Related Research Articles

County Dublin is a county in Ireland, and holds its capital city, Dublin. It is located on the island's east coast, within the province of Leinster. Until 1994, County Dublin was a single local government area; in that year, the county council was divided into three new administrative counties: Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, Fingal and South Dublin. The three administrative counties together with Dublin City proper form a NUTS III statistical region of Ireland. County Dublin remains a single administrative unit for the purposes of the courts and Dublin County combined with Dublin City forms the Judicial County of Dublin, including Dublin Circuit Court, the Dublin County Registrar and the Dublin Metropolitan District Court). Dublin also sees law enforcement and fire services administered county-wide.
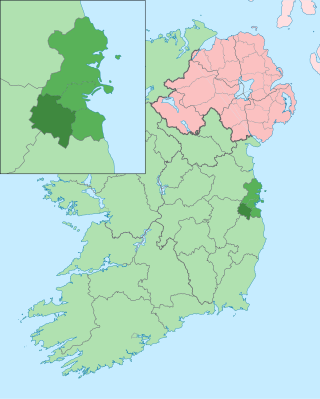
South Dublin is a county in Ireland, within the province of Leinster and the Eastern and Midland Region. It is one of three successor counties to County Dublin, which was disestablished for administrative purposes in 1994. South Dublin County Council is the local authority for the county. The county contains both dense suburbs of Dublin and stretches of unpopulated mountains. In 2022 it had a population of 301,705, making it the fourth most populous county in the state.
Dublin County Council was a local authority for the administrative county of County Dublin in Ireland.

Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and the Eastern and Midland Region. It is one of three successor counties to County Dublin, which was disestablished in 1994. It is named after the former borough of Dún Laoghaire and the barony of Rathdown. Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown County Council is the local authority for the county. The population of the county was 233,860 at the time of the 2022 census.
A municipal borough was a type of local government district which existed in England and Wales between 1836 and 1974, in Northern Ireland from 1840 to 1973 and in the Republic of Ireland from 1840 to 2002. Broadly similar structures existed in Scotland from 1833 to 1975 with the reform of royal burghs and creation of police burghs.

The Greater Dublin Area, or simply Greater Dublin, is an informal term that is taken to include the city of Dublin and its hinterland, with varying definitions as to its extent. At the expansive end, it has been defined as including all of the traditional County Dublin and three neighbouring counties, while more commonly it is taken as the contiguous metropolitan area of Dublin plus suburban and commuter towns. The area is defined for strategic planning, and, for example, transport, and it is not a formal administrative or political unit.

The functions of local government in the Republic of Ireland are mostly exercised by thirty-one local authorities, termed County, City, or City and County Councils. The principal decision-making body in each of the thirty-one local authorities is composed of the members of the council, elected by universal franchise in local elections every five years from multi-seat local electoral areas using the single transferable vote. Many of the authorities' statutory functions are, however, the responsibility of ministerially appointed career officials termed Chief executives. The competencies of the city and county councils include planning, transport infrastructure, sanitary services, public safety and the provision of public libraries. Each local authority sends representatives to one of three Regional Assemblies.

The Borough of Dún Laoghaire was a borough on the southern coast of County Dublin, Ireland from 1930 to 1994. Its local authority was the Corporation of Dún Laoghaire.

Cavan County Council is the authority responsible for local government in County Cavan, Ireland. As a county council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. The council is responsible for housing and community, roads and transportation, urban planning and development, amenity and culture, and environment. The council has 18 elected members. Elections are held every five years and are by single transferable vote. The head of the council has the title of Cathaoirleach (chairperson). The county administration is headed by a chief executive, Tommy Ryan. The county town is Cavan.

Carlow County Council is the local authority of County Carlow, Ireland. As a county council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. The council is responsible for housing and community, roads and transportation, urban planning and development, amenity and culture, and environment. The council has 18 elected members. The head of the council has the title of Cathaoirleach (chairperson). The county administration is headed by a chief executive, Kathleen Holohan. The county town is Carlow.

Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown County Council is the local authority of the county of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, Ireland. It is one of three local authorities that succeeded the former Dublin County Council on its abolition on 1 January 1994 and one of four councils in the old County Dublin. As a county council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. The council is responsible for housing and community, roads and transportation, urban planning and development, amenity and culture, and environment. The council has 40 elected members. Elections are held every five years and are by single transferable vote. The head of the council has the title of Cathaoirleach (chairperson). The county administration is headed by a chief executive, Frank Curran. The county town is Dún Laoghaire. It serves a population of approximately 206,260.
Dublin Townships was a parliamentary constituency represented in Dáil Éireann, the lower house of the Irish parliament or Oireachtas from 1937 to 1948. The constituency elected 3 deputies to the Dáil, using proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote (PR-STV).
Dún Laoghaire and Rathdown was a parliamentary constituency represented in Dáil Éireann, the lower house of the Irish parliament or Oireachtas from 1948 to 1977. The constituency elected 3 deputies to the Dáil, on the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote (PR-STV).

