
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends beyond the swelling. Carbuncles and boils are types of abscess that often involve hair follicles, with carbuncles being larger.

In medicine, triage is a practice invoked when acute care cannot be provided for lack of resources. The process rations care towards those who are most in need of immediate care, and who benefit most from it. More generally it refers to prioritisation of medical care as a whole. In its acute form it is most often required on the battlefield, or at peacetime when an accident results in a mass casualty which swamps nearby healthcare facilities' capacity.

Back pain is pain felt in the back. Back pain is divided into neck pain (cervical), middle back pain (thoracic), lower back pain (lumbar) or coccydynia based on the segment affected. The lumbar area is the most common area affected. An episode of back pain may be acute, sub-acute, or chronic depending on the duration. The pain may be characterized as a dull ache, shooting or piercing pain, or a burning sensation. Discomfort can radiate into the arms and hands as well as the legs or feet, and may include numbness, or weakness in the legs and arms.

Shortness of breath (SOB), also known as dyspnea, is a feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity", and recommends evaluating dyspnea by assessing the intensity of the distinct sensations, the degree of distress involved, and its burden or impact on activities of daily living. Distinct sensations include effort/work, chest tightness, and air hunger. The tripod position is often assumed.

Digital rectal examination is an internal examination of the rectum, performed by a healthcare provider.

Respiratory arrest is caused by apnea or respiratory dysfunction severe enough it will not sustain the body. Prolonged apnea refers to a patient who has stopped breathing for a long period of time. If the heart muscle contraction is intact, the condition is known as respiratory arrest. An abrupt stop of pulmonary gas exchange lasting for more than five minutes may damage vital organs especially the brain, possibly permanently. Lack of oxygen to the brain causes loss of consciousness. Brain injury is likely if respiratory arrest goes untreated for more than three minutes, and death is almost certain if more than five minutes.

Major trauma is any injury that has the potential to cause prolonged disability or death. There are many causes of major trauma, blunt and penetrating, including falls, motor vehicle collisions, stabbing wounds, and gunshot wounds. Depending on the severity of injury, quickness of management, and transportation to an appropriate medical facility may be necessary to prevent loss of life or limb. The initial assessment is critical, and involves a physical evaluation and also may include the use of imaging tools to determine the types of injuries accurately and to formulate a course of treatment.

A spinal board, is a patient handling device used primarily in pre-hospital trauma care. It is designed to provide rigid support during movement of a person with suspected spinal or limb injuries. They are most commonly used by ambulance staff, as well as lifeguards and ski patrollers. Historically, backboards were also used in an attempt to "improve the posture" of young people, especially girls.
Casualty lifting is the first step of casualty movement, an early aspect of emergency medical care. It is the procedure used to put the casualty on a stretcher.

The patellar reflex, also called the knee reflex or knee-jerk, is a stretch reflex which tests the L2, L3, and L4 segments of the spinal cord.
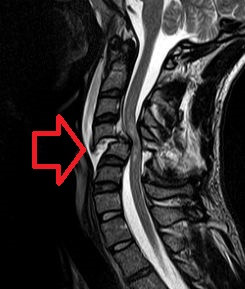
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cord below the level of the injury. Injury can occur at any level of the spinal cord and can be complete, with a total loss of sensation and muscle function at lower sacral segments, or incomplete, meaning some nervous signals are able to travel past the injured area of the cord up to the Sacral S4-5 spinal cord segments. Depending on the location and severity of damage, the symptoms vary, from numbness to paralysis, including bowel or bladder incontinence. Long term outcomes also range widely, from full recovery to permanent tetraplegia or paraplegia. Complications can include muscle atrophy, loss of voluntary motor control, spasticity, pressure sores, infections, and breathing problems.

The scoop stretcher is a device used specifically for moving injured people. It is Ideal for carrying casualties with possible spinal injuries.
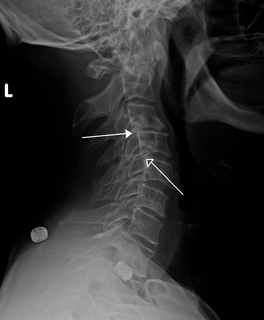
A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to the subjacent vertebra to a degree less than a luxation (dislocation). Retrolistheses are most easily diagnosed on lateral x-ray views of the spine. Views where care has been taken to expose for a true lateral view without any rotation offer the best diagnostic quality.

Spondylolisthesis is the displacement of one spinal vertebra compared to another. While some medical dictionaries define spondylolisthesis specifically as the forward or anterior displacement of a vertebra over the vertebra inferior to it, it is often defined in medical textbooks as displacement in any direction. Spondylolisthesis is graded based upon the degree of slippage of one vertebral body relative to the subsequent adjacent vertebral body. Spondylolisthesis is classified as one of the six major etiologies: degenerative, traumatic, dysplastic, isthmic, pathologic, or post-surgical. Spondylolisthesis most commonly occurs in the lumbar spine, primarily at the L5-S1 level with the L5 vertebral body anteriorly translating over the S1 vertebral body.
Abnormal posturing is an involuntary flexion or extension of the arms and legs, indicating severe brain injury. It occurs when one set of muscles becomes incapacitated while the opposing set is not, and an external stimulus such as pain causes the working set of muscles to contract. The posturing may also occur without a stimulus. Since posturing is an important indicator of the amount of damage that has occurred to the brain, it is used by medical professionals to measure the severity of a coma with the Glasgow Coma Scale and the Pediatric Glasgow Coma Scale.

Tuberculous meningitis, also known as TB meningitis or tubercular meningitis, is a specific type of bacterial meningitis caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection of the meninges—the system of membranes which envelop the central nervous system.
Grady straps are a specific strapping configuration used in full body spinal immobilization.

Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Symptoms are typically gradual in onset and improve with bending forwards. Severe symptoms may include loss of bladder control, loss of bowel control, or sexual dysfunction.
A wilderness medical emergency is a medical emergency that takes place in a wilderness or remote setting affinitive care. Such an emergency can require specialized skills, treatment techniques, and knowledge in order to manage the patient for an extended period of time before and during evacuation.
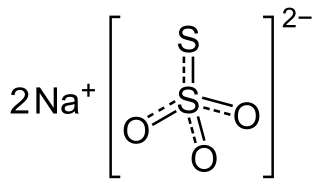
Sodium thiosulfate, also spelled sodium thiosulphate, is used as a medication to treat cyanide poisoning, pityriasis versicolor, and to decrease side effects from cisplatin. For cyanide poisoning it is often used after the medication sodium nitrite and typically only recommended for severe cases. It is either given by injection into a vein or applied to the skin.

















