
The First Punic War was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the mid-3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated.
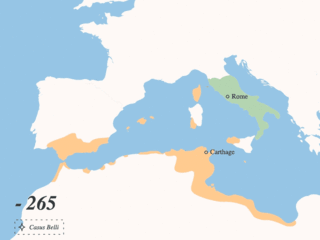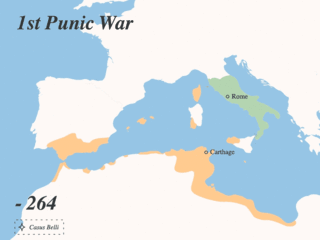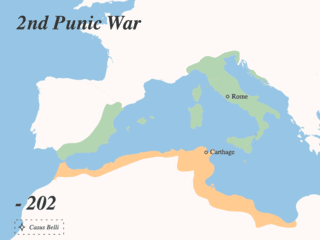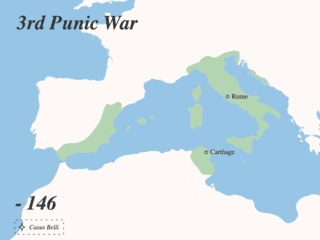
The Punic Wars were a series of wars that were fought between the Roman Republic and Ancient Carthage.

Palermo is a city in southern Italy, the capital of both the autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan province. The city is noted for its history, culture, architecture and gastronomy, playing an important role throughout much of its existence; it is over 2,700 years old. Palermo is in the northwest of the island of Sicily, by the Gulf of Palermo in the Tyrrhenian Sea.

Barcellona Pozzo di Gotto is a town and comune of about 50,000 inhabitants in the north coast of Sicily, Italy, 40 kilometres (25 mi) from Messina towards Palermo. It belongs to the Metropolitan City of Messina.

Magna Graecia was the name given by the Romans to the coastal areas of Southern Italy in the present-day regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata and Campania; these regions were extensively populated by Greek settlers. The settlers who began arriving in the 8th century BC brought with them their Hellenic civilization which left a lasting imprint in those territories such as in the culture of ancient Rome. They also influenced the native peoples, especially the Oenotrians, who became Hellenised after they adopted the Greek culture as their own.
Hamilcar Barca or Barcas was a Carthaginian general and statesman, leader of the Barcid family, and father of Hannibal, Hasdrubal and Mago. He was also father-in-law to Hasdrubal the Fair.

Euthydemus I c. 260 BC – 200/195 BC) was a Greco-Bactrian king and founder of the Euthydemid dynasty. He is thought to have originally been a governor of Sogdia, who seized the throne by force from Diodotus II in 224 BC. Literary sources, notably Polybius, record how he and his son Demetrius resisted an invasion by the Seleucid king Antiochus III from 209 to 206 BC. Euthydemus expanded the Bactrian territory into Sogdia, constructed several fortresses, including the Wall of Darbent, and issued a very substantial coinage.

The Mercenary War, also known as the Truceless War, was a mutiny by troops that were employed by Carthage at the end of the First Punic War (264–241 BC), supported by uprisings of African settlements revolting against Carthaginian control. It lasted from 241 to late 238 or early 237 BC and ended with Carthage suppressing both the mutiny and the revolt.
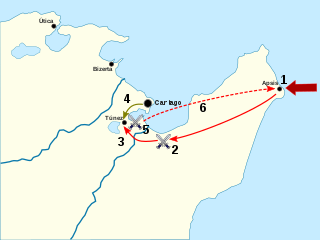
The Battle of the Bagradas River, also known as the Battle of Tunis, was a victory by a Carthaginian army led by Xanthippus over a Roman army led by Marcus Atilius Regulus in the spring of 255 BC, nine years into the First Punic War. The previous year, the newly constructed Roman navy established naval superiority over Carthage. The Romans used this advantage to invade Carthage's homeland, which roughly aligned with modern-day Tunisia in North Africa. After landing on the Cape Bon Peninsula and conducting a successful campaign, the fleet returned to Sicily, leaving Regulus with 15,500 men to hold the lodgement in Africa over the winter.
The Province of Palermo was a province in the autonomous region of Sicily, a major island in Southern Italy. Its capital was the city of Palermo. On 4 August 2015, it was replaced by the Metropolitan City of Palermo.

