In computer science, LR parsers are a type of bottom-up parser that analyse deterministic context-free languages in linear time. There are several variants of LR parsers: SLR parsers, LALR parsers, Canonical LR(1) parsers, Minimal LR(1) parsers, and GLR parsers. LR parsers can be generated by a parser generator from a formal grammar defining the syntax of the language to be parsed. They are widely used for the processing of computer languages.
GNU Bison, commonly known as Bison, is a parser generator that is part of the GNU Project. Bison reads a specification in the BNF notation, warns about any parsing ambiguities, and generates a parser that reads sequences of tokens and decides whether the sequence conforms to the syntax specified by the grammar.
In computer science, an LL parser is a top-down parser for a restricted context-free language. It parses the input from Left to right, performing Leftmost derivation of the sentence.
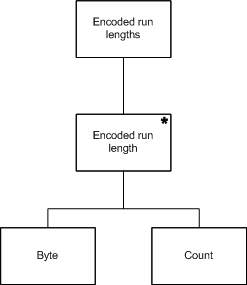
Jackson structured programming (JSP) is a method for structured programming developed by British software consultant Michael A. Jackson and described in his 1975 book Principles of Program Design. The technique of JSP is to analyze the data structures of the files that a program must read as input and produce as output, and then produce a program design based on those data structures, so that the program control structure handles those data structures in a natural and intuitive way.
In computer science, lexical analysis, lexing or tokenization is the process of converting a sequence of characters into a sequence of lexical tokens. A program that performs lexical analysis may be termed a lexer, tokenizer, or scanner, although scanner is also a term for the first stage of a lexer. A lexer is generally combined with a parser, which together analyze the syntax of programming languages, web pages, and so forth.
In computer programming, lazy initialization is the tactic of delaying the creation of an object, the calculation of a value, or some other expensive process until the first time it is needed. It is a kind of lazy evaluation that refers specifically to the instantiation of objects or other resources.
In computer programming, the interpreter pattern is a design pattern that specifies how to evaluate sentences in a language. The basic idea is to have a class for each symbol in a specialized computer language. The syntax tree of a sentence in the language is an instance of the composite pattern and is used to evaluate (interpret) the sentence for a client. See also Composite pattern.
In computer programming, a parameter or a formal argument is a special kind of variable used in a subroutine to refer to one of the pieces of data provided as input to the subroutine. These pieces of data are the values of the arguments with which the subroutine is going to be called/invoked. An ordered list of parameters is usually included in the definition of a subroutine, so that, each time the subroutine is called, its arguments for that call are evaluated, and the resulting values can be assigned to the corresponding parameters.
The syntax of the C programming language is the set of rules governing writing of software in the C language. It is designed to allow for programs that are extremely terse, have a close relationship with the resulting object code, and yet provide relatively high-level data abstraction. C was the first widely successful high-level language for portable operating-system development.
The syntax of Java is the set of rules defining how a Java program is written and interpreted.
In computer science, an operator precedence parser is a bottom-up parser that interprets an operator-precedence grammar. For example, most calculators use operator precedence parsers to convert from the human-readable infix notation relying on order of operations to a format that is optimized for evaluation such as Reverse Polish notation (RPN).
xHarbour is a free multi-platform extended Clipper compiler, offering multiple graphic terminals (GTs), including console drivers, GUIs, and hybrid console/GUIs. xHarbour is backward-compatible with Clipper and supports many language syntax extensions, greatly extended run-time libraries, and extensive third party support.
Metadata, in the Common Language Infrastructure (CLI), refers to certain data structures embedded within the Common Intermediate Language (CIL) code that describes the high-level structure of the code. Metadata describes all classes and class members that are defined in the assembly, and the classes and class members that the current assembly will call from another assembly. The metadata for a method contains the complete description of the method, including the class, the return type and all of the method parameters.
In computer programming, a sentinel value is a special value in the context of an algorithm which uses its presence as a condition of termination, typically in a loop or recursive algorithm.
This article describes the syntax of the C# programming language. The features described are compatible with .NET Framework and Mono.
The syntax and semantics of PHP, a programming language, form a set of rules that define how a PHP program can be written and interpreted.
In computer science, recursive ascent parsing is a technique for implementing an LALR parser which uses mutually-recursive functions rather than tables. Thus, the parser is directly encoded in the host language similar to recursive descent. Direct encoding usually yields a parser which is faster than its table-driven equivalent for the same reason that compilation is faster than interpretation. It is also (nominally) possible to hand edit a recursive ascent parser, whereas a tabular implementation is nigh unreadable to the average human.
In database management systems (DBMS), a prepared statement, parameterized statement, or parameterized query is a feature used to pre-compile SQL code, separating it from data. Benefits of prepared statements are:
In software engineering, the module pattern is a design pattern used to implement the concept of software modules, defined by modular programming, in a programming language with incomplete direct support for the concept.

Yesod is a free and open-source web framework based on Haskell for productive development of type-safe, REST model based, high performance web applications, developed by Michael Snoyman et al.


