Related Research Articles

Pau Casals i Defilló, known in English by his Castilian Spanish name Pablo Casals, was a Catalan and Puerto Rican cellist, composer, and conductor. He made many recordings throughout his career of solo, chamber, and orchestral music, including some as conductor, but he is perhaps best remembered for the recordings he made of the Cello Suites by Bach. He was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 1963 by President John F. Kennedy.

Paul Tortelier was a French cellist and composer. After an outstanding student career at the Conservatoire de Paris he played in orchestras in France and the US before the Second World War. After the war he became a well-known soloist, playing in countries round the globe. He taught at conservatoires in France, Germany and China, and gave televised masterclasses in England. He was particularly associated with the solo part in Richard Strauss's Don Quixote, cello concertos by Elgar and others, and Bach's Cello Suites.
Édouard Nanny was an important French double bass player, teacher, and composer. He was a longtime professor of double bass at the Paris Conservatory.

Adrien-François Servais was one of the most influential cellists of the nineteenth century. He was born and died in Halle, Belgium. He is one of the founders of the Modern Cellistic Schools of Paris and Madrid, which began through collaboration with his friend Auguste Franchomme and his disciple Víctor Mirecki Larramat. His compositions are still being studied, performed and recorded all over the world. Two of his sons also had musical careers and performed his music.

Léon Boëllmann was a French composer, known for a small number of compositions for organ. His best-known composition is Suite gothique (1895), which is a staple of the organ repertoire, especially its concluding Toccata.

Jean-Louis Duport, sometimes known as Duport the Younger to distinguish him from his older brother Jean-Pierre (1741-1818), was a cellist, pedagogue, and composer.

Jean-Baptiste Sebastien Bréval was a French cellist and composer. He wrote mostly for his own instrument, including pedagogical works as well as virtuoso display pieces.
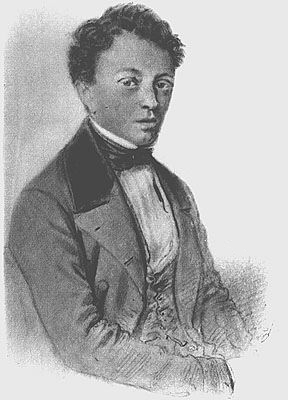
Auguste-Joseph Franchomme was a French cellist and composer. In addition to his work in Paris, he collaborated with Spanish cellist Víctor Mirecki Larramat and Belgian cellist Adrien-François Servais in founding what is considered the Spanish school of cellists, influencing future generations there. For his many contributions to music, he was decorated with the French Légion d'honneur in 1884.

Paul Grümmer was a German-born cellist and teacher.
Sebastian Lee was a German cellist and pedagogue active in France and Germany.

There is a long tradition in classical music of writing music in sets of pieces that cover all the major and minor keys of the chromatic scale. These sets typically consist of 24 pieces, one for each of the major and minor keys.
Pierre François Olivier Aubert was a French cellist, guitarist and composer. He mostly abbreviated his name as "P. F. Olivier Aubert".
Joseph Alexander was a cellist active in Duisburg, Germany, noted for his teaching and pedagogical works.
Antoine Benoit Tranquille Berbiguier was an early 19th-century French flautist, pedagog and composer.

Jérôme Pernoo is a French contemporary cellist.
Xavier Gagnepain is a French contemporary classical cellist.
François Cupis de Renoussard Seigneur de Renoussard, called le cadet was an 18th-century classical French composer, cellist and music educator.
Jean-Henri Levasseur, called "the younger" was a French cellist, composer and music educator.
Adrien Frasse-Sombet is a French classical cellist. He plays on a 1710 cello by Matteo Goffriller.
Sébastien Hurtaud is a French classical cellist.
References
- ↑ See BNF file
- ↑ Raychev, Evgeni Dimitrov. “The Virtuoso Cellist-Composers from Luigi Boccherini to David Popper: A Review of Their Lives and Works.” Florida State University, FSU Libraries, 2003, pp. 48–51.
- ↑ Daily exercises on IMLSP
- ↑ "Etudes du Jeune Violoncelliste (Feuillard, Louis R.) - IMSLP: Free Sheet Music PDF Download". imslp.org. Retrieved 2023-04-26.
- ↑ "La Technique du Violoncelle (Feuillard, Louis R.) - IMSLP: Free Sheet Music PDF Download". imslp.org. Retrieved 2023-04-26.
- ↑ "40 Variations, Op.3 (Ševčík, Otakar) - IMSLP: Free Sheet Music PDF Download". imslp.org. Retrieved 2023-04-26.
- 1 2 3 Tortelier, Paul (1984). A Self-Portrait: In Conversation with David Blum. London: William Heinemann Ltd. pp. 36–37.