Related Research Articles

The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) is a part of the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH). It conducts and funds research on brain and nervous system disorders and has a budget of just over US$2.03 billion. The mission of NINDS is "to reduce the burden of neurological disease—a burden borne by every age group, every segment of society, and people all over the world". NINDS has established two major branches for research: an extramural branch that funds studies outside the NIH, and an intramural branch that funds research inside the NIH. Most of NINDS' budget goes to fund extramural research. NINDS' basic science research focuses on studies of the fundamental biology of the brain and nervous system, genetics, neurodegeneration, learning and memory, motor control, brain repair, and synapses. NINDS also funds clinical research related to diseases and disorders of the brain and nervous system, e.g. AIDS, Alzheimer's disease, epilepsy, muscular dystrophy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, spinal cord injury, stroke, and traumatic brain injury.

The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability and deaths caused by cardiovascular disease and stroke. They are known for publishing guidelines on cardiovascular disease and prevention, standards on basic life support, advanced cardiac life support (ACLS), pediatric advanced life support (PALS), and in 2014 issued the first guidelines for preventing strokes in women. The American Heart Association is also known for operating a number of highly visible public service campaigns starting in the 1970s, and also operates several fundraising events.
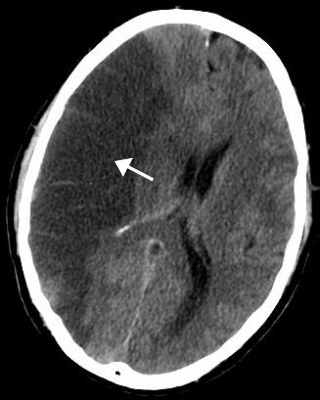
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly.
Dr. H. Richard Winn is an American neurosurgeon, and professor of neurosurgery and neuroscience at Mount Sinai School of Medicine. Winn was chairman of neurological surgery at the University of Washington School of Medicine from 1983 to 2002. Winn has made numerous contributions to the field of neurosurgery, specifically to the physiology of cerebral blood flow regulation and clinical studies of the natural history of cerebral aneurysms. A leading international Neurosurgical Prize is named after Dr. Winn.
The Center for Cerebrovascular Research at the University of California, San Francisco is a collective of faculty and staff investigating matters related to cerebral circulation, particularly cerebrovascular disease resulting from narrowing of major blood vessels in the brain and vascular malformation of the brain. While research offices are located on Parnassus campus, San Francisco General Hospital hosts the center's laboratories and facilities. The center coordinates with additional faculty in various fields of neuroscience and vascular biology. Sponsors include the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the UCSF departments of Anesthesia, Neurological Surgery and Neurology.

George Ojemann is a professor emeritus of neurologic surgery in the Department of Neurological Surgery at the University of Washington School of Medicine.

Memorial Hermann–Texas Medical Center is a nationally ranked hospital at the Texas Medical Center. It is the first hospital founded in the Texas Medical Center in Houston, Texas. Founded in 1925, it is the primary teaching hospital for McGovern Medical School and the flagship location of 13 hospitals in the Memorial Hermann Healthcare System. It is one of two certified Level I Trauma Centers in the greater Houston area. The Memorial Hermann Life Flight air ambulance service operates its fleet of helicopters from Memorial Hermann–Texas Medical Center. Pediatric care to the hospital is provided by Children's Memorial Hermann Hospital which treats infants, children, teens, and young adults age 0-21.

Vladimir Hachinski is a Canadian clinical neuroscientist and researcher based at the Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry at Western University. He is also a Senior Scientist at London's Robarts Research Institute. His research pertains in the greatest part to stroke and dementia, the interactions between them and their joint prevention through holistic brain health promotion. He and John W. Norris helped to establish the world's first successful stroke unit at Sunnybrook Hospital in Toronto, and, by extension, helped cement stroke units as the standard of care for stroke patients everywhere. He discovered that the control of the heart by the brain is asymmetric, the fight/flight (sympathetic) response being controlled by the right hemisphere and the rest and digest (parasympathetic) response being controlled by the left hemisphere and damage to one key component can lead to heart irregularities and sudden death. This discovery has added fundamental knowledge to how the brain controls the heart and blood pressure and lays the foundation for helping prevent sudden death.

Rajiv Ratan is an Indian American academic, professor, administrator and scientist based in New York. He is the Burke Professor of Neurology and Neuroscience at Weill Cornell Medicine. Since 2003, he has served as the executive director of Burke Neurological Institute and as a member of the Council of Affiliated Deans of Weill Cornell Medicine.

Amy Jo Bastian is an American neuroscientist, who has made important contributions to the neuroscience of sensorimotor control. From 2011 she has been a professor of neuroscience at Johns Hopkins University. In 2015 Bastian was appointed Chief Science Officer at the Kennedy Krieger Institute. Bastian is a member of the National Academy of Sciences.