Fingal County Council is the local authority of the county of Fingal, Ireland. It is one of three local authorities that succeeded the former Dublin County Council on abolition on 1 January 1994 and is one of four local authorities in County Dublin. As a county council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. The council is responsible for housing and community, roads and transport, urban planning and development, amenity and culture, and environment. The council has 40 elected members. Elections are held every five years on the electoral system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote (PR-STV). The head of the council has the title of Mayor. The county administration is headed by a chief executive, AnnMarie Farrelly. The county town is Swords.

South Dublin County Council is the local authority of the county of South Dublin, Ireland. It is one of three local authorities created by the Local Government (Dublin) Act 1993 to succeed the former Dublin County Council before its abolition on 1 January 1994 and one of four councils in County Dublin. As a county council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. The council is responsible for housing and community, roads and transportation, urban planning and development, amenity and culture, and environment. The council has 40 elected members. Elections are held every five years and are by single transferable vote. The head of the council has the title of Mayor. The county administration is headed by a chief executive, Daniel McLoughlin. The county town is Tallaght, with a civic centre at Monastery Road, Clondalkin. It serves a population of approximately 192,000.

Rathmines and Rathgar is a former second-tier local government area within County Dublin. It was created as the Township of Rathmines in 1847. In 1862, its area was expanded and it became the Township of Rathmines and Rathgar. In 1899, it became an urban district. It was abolished in 1930, and its area absorbed into the city of Dublin.

An election to Dublin County Council in the electoral county of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown within Dublin County took place on 27 June 1991 as part of that year's Irish local elections. 28 councillors were elected from 7 local electoral areas on the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote for a five-year term of office. It was one of three electoral counties within Dublin County at this election, the others being Fingal and South Dublin.
Killiney and Ballybrack is a former second-tier local government area within County Dublin. It was created as a township in 1866. In 1899, it became an urban district. It was abolished in 1900, with its area becoming part of the borough of Dún Laoghaire.
Local government in Dublin, the capital city of Ireland, is currently administered through the local authorities of four local government areas. The historical development of these councils dates back to medieval times.
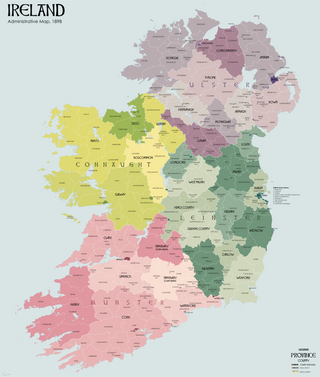
Urban and rural districts were divisions of administrative counties in Ireland created in 1899. These local government areas elected urban district councils (UDCs) and rural district councils (RDCs) respectively which shared responsibilities with a county council. They were established when all of Ireland was part of the United Kingdom.
References
- ↑ Local Government (Dublin) Act 1930, s. 2: Inclusion of certain urban districts in the city ( No. 27 of 1930, s. 2 ). Enacted on 17 July 1930. Act of the Oireachtas .Retrieved from Irish Statute Book .
- ↑ Local Government (Dublin) Act 1930, s. 3: Formation of the Borough of Dun Laoghaire ( No. 27 of 1930, s. 3 ). Enacted on 17 July 1930. Act of the Oireachtas .Retrieved from Irish Statute Book .
- ↑ Local Government (Dublin) Act 1930, s. 17: Inclusion of certain rural areas in the City ( No. 27 of 1930, s. 17 ). Enacted on 17 July 1930. Act of the Oireachtas .Retrieved from Irish Statute Book .; Local Government (Dublin) Act 1930, 1st Sch.: Added rural area ( No. 27 of 1930, 1st Sch. ). Enacted on 17 July 1930. Act of the Oireachtas .Retrieved from Irish Statute Book .
- ↑ Local Government (Dublin) Act 1930, s. 82: Abolition of rural district councils in the County ( No. 27 of 1930, s. 82 ). Enacted on 17 July 1930. Act of the Oireachtas .Retrieved from Irish Statute Book .