
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a landlocked federal state of Germany, occupying its southeastern corner. With an area of 70,550.19 square kilometres, Bavaria is the largest German state by land area comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With 13 million inhabitants, it is Germany's second-most-populous state after North Rhine-Westphalia. Bavaria's main cities are Munich, Nuremberg and Augsburg.

Franconia is a region in Germany, characterised by its culture and language, and may be roughly associated with the areas in which the East Franconian dialect group, colloquially referred to as "Franconian", is spoken. There are several other Franconian dialects, but only the East Franconian ones are colloquially referred to as "Franconian".

The Palatinate, historically also Rhenish Palatinate, is a region in southwestern Germany. It occupies roughly the southernmost quarter of the German federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate (Rheinland-Pfalz), covering an area of 5,451 square kilometres (2,105 sq mi) with about 1.4 million inhabitants. Its residents are known as Palatines.

Upper Austria is one of the nine states or Bundesländer of Austria. Its capital is Linz. Upper Austria borders on Germany and the Czech Republic, as well as on the other Austrian states of Lower Austria, Styria, and Salzburg. With an area of 11,982 km2 (4,626 sq mi) and 1.437 million inhabitants, Upper Austria is the fourth-largest Austrian state by land area and the third-largest by population.

Tyrol is a federal state (Bundesland) in western Austria. It comprises the Austrian part of the historical Princely County of Tyrol. It is a constituent part of the present-day Euroregion Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino. The capital of Tyrol is Innsbruck.
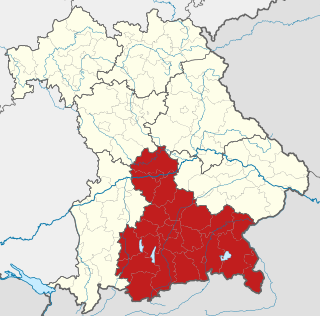
Upper Bavaria is one of the seven administrative districts of Bavaria, Germany.
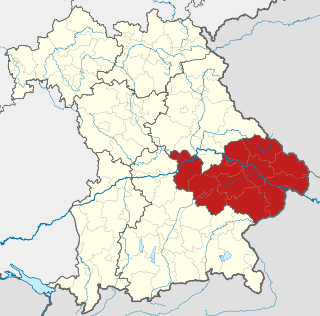
Lower Bavaria is one of the seven administrative regions of Bavaria, Germany, located in the east of the state.

The Upper Palatinate is one of the seven administrative districts of Bavaria, Germany, located in the east of Bavaria.
Altötting is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by Austria and the Bavarian districts of Traunstein, Mühldorf and Rottal-Inn.
Berchtesgadener Land is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by the district of Traunstein and by the state of Austria.
Miltenberg is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by the city of Aschaffenburg, the districts of Aschaffenburg and Main-Spessart, and the states of Baden-Württemberg and Hesse.

Bavarian Alps is a summarizing term of several mountain ranges of the Northern Limestone Alps in the German state of Bavaria.

Kelheim is a town and municipality in Bavaria, Germany. It is the capital of the district Kelheim and is situated at the confluence of the rivers Altmühl and Danube. Kelheim has a population of around 15,750.

The Duchy of Bavaria was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (duces) under Frankish overlordship. A new duchy was created from this area during the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the late ninth century. It became one of the stem duchies of the East Frankish realm which evolved as the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire.

The Würm is a river in Bavaria, Germany, right tributary of the Amper. The length of the river is 39.8 kilometres (24.7 mi), or 76.3 kilometres (47.4 mi) including the Steinbach, the main feed of Lake Starnberg. It drains the overflow from Lake Starnberg and flows swiftly through the villages of Gauting, Krailling, Planegg, Gräfelfing and Lochham as well as part of Munich before joining, near Dachau, the Amper, which soon afterwards flows into the Isar and eventually flowing into the Danube. Although the Würm is not a very large river, it is well known as it gave its name to the Würm glaciation.
Southern Germany as a region has no exact boundary but is generally taken to include the areas in which Upper German dialects are spoken. That corresponds roughly to the historical stem duchies of Bavaria and Swabia or, in a modern context, to Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg within the Federal Republic of Germany, to the exclusion of the areas of the modern states of Austria and Switzerland. The Saarland and the southern parts of Hesse and Rhineland-Palatinate are sometimes included as well and correspond to the historical Franconia.

The Rott is a 111 km (69 mi) long river in Bavaria, Germany, left tributary of the Inn. Its source is in the municipality Wurmsham in Lower Bavaria, between Landshut and Waldkraiburg. It flows east through a rural area with small towns, including Neumarkt-Sankt Veit, Eggenfelden, Pfarrkirchen and Pocking. It flows into the Inn near Neuhaus am Inn, opposite of Schärding, on the border with Austria.

The Günz is a river in Bavaria, Germany.

The Danube is Europe's second longest river, after the Volga. It is located in Central and Eastern Europe.