Charlotte Jane Sumner is an American neurologist. She is a professor in the Departments of Neurology and Neuroscience at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine. Dr. Sumner cares for patients with genetically mediated neuromuscular diseases and directs a laboratory focused on developing treatments for these diseases. She co-directs the Johns Hopkins Muscular Dystrophy Association Care Center, the Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), and the Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) clinics, which deliver multidisciplinary clinical care, engage in international natural history studies, and provide therapeutics.

Stephanie J. Murphy is an American veterinary scientist. She is the director of the Division of Comparative Medicine (DCM) in the Office of Research Infrastructure Programs at the National Institutes of Health. Murphy was previously a faculty member at the Oregon Health & Science University.
HollisT. Cline is an American neuroscientist and the Director of the Dorris Neuroscience Center at the Scripps Research Institute in California. Her research focuses on the impact of sensory experience on brain development and plasticity.
Dena Dubal is the David A. Coulter Endowed Chair in Ageing and Neurodegenerative Disease at University of California, San Francisco. Dubal has demonstrated that the hormone Klotho can enhance cognition and protect the brain from neurodegenerative decline.
Maria G. Castro is an Argentine neuroscientist. She is the R. C. Schneider Collegiate Professor of Neurosurgery and a Professor of Cell and Developmental Biology at the University of Michigan Medical School. Her research focuses on cancer immunology and gliomas.
Ralph Lewis Sacco was an American neurologist. He held the Olemberg Family Chair in Neurological Disorders, Miller Professor of Neurology, Public Health Sciences, Human Genetics, and Neurosurgery at the Miller School of Medicine at the University of Miami and Chief of the Neurology Service at Jackson Memorial Hospital. In 2020, Sacco was named editor-in-chief of the Stroke journal and the inaugural recipient of the Edgar J. Kenton III Lecture Award from the American Stroke Association.
Lynda D. Lisabeth is an American epidemiologist who is Professor and Senior Associate Dean for Faculty Affairs in the School of Public Health at the University of Michigan. Her research considers the epidemiology of stroke in the United States, and she has worked with the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke on the advancement of stroke research.

Tara A. Schwetz is an American biophysicist and government administrator who serves as a deputy director of the National Institutes of Health. She previously served as Acting Principal Deputy Director.

Jessica M. Gill is an American nurse scientist working as a Bloomberg Distinguished Professor of Trauma Recovery Biomarkers in the department of neurology at the Johns Hopkins School of Nursing and School of Medicine since 2021. She was the acting deputy director of the National Institute of Nursing Research from 2019 to 2020 and deputy director of the Center for Neuroscience and Regenerative Medicine at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences until 2021.

Bruce Ovbiagele is a Nigerian-American vascular neurologist, biomedical researcher, health systems executive, academic leader, organization founder, and scientific journal editor. He serves as Professor of Neurology and Associate Dean at the University of California, San Francisco, Chief of Staff at the San Francisco VA Medical Center, Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of the American Heart Association. and Founding President of the Society for Equity Neuroscience. He is a member of the Board of Directors of the World Stroke Organization, and Northern California Institute of Research and Education.
References
- 1 2 3 "Visiting Professor Dr. Louise D. McCullough, MD, PhD". Department of Neurological Surgery. 606. Retrieved 2022-08-22.
- 1 2 "Averting the Devastating Effects of Stroke". UConn Today. 2013-05-30. Retrieved 2022-08-22.
- ↑ Averting the Devastating Effects of Stroke , retrieved 2022-08-22
- ↑ "Health Center Teaching and Faculty Award Winners Announced". UConn Today. 2012-05-07. Retrieved 2022-08-22.
- 1 2 "New members inducted into Johns Hopkins Society of Scholars". The Hub. 2018-04-10. Retrieved 2022-08-22.
- ↑ "Improving Patient Outcomes, Balancing Cost of Mobile Stroke Units with Louise McCullough, MD, PhD". Practical Cardiology. Retrieved 2022-08-22.
- ↑ "Science News 2022 - International Stroke Conference". professional.heart.org. Retrieved 2022-08-22.
- ↑ "McCullough honored with prestigious NIH Javits Award for stroke research". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 2022-08-22.
- ↑ "McCullough wins AHA/ASA Neuroscience Visionary Award". John P. and Kathrine G. McGovern Medical School at UTHealth. 2021-09-27. Retrieved 2022-08-22.
- ↑ McCullough LD, Zeng Z, Blizzard KK, Debchoudhury I, Hurn PD (2005). "Ischemic nitric oxide and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 in cerebral ischemia: male toxicity, female protection". J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 25 (4): 502–12. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600059 . PMID 15689952.
- ↑ "McCullough and Liu awarded $3.7M NIH grant to study sex differences in COVID-19 outcomes". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 2021-11-16.