Related Research Articles
Professional certification, trade certification, or professional designation, often called simply certification or qualification, is a designation earned by a person to assure qualification to perform a job or task. Not all certifications that use post-nominal letters are an acknowledgement of educational achievement, or an agency appointed to safeguard the public interest.

Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to hedge against the risk of a contingent or uncertain loss.

Safety is the state of being "safe", the condition of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.

The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Despite its name, it is not part of the National Institutes of Health. Its current director is John Howard.

Occupational hygiene is the anticipation, recognition, evaluation, control, and confirmation (ARECC) of protection from risks associated with exposures to hazards in, or arising from, the workplace that may result in injury, illness, impairment, or affect the well-being of workers and members of the community. These hazards or stressors are typically divided into the categories biological, chemical, physical, ergonomic and psychosocial. The risk of a health effect from a given stressor is a function of the hazard multiplied by the exposure to the individual or group. For chemicals, the hazard can be understood by the dose response profile most often based on toxicological studies or models. Occupational hygienists work closely with toxicologists for understanding chemical hazards, physicists for physical hazards, and physicians and microbiologists for biological hazards. Environmental and occupational hygienists are considered experts in exposure science and exposure risk management. Depending on an individual's type of job, a hygienist will apply their exposure science expertise for the protection of workers, consumers and/or communities.
A professional employer organisation (PEO) is an outsourcing firm that provides services to small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). Typically, the PEO offering may include human resource consulting, safety and risk mitigation services, payroll processing, employer payroll tax filing, workers' compensation insurance, health benefits, employers' practice and liability insurance (EPLI), retirement vehicles, regulatory compliance assistance, workforce management technology, and training and development. The PEO enters into a contractual co-employment agreement with its clientele. Through co-employment, the PEO becomes the employer of record (EoR) for tax purposes through filing payroll taxes under its own tax identification numbers. As the legal employer, the PEO is responsible for withholding proper taxes, paying unemployment insurance taxes and providing workers’ compensation coverage.

Fire safety is the set of practices intended to reduce destruction caused by fire. Fire safety measures include those that are intended to prevent the ignition of an uncontrolled fire and those that are used to limit the spread and impact of a fire.
Safety engineers focus on development and maintenance of the integrated management system. They act as a quality assurance and conformance specialist.
The Certified Safety Professional is a certification offered by the Board of Certified Safety Professionals. The accreditation is used in the United States by the National Commission for Certifying Agencies and internationally by the International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission and 193 Countries Consortium.
American Society of Safety Professionals (ASSP), formerly known as American Society of Safety Engineers (ASSE) until June 2018, is a global organization of more than 37,000 occupational safety and health (OSH) professional members who manage, supervise, research and consult on work-related OSH concerns in all industries, government and education. The Society's members use risk-based approaches to prevent workplace fatalities, injuries and illnesses.
An occupational exposure limit is an upper limit on the acceptable concentration of a hazardous substance in workplace air for a particular material or class of materials. It is typically set by competent national authorities and enforced by legislation to protect occupational safety and health. It is an important tool in risk assessment and in the management of activities involving handling of dangerous substances. There are many dangerous substances for which there are no formal occupational exposure limits. In these cases, hazard banding or control banding strategies can be used to ensure safe handling.
Bioenvironmental Engineers (BEEs) within the United States Air Force (USAF) blend the understanding of fundamental engineering principles with a broad preventive medicine mission to identify, evaluate and recommend controls for hazards that could harm USAF Airmen, employees, and their families. The information from these evaluations help BEEs design control measures and make recommendations that prevent illness and injury across multiple specialty areas, to include: Occupational Health, Environmental Health, Radiation Safety, and Emergency Response. BEEs are provided both initial and advanced instruction at the United States Air Force School of Aerospace Medicine at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in Dayton, Ohio.
The Institute for Occupational Safety and Health of the German Social Accident Insurance is a German institute located in Sankt Augustin near Bonn and is a main department of the German Social Accident Insurance. Belonging to the Statutory Accident Insurance means that IFA is a non-profit institution.
Workplace health surveillance or occupational health surveillance (U.S.) is the ongoing systematic collection, analysis, and dissemination of exposure and health data on groups of workers. The Joint ILO/WHO Committee on Occupational Health at its 12th Session in 1995 defined an occupational health surveillance system as "a system which includes a functional capacity for data collection, analysis and dissemination linked to occupational health programmes".
A safety management system (SMS) is designed to manage safety risk in the workplace, occupational safety being defined as the reduction of risk to a level that is as low as is reasonably practicable (ALARP) to prevent people getting hurt.
The Fire Protection Association is the UK's National Fire Safety Organisation. Established in 1946, it works to identify and draw attention to the dangers of fire and the means by which their potential for occurrence and loss is kept to a minimum. Recognized as an independent and authoritative source of fire safety information and advice it offers education and training, a fire risk assessment service, a nationwide risk management survey service for insurers, a membership journal, all underpinned by proactive research consultancy conducted on behalf of insurers and commercial clients.

Occupational safety and health (OSH), also commonly referred to as occupational health and safety (OHS), occupational health, or occupational safety, is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the safety, health, and welfare of people at work. These terms also refer to the goals of this field, so their use in the sense of this article was originally an abbreviation of occupational safety and health program/department etc.
Engineering controls are strategies designed to protect workers from hazardous conditions by placing a barrier between the worker and the hazard or by removing a hazardous substance through air ventilation. Engineering controls involve a physical change to the workplace itself, rather than relying on workers' behavior or requiring workers to wear protective clothing.
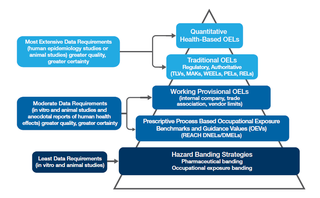
Occupational exposure banding, also known as hazard banding, is a process intended to quickly and accurately assign chemicals into specific categories (bands), each corresponding to a range of exposure concentrations designed to protect worker health. These bands are assigned based on a chemical’s toxicological potency and the adverse health effects associated with exposure to the chemical. The output of this process is an occupational exposure band (OEB). Occupational exposure banding has been used by the pharmaceutical sector and by some major chemical companies over the past several decades to establish exposure control limits or ranges for new or existing chemicals that do not have formal OELs. Furthermore, occupational exposure banding has become an important component of the Hierarchy of Occupational Exposure Limits (OELs).
Anticipate, recognize, evaluate, control, and confirm (ARECC) is a decision-making framework and process used in the field of industrial hygiene (IH) to anticipate and recognize hazards, evaluate exposures, and control and confirm protection from risks. ARECC supports hazard-informed exposure assessment, exposure-informed hazard assessment, and risk-informed decision making in any endeavor.