Related Research Articles
Systems design is the process of defining the architecture, product design, modules, interfaces, and data for a system to satisfy specified requirements. Systems design could be seen as the application of systems theory to product development. There is some overlap with the disciplines of systems analysis, systems architecture and systems engineering.
Systems analysis is "the process of studying a procedure or business to identify its goal and purposes and create systems and procedures that will efficiently achieve them". Another view sees system analysis as a problem-solving technique that breaks down a system into its component pieces, and how well those parts work and interact to accomplish their purpose.
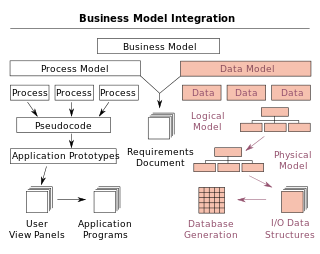
A data model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to the properties of real-world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be composed of a number of other elements which, in turn, represent the color and size of the car and define its owner.
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, store, and distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, information systems are composed by four components: task, people, structure, and technology. Information systems can be defined as an integration of components for collection, storage and processing of data of which the data is used to provide information, contribute to knowledge as well as digital products that facilitate decision making.
Rapid application development (RAD), also called rapid application building (RAB), is both a general term for adaptive software development approaches, and the name for James Martin's method of rapid development. In general, RAD approaches to software development put less emphasis on planning and more emphasis on an adaptive process. Prototypes are often used in addition to or sometimes even instead of design specifications.

In systems engineering, information systems and software engineering, the systems development life cycle (SDLC), also referred to as the application development life-cycle, is a process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an information system. The systems development life cycle concept applies to a range of hardware and software configurations, as a system can be composed of hardware only, software only, or a combination of both. There are usually six stages in this cycle: requirement analysis, design, development and testing, implementation, documentation, and evaluation.

In industry, product lifecycle management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its inception through the engineering, design, and manufacture, as well as the service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM integrates people, data, processes and business systems and provides a product information backbone for companies and their extended enterprise.

Data modeling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying certain formal techniques.
System of systems is a collection of task-oriented or dedicated systems that pool their resources and capabilities together to create a new, more complex system which offers more functionality and performance than simply the sum of the constituent systems. Currently, systems of systems is a critical research discipline for which frames of reference, thought processes, quantitative analysis, tools, and design methods are incomplete. The methodology for defining, abstracting, modeling, and analyzing system of systems problems is typically referred to as system of systems engineering.
A feasibility study is an assessment of the practicality of a proposed project or system. A feasibility study aims to objectively and rationally uncover the strengths and weaknesses of an existing business or proposed venture, opportunities and threats present in the natural environment, the resources required to carry through, and ultimately the prospects for success. In its simplest terms, the two criteria to judge feasibility are cost required and value to be attained.

Unicom System Architect is an enterprise architecture tool that is used by the business and technology departments of corporations and government agencies to model their business operations and the systems, applications, and databases that support them. System Architect is used to build architectures using various frameworks including TOGAF, ArchiMate, DoDAF, MODAF, NAF and standard method notations such as sysML, UML, BPMN, and relational data modeling. System Architect is developed by UNICOM Systems, a division of UNICOM Global, a United States-based company.
Resources, events, agents (REA) is a model of how an accounting system can be re-engineered for the computer age. REA was originally proposed in 1982 by William E. McCarthy as a generalized accounting model, and contained the concepts of resources, events and agents.

Enterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization.

Jean Leonardus Gerardus (Jan) Dietz is a Dutch Information systems researcher, Emeritus Professor of Information Systems Design, and part-time Professor of Enterprise Engineering at the Delft University of Technology, known for the development of the Design & Engineering Methodology for Organizations. and his work on enterprise ontology.
In software engineering, a software development process is the process of dividing software development work into smaller, parallel or sequential steps or subprocesses to improve design, product management. It is also known as a software development life cycle (SDLC). The methodology may include the pre-definition of specific deliverables and artifacts that are created and completed by a project team to develop or maintain an application.

Electronic engineering is an electrical engineering discipline which utilizes nonlinear and active electrical components to design electronic circuits, devices, integrated circuits and their systems. The discipline typically also designs passive electrical components, usually based on printed circuit boards.
Jeffrey L. Whitten is an American computer scientist, and professor of information technology at Purdue University, known with Kevin C. Dittman and Lonnie D. Bentley as co-author of the textbook Systems Analysis and Design Methods, which is now in its 7th edition.
Kevin C. Dittman is an American computer scientist, IT consultant and Professor of Information Technology at the Purdue University, especially known for his textbook Systems analysis and design methods written with Lonnie D. Bentley and Jeffrey L. Whitten, which is in its 7th edition.
Tapan Kumar Sarkar was an Indian-American electrical engineer and Professor Emeritus at the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at Syracuse University. He was best known for his contributions to computational electromagnetics and antenna theory.
References
- ↑ Walls, Joseph G., George R. Widmeyer, and Omar A. El Sawy. "Building an information system design theory for vigilant EIS. Archived 2013-10-24 at the Wayback Machine " Information systems research 3.1 (1992): 36-59.
- ↑ Lonnie D. Bentley at tech.purdue.edu, 2009
- ↑ Broadband Antenna Tracking Systems (BATS).