Related Research Articles

The Amstrad CPC is a series of 8-bit home computers produced by Amstrad between 1984 and 1990. It was designed to compete in the mid-1980s home computer market dominated by the Commodore 64 and the ZX Spectrum, where it successfully established itself primarily in the United Kingdom, France, Spain, and the German-speaking parts of Europe.
Amstrad was a British electronics company, founded in 1968 by Alan Sugar at the age of 21. The name is a contraction of Alan Michael Sugar Trading. It was first listed on the London Stock Exchange in April 1980. During the late 1980s, Amstrad had a substantial share of the PC market in the UK. Amstrad was once a FTSE 100 Index constituent, but since 2007 has been wholly owned by Sky UK. As of 2006, Amstrad's main business was manufacturing Sky UK interactive boxes. In 2010, Sky integrated Amstrad's satellite division as part of Sky so they could make their own set-top boxes in-house.

CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc. Initially confined to single-tasking on 8-bit processors and no more than 64 kilobytes of memory, later versions of CP/M added multi-user variations and were migrated to 16-bit processors.

The Amstrad PCW series is a range of personal computers produced by British company Amstrad from 1985 to 1998, and also sold under licence in Europe as the "Joyce" by the German electronics company Schneider in the early years of the series' life. The PCW, short for Personal Computer Word-processor, was targeted at the word processing and home office markets. When it was launched the cost of a PCW system was under 25% of the cost of almost all IBM-compatible PC systems in the UK, and as a result the machine was very popular both in the UK and in Europe, persuading many technophobes to venture into using computers. The series is reported to have sold 1.5 million units. However the last two models, introduced in the mid-1990s, were commercial failures, being squeezed out of the market by the falling prices, greater capabilities and wider range of software for IBM-compatible PCs.

Locomotive Basic is a proprietary dialect of the BASIC programming language written by Locomotive Software on the Amstrad CPC and the later Locomotive BASIC-2 as a GEM application on the Amstrad PC1512 and 1640. It was the main descendant of Mallard BASIC, the interpreter for CP/M supplied with the Amstrad PCW.

The Enterprise is a Zilog Z80-based home computer announced in 1983, but due to a series of delays, was not commercially available until 1985. It was developed by British company Intelligent Software and marketed by Enterprise Computers.

LocoScript is a word processing software package created by Locomotive Software and first released with the Amstrad PCW, a personal computer launched in 1985. Early versions of LocoScript were noted for combining a wide range of facilities with outstanding ease of use. This and the low price of the hardware made it one of the best-selling word processors of the late 1980s. Four major versions of LocoScript were published for the PCW, and two for IBM-compatible PCs running MS-DOS. LocoScript's market share didn't expand with the PC versions, which were not released until after Windows had become the dominant PC operating system.
Mallard BASIC is a BASIC interpreter for CP/M produced by Locomotive Software and supplied with the Amstrad PCW range of small business computers, the ZX Spectrum +3 version of CP/M Plus, and the Acorn BBC Micro's Zilog Z80 second processor.
AMSDOS is a disk operating system for the 8-bit Amstrad CPC Computer. The name is a contraction of Amstrad Disk Operating System.

Amstrad Computer User was the official magazine for the Amstrad CPC series of 8-bit home computers. This monthly publication, usually referred to as ACU by its readers, concentrated more on the hardware and technical side of the Amstrad range, although it had a small dedicated games section as well.
Amsoft was a wholly owned subsidiary of Amstrad, PLC, founded in 1984 and re-integrated with its parent company in 1989. Its purpose was to provide an initial infrastructure of software and services for users of Amstrad's range of home computers, the Amstrad CPC and, from 1986, the ZX Spectrum. Many people's first contact with software on an Amstrad home computer would have been an Amsoft title, as several titles were included in the sales bundles.
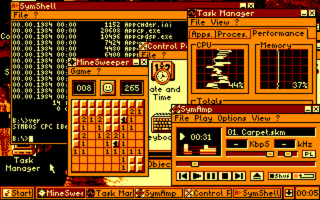
SYmbiosis Multitasking Based Operating System (SymbOS) is a multitasking operating system for Zilog Z80-based 8-bit computer systems.

La abadía del crimen is a video game written by Paco Menéndez with graphics made by Juan Delcán and published in 1987 by Opera Soft. It was conceived as a version of Umberto Eco's 1980 book The Name of the Rose. Paco Menéndez and Opera Soft were unable to secure the rights for the name, so the game was released as La abadía del crimen. "The Abbey of the Crime" was the working title of the novel The Name of the Rose.
Tasword is a word processor for microcomputers developed by Tasman Software. The first version was released for the ZX81 in 1982 and spawned two major revisions in addition to several add-ons and, later, tailored versions for the +2 and +3 Spectrum models, the SAM Coupé, the MSX, the Timex Sinclair 2068 and the Amstrad CPC range.
Protext is a British word processing program, developed by Arnor Ltd, of Peterborough in the decade following 1985. Originally written for the Amstrad CPC 464, it was later sold for the Amstrad PCW series of word processors, for MS-DOS based PCs, the Atari ST, and the Commodore Amiga.
Workwriter was a word processor software written in C, in 1983 and 1984, by Peter P. Vekinis, similar in features and operation to dedicated word processors marketed by AES Data Inc.
The Amstrad CP/M Plus character set is any of a group of 8-bit character sets introduced by Amstrad/Locomotive Software for use in conjunction with their adaptation of Digital Research's CP/M Plus on various Amstrad CPC / Schneider CPC and Amstrad PCW / Schneider Joyce machines. The character set was also used on the Amstrad ZX Spectrum +3 version of CP/M.
The Amstrad CPC character set is the character set used in the Amstrad CPC series of 8-bit personal computers when running BASIC. This character set existed in the built-in "lower" ROM chip. It is based on ASCII-1967, with the exception of character 0x5E which is the up arrow instead of the circumflex, as it is in ASCII-1963, a feature shared with other character sets of the time. Apart from the standard printable ASCII range (0x20-0x7e), it is completely different from the Amstrad CP/M Plus character set. The BASIC character set had symbols of particular use in games and home computing, while the CP/M Plus character reflected the International and Business flavor of the CP/M Plus environment. This character set is represented in Unicode as of the March 2020 release of Unicode 13.0, which added symbols for legacy computing.
References
- 1 2 Smith, Tony (12 February 2014). "You're NOT fired: The story of Amstrad's amazing CPC 464". The Register. Retrieved 18 August 2018.
- ↑ "Order Form". Locomotive Software. 1990. Retrieved 18 August 2018.
- 1 2 Simon Rockman (9 September 2015). "'A word processor so simple my PA could use it': Joyce turns 30". The Register. Retrieved 8 November 2015.