Related Research Articles

The Regional District of Kootenay Boundary (RDKB) is one of 29 regional districts in the province of British Columbia, Canada. As of the 2016 census, the population was 31,447. The area is 8,095.62 km². The RDKB was incorporated in 1966 and consists of eight incorporated municipalities and five unincorporated electoral areas. The regional district's offices are in the City of Trail, with secondary offices in the City of Grand Forks. Other major population centres include the cities of Rossland and Greenwood, and the villages of Fruitvale, Warfield, and Montrose. The region also encompasses electoral areas A, B/Lower Columbia-Old Glory, C/Christina Lake, D/Rural Grand Forks and E/West Boundary including Rock Creek, Bridesville, Beaverdell and Big White Ski Resort.

The Squamish-Lillooet Regional District is a quasi-municipal administrative area in British Columbia, Canada. It stretches from Britannia Beach in the south to Pavilion in the north. Lillooet, Pemberton, Whistler and Squamish are the four municipalities in the regional district. Its administrative offices are in the Village of Pemberton, although the district municipalities of Squamish, Whistler, and Lillooet are all larger population centres. The district covers 16,353.68 km² of land area.

The qathet Regional District is a regional district in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It includes the City of Powell River and a number of unincorporated areas. The district encompasses a land area of 5,092.06 square kilometres (1,966.06 sq mi). Formerly known as the formerly the Powell River Regional District, its name was changed in 2018 to qathet, meaning "working together" in the language of the Tla'amin Nation.

The Fraser Valley Regional District (FVRD) is a regional district in British Columbia, Canada. Its headquarters are in the city of Chilliwack. The FVRD covers an area of 13,361.74 km² (5,159 sq mi). It was created by an amalgamation of the Fraser-Cheam Regional District and Central Fraser Valley Regional District and the portion of the Dewdney-Alouette Regional District from and including the District of Mission eastwards.
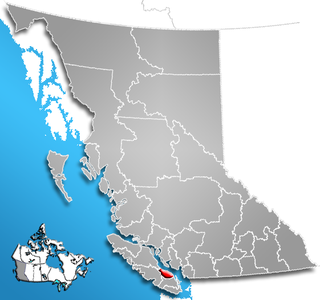
The Regional District of Nanaimo is a regional district located on the eastern coast of Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. It is bordered to the south by the Cowichan Valley Regional District, to the west by the Alberni-Clayoquot Regional District, and to the northwest by the Comox Valley Regional District. Its administration offices are located in Nanaimo. During the 2011 census, its population was established at 146,567.

The Columbia-Shuswap Regional District is a regional district in the Canadian province of British Columbia, located in the Southern Interior region on the Trans-Canada Highway between Vancouver and Calgary, Alberta. The regional district borders the Province of Alberta across the Rocky Mountains.

The Cowichan Valley Regional District is a regional district in the Canadian province of British Columbia is on the southern part of Vancouver Island, bordered by the Nanaimo and Alberni-Clayoquot Regional Districts to the north and northwest, and by the Capital Regional District to the south and east. As of the 2011 Census, the Regional District had a population of 80,332. The regional district offices are in Duncan.

The Regional District of North Okanagan (RDNO) is a regional district in the Canadian province of British Columbia, Canada. The Canada 2011 Census population was 81,237. The land area is 7,512.58 km². The regional district's head office is in the district municipality of Coldstream, although the largest population centre is its immediate neighbour, the city of Vernon.
Premier Lake Provincial Park is a provincial park near Sparwood, British Columbia, Canada. It is located on the south and western shores of Premier Lake in the East Kootenays, a small lake situated on the eastern flank of the Kootenay trench about 50 km north of Cranbrook. Also contained within the park are several smaller lakes, including Rockbluff (Quartz) Lake, Yankee Lake and Canuck Lake, all notable for the vivid green colour of their water.

The Regional District of Fraser-Fort George (RDFFG) is a regional district located in the Central Interior of British Columbia. It is bounded by the Alberta border to the east, the Columbia-Shuswap and Thompson-Nicola Regional Districts to the south/southeast, Cariboo Regional District to the southwest, the Regional District of Bulkley-Nechako to the west, and the Peace River Regional District to the north/northeast. As of the Canada 2011 Census, the Regional District had a population of 91,879, and a land area of 51,083.73 km². The offices of the Regional District are located at Prince George.
Kootenay Lake Crossing was a powerline crossing of Kootenay Lake, British Columbia, Canada. The idea was to move electricity from the Hydro dam on the Kootenay River at Brilliant to the Cominco Sullivan Mine at Kimberley. The most direct route was across Kootenay Lake. It was with a span width of 3,248 metres (10,656 ft) the longest powerline span of North America and was fixed on two 90 metres (300 ft) tall electricity pylons. Roebling cable provided the steel support cable for the conductor. The height of conductor over Kootenay Lake was 37 metres (121 ft). There was a 100 metres (330 ft) steel support tower on the east shore, and rock anchored shorter towers high up on the west shore. Kootenay Lake Crossing was inaugurated in 1958, but was demolished in 1962 by explosives placed by the Sons of Freedom religious sect of the Doukhobors. The tower was rebuilt and the span lengthened in course. The powerline is still in operation today, but uses today on each site of the lake situated at 49°42'2"N 116°51'59"W and at 49°42'29"N 116°54'44"W.
The Alkali Lake Indian Band, also known as the Esketemc First Nation, is a First Nations government of the Secwepemc (Shuswap) people, located at Alkali Lake in the Cariboo region of the Central Interior of the Canadian province of British Columbia. It was created when the government of the then-Colony of British Columbia established an Indian Reserve system in the 1860s. It is one of three Secwepemc bands that is not a member of either the Shuswap Nation Tribal Council or the Northern Shuswap Tribal Council.
Ptarmigan Lake may refer to:
Gwyneth Lake Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, located 70 kilometres west of Lillooet, British Columbia. The park, which is 132 ha. in size, was established in 2010.
The Lillooet Land District is one of the 59 cadastral subdivisions of British Columbia, which were created by the Lands Act of the Colony of British Columbia in 1859, defined as "a territorial division with legally defined boundaries for administrative purposes". The land district's boundaries came to be used as the boundary of the initial Lillooet riding for the provincial Legislature from 1871, when the colony became a province. In addition to use in descriptions of land titles and lot surveys, the Land District was also the basis of the Lillooet Mining District.
There are 20 lakes named Long Lake in British Columbia, Canada.
The Cariboo Land District is a cadastral survey subdivision of the province of British Columbia, Canada, created with rest of those on Mainland British Columbia via the Lands Act of the Colony of British Columbia in 1860. The British Columbia government's BC Names system, a subdivision of GeoBC, defines a land district as "a territorial division with legally defined boundaries for administrative purposes" All land titles and surveys use the Land District system as the primary point of reference, and entries in BC Names for placenames and geographical objects are so listed.
References
- ↑ "Search results for Loon Lake". Natural Resources Canada. Retrieved 17 May 2017.