, is an emerging body of environmental law using legal practice to set case law precedent to further climate change mitigation efforts from public institutions, such as governments and companies. In the face of slow climate change politics delaying climate change mitigation, activists and lawyers have increased efforts to use national and international judiciary systems to advance the effort. Climate litigation typically engages in one of five types of legal claims: Constitutional law, administrative law, private law (challenging corporations or other organizations for negligence, nuisance, etc., fraud or consumer protection, or human rights.

State of the Netherlands v Urgenda Foundation (2019) is climate change litigation heard by the Supreme Court of the Netherlands related to government efforts to curtail carbon dioxide emissions. The case was brought against the Dutch government in 2013, arguing the government, by not meeting a minimum carbon dioxide emission-reduction goal established by scientists to avert harmful climate change, was endangering the human rights of Dutch citizens as set by national and European Union laws.

Milieudefensie v Royal Dutch Shell (2021) is a human rights law and tort law case heard by the district court of The Hague in the Netherlands in 2021 related to efforts by several NGO's to curtail carbon dioxide emissions by multinational corporations. It was brought by the Dutch branch of Friends of the Earth and a group of other NGO's against the oil corporation, Shell plc. In May 2021, the court ordered Shell to reduce its global carbon emissions from its 2019 levels by 45% by 2030, relating not only to the emissions from its operations, but also those from the products it sells. It is considered to be the first major climate change litigation ruling against a corporation.
Neubauer v Germany 1 BvR 2656/18 is a landmark German constitutional law case, concerning the duty of the German federal government to take action to prevent climate damage.

Smith v Fonterra Co-Operative Group Ltd [2024] NZSC 5 is a landmark New Zealand tort law case, concerning liability of major fossil fuel polluters for climate damage. The NZ Supreme Court held that polluting companies could be liable in tort to pay damages from global warming and rising sea levels to people whose coastal property is damaged, overturning courts below.