Acireale is a coastal city and comune in the north-east of the Metropolitan City of Catania, Sicily, southern Italy, at the foot of Mount Etna, on the coast facing the Ionian Sea. It is home to numerous churches, including the Neo-Gothic St. Peter's Basilica, St. Sebastian's Basilica in the Sicilian Baroque style, and the 17th century Acireale Cathedral, and a seminary, for the training of priests. Acireale is also noted for its art and paintings: the oldest academy in Sicily, the "Accademia dei Dafnici e degli Zelanti", is located here.

The Battle of Panormus was fought in Sicily in 250 BC during the First Punic War between a Roman army led by Lucius Caecilius Metellus and a Carthaginian force led by Hasdrubal. The Roman force of two legions defending the city of Panormus defeated the much larger Carthaginian army of 30,000 men and between 60 and 142 war elephants.

Pednelissus or Petnelissus was a city on the border between Pamphylia and Pisidia in Asia Minor.

Fondachelli-Fantina is a comune (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Messina, Sicily, southern Italy. Situated between Novara and Francavilla di Sicilia, in the southern Peloritani mountains, it is 604 metres (1,982 ft) above sea level. The community borders the municipalities of Antillo and Rodì Milici. The most populated villages are Rubino, Evangelisti, Chiesa, Figheri and Fantina. It is 73 kilometres (45 mi) from Messina.

Rodì Milici is an Italian comune in the Metropolitan City of Messina in Sicily. The comune is located about 160 kilometres (99 mi) east of Palermo and about 35 kilometres (22 mi) west of Messina.
The Treaty of Lutatius was the agreement between Carthage and Rome of 241 BC, that ended the First Punic War after 23 years of conflict. Most of the fighting during the war took place on, or in the waters around, the island of Sicily and in 241 BC a Carthaginian fleet was defeated by a Roman fleet commanded by Gaius Lutatius Catulus while attempting to lift the blockade of its last, beleaguered, strongholds there. Accepting defeat, the Carthaginian Senate ordered their army commander on Sicily, Hamilcar Barca, to negotiate a peace treaty with the Romans, on whatever terms he could negotiate. Hamilcar refused, claiming the surrender was unnecessary, and the negotiation of the peace terms was left to Gisco, the commander of Lilybaeum, as the next most senior Carthaginian on the island. A draft treaty was rapidly agreed, but when it was referred to Rome for ratification it was rejected.

The Battle of Utica was fought in 203 BC between armies of Rome and Carthage during the Second Punic War. Through a surprise attack, the Roman commander Scipio Africanus managed to destroy a numerous force of Carthaginians and their Numidian allies not far from the outflow of the Medjerda River in modern Tunisia. Thus he gained a decisive strategic advantage, switched the focus of the war from Italy and Iberia to Carthaginian north Africa, and contributed largely to the final Roman victory.

Milici is a village in the Province of Messina of Sicily, Italy.

The siege of Lilybaeum lasted for nine years, from 250 to 241 BC, as the Roman army laid siege to the Carthaginian-held Sicilian city of Lilybaeum during the First Punic War. Rome and Carthage had been at war since 264 BC, fighting mostly on the island of Sicily or in the waters around it, and the Romans were slowly pushing the Carthaginians back. By 250 BC, the Carthaginians held only the cities of Lilybaeum and Drepana; these were well-fortified and situated on the west coast, where they could be supplied and reinforced by sea without the Romans being able to use their superior army to interfere.

Etenna was a city in the late Roman province of Pamphylia Prima. Centuries earlier, it was reckoned as belonging to Pisidia, as by Polybius, who wrote that in 218 BC the people of Etenna "who live in the highlands of Pisidia above Side" provided 8000 hoplites to assist the Seleucid usurper Achaeus.



















